Chapter 20
Sustainability and ESG Factors in M&A
"Incorporating sustainability and ESG into M&A is no longer optional; it’s essential for long-term value creation. Companies that embrace this shift will not only reduce risks but also unlock new growth opportunities in an increasingly conscious market." — Larry Fink, CEO, BlackRock.
This chapter explores how sustainability and ESG factors are reshaping M&A strategy in today’s business environment. It discusses the role of ESG in evaluating acquisition targets, the impact of climate change policies on deal-making, and the importance of transparency in meeting stakeholder expectations. Companies that integrate ESG into their M&A strategy are better positioned to manage risks, meet regulatory demands, and create long-term value while driving positive social and environmental outcomes.
20.1. Introduction
As the global business environment evolves, ESG considerations have shifted from being optional add-ons to becoming integral components of corporate strategy and M&A decision-making. Investors, regulators, and consumers are increasingly expecting companies to adopt sustainable practices and demonstrate responsible corporate governance, driving the need to integrate ESG factors into the M&A process. This section examines how companies can leverage sustainability and ESG factors to unlock long-term value, mitigate risks, and align their business strategies with broader societal and environmental goals.
The growing prominence of ESG factors in M&A stems from heightened awareness of climate change, social justice movements, and the demand for greater corporate accountability. Investors, particularly institutional investors, are prioritizing ESG criteria when evaluating potential acquisitions. Firms that fail to consider these factors risk reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and financial underperformance. As a result, ESG considerations now play a crucial role in how companies evaluate acquisition targets, execute deals, and plan for post-merger integration.
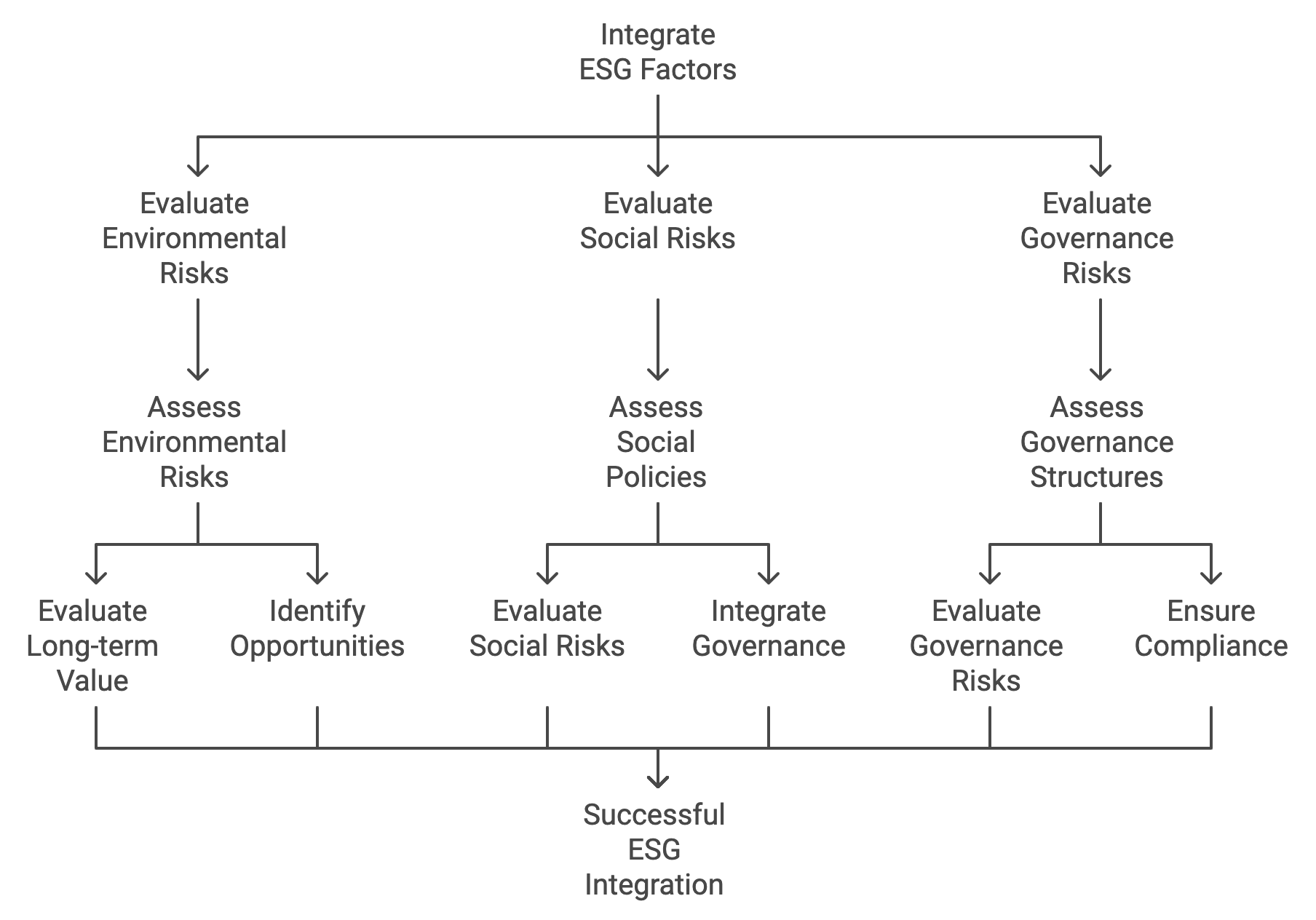
Figure 20.1: Key elements of ESG in M&A.
Environmental factors are central to this shift, as climate change and environmental degradation have become pressing concerns for businesses and governments alike. When evaluating potential acquisition targets, companies must assess environmental risks associated with the target's operations. This includes analyzing the company’s carbon footprint, waste management practices, water usage, and potential liabilities related to environmental regulations. Failure to account for these risks can result in significant financial penalties, operational disruptions, and reputational damage, especially in industries such as energy, manufacturing, and agriculture, where environmental impact is substantial. Furthermore, the transition to a low-carbon economy presents both risks and opportunities. Companies that acquire businesses with strong environmental credentials—such as renewable energy firms or those with advanced sustainability practices—can gain a competitive advantage in a marketplace that increasingly favors environmentally conscious businesses.
Incorporating environmental assessments into the M&A process is also crucial for long-term valuation. Companies that proactively address environmental risks are often seen as more resilient and better positioned to capitalize on regulatory shifts toward stricter environmental standards. Additionally, ESG-driven acquisitions can unlock opportunities for innovation and growth, as companies invest in cleaner technologies, energy efficiency, and sustainable supply chains. Acquirers can enhance long-term value by integrating sustainability into their operations, improving resource efficiency, reducing emissions, and tapping into emerging green markets. These considerations not only improve the immediate financial outlook but also align the company with broader global efforts to combat climate change.
Social factors in M&A revolve around labor practices, human rights, and the broader impact that companies have on their employees, communities, and stakeholders. Acquirers must assess the target company’s social policies, particularly in areas such as employee treatment, workplace safety, diversity and inclusion, and community engagement. Social risks, such as poor labor conditions or lack of diversity, can lead to reputational harm, legal challenges, and potential disruptions in business operations. For example, a company that acquires a target with a history of poor labor practices could face backlash from consumers, regulators, and employees, which may erode brand value and result in costly legal battles.
Furthermore, strong social governance is increasingly linked to financial performance. Companies with robust social policies are often seen as more attractive to top talent, more resilient in times of crisis, and better positioned to build long-term relationships with consumers and partners. In M&A, acquiring firms that prioritize employee well-being, workplace diversity, and ethical supply chain practices can enhance corporate reputation, foster innovation, and drive long-term growth. Post-merger, integrating the social governance policies of both companies is crucial to creating a cohesive corporate culture that supports long-term success.
Governance factors, which focus on corporate governance structures, ethical business practices, and transparency, are equally important in the M&A process. Good governance is essential for maintaining investor confidence, ensuring regulatory compliance, and reducing the risk of financial misconduct. When evaluating a potential acquisition, companies must thoroughly assess the target’s governance structures, including board composition, executive compensation practices, anti-corruption policies, and overall corporate transparency. A failure in governance can lead to scandals, legal penalties, and significant financial losses, making it critical to incorporate governance considerations into due diligence.
The integration of ESG factors into governance not only mitigates risks but also enhances the long-term sustainability of the business. Companies that adopt ethical business practices, uphold strong governance principles, and maintain transparency are better positioned to navigate regulatory changes and adapt to evolving market conditions. Additionally, a focus on governance helps ensure that the post-merger entity is aligned with shareholder expectations, regulatory standards, and ethical business practices, thereby fostering trust and stability.
From an academic perspective, the incorporation of ESG factors into M&A aligns with stakeholder theory, which argues that companies must consider the interests of all stakeholders—including employees, customers, communities, and the environment—when making strategic decisions. Stakeholder theory contrasts with the traditional shareholder-centric model, which focuses solely on maximizing profits. In the context of M&A, ESG factors reflect a more holistic approach to value creation, where long-term sustainability and stakeholder engagement are prioritized over short-term financial gains. This shift is supported by growing evidence that companies with strong ESG performance tend to outperform their peers financially, attract more investment, and demonstrate greater resilience in the face of economic downturns or regulatory challenges.
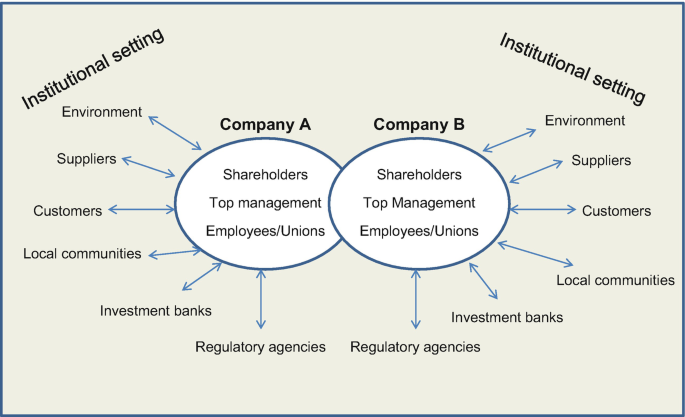
Figure 20.2: Elements of shareholder theory in M&A.
In industry practice, the integration of ESG factors into M&A has become increasingly common, as companies seek to align their growth strategies with global sustainability goals. Many large corporations, particularly in sectors such as energy, technology, and finance, are incorporating ESG assessments into their due diligence processes to identify potential risks and opportunities. For example, companies are using ESG criteria to assess the carbon footprint of potential acquisitions, evaluate labor practices in supply chains, and ensure compliance with governance standards. Furthermore, private equity firms and institutional investors are increasingly using ESG benchmarks to guide their investment decisions, leading to greater scrutiny of ESG performance in M&A transactions.
The rise of sustainability-linked financing is also driving the importance of ESG factors in M&A. Banks and financial institutions are offering more financing options that are tied to a company’s ESG performance, providing incentives for acquirers to prioritize sustainability in their deals. Companies that meet specific ESG targets, such as reducing emissions or improving diversity metrics, can benefit from lower interest rates or more favorable loan terms. This trend highlights the financial benefits of integrating ESG factors into M&A strategy, as companies that demonstrate strong ESG performance can access capital more easily and at lower costs.
In conclusion, ESG factors are reshaping the M&A landscape, influencing how companies evaluate acquisition targets, execute deals, and integrate operations post-merger. By incorporating environmental, social, and governance considerations into the M&A process, companies can mitigate risks, unlock long-term value, and align their growth strategies with global sustainability efforts. The integration of ESG factors not only enhances financial performance but also strengthens stakeholder relationships, improves regulatory compliance, and ensures that companies are well-positioned to navigate the evolving demands of investors, regulators, and consumers in a rapidly changing business environment. As ESG considerations continue to gain prominence, they will play an increasingly central role in shaping the future of M&A.
20.2. Incorporating ESG into M&A Strategy
ESG integration is not just an ethical or regulatory compliance requirement; it has become a strategic imperative that influences deal valuation, operational synergies, and long-term value creation. This section examines how companies can embed ESG into each stage of the M&A lifecycle—from due diligence to post-merger integration—and the tangible benefits this brings in terms of market differentiation, stakeholder trust, and enhanced reputation.
The process of incorporating ESG into M&A begins with the due diligence phase. Traditionally, due diligence has focused on financial, operational, and legal factors, but with the growing emphasis on sustainability, ESG considerations are now critical. Companies must develop robust frameworks for assessing ESG-related risks and opportunities. These frameworks should evaluate a wide range of factors, such as the target company's carbon footprint, water usage, waste management, supply chain sustainability, diversity and inclusion policies, and corporate governance practices. By conducting ESG due diligence, companies can identify potential liabilities—such as exposure to environmental regulations, labor disputes, or governance failures—that could impact the financial viability or reputational standing of the deal.
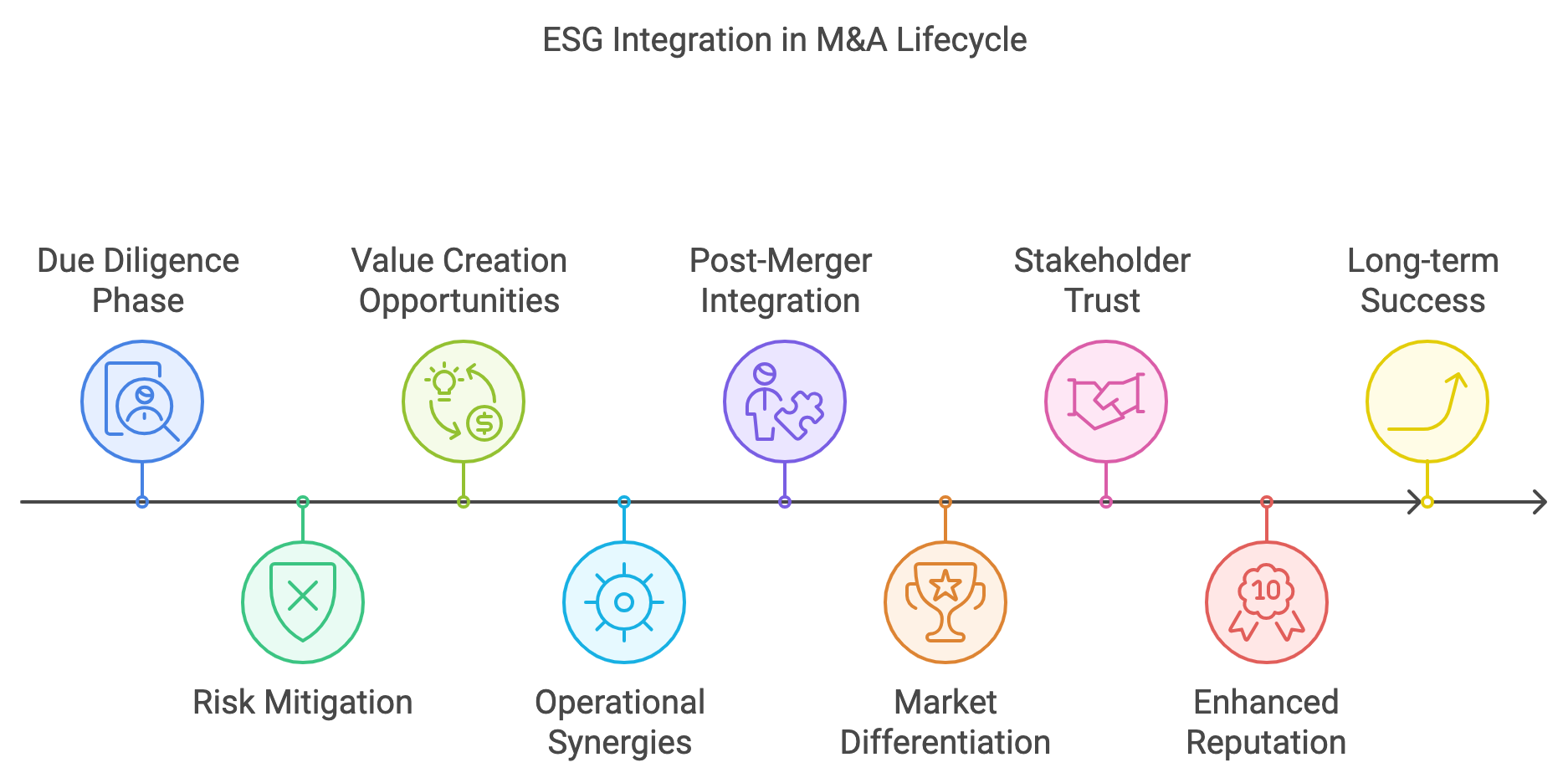
Figure 20.3: ESG integration in M&A lifecycle.
For example, if a company is acquiring a business in the energy or manufacturing sector, it is essential to assess how the target's operations align with evolving environmental regulations, such as those aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Failure to account for these risks could result in significant post-acquisition costs related to environmental remediation, compliance penalties, or necessary upgrades to meet sustainability standards. By integrating ESG into the due diligence process, companies can identify red flags early and take proactive steps to mitigate these risks, ensuring that the deal is financially and operationally sound.
Beyond risk mitigation, incorporating ESG considerations into the M&A process also presents significant opportunities for value creation. Acquiring companies with strong sustainability credentials—such as those with energy-efficient operations, responsible sourcing practices, or diverse and inclusive workforces—can enhance the overall value proposition of the deal. In this context, ESG factors become an important part of the deal valuation process. Acquirers can use ESG metrics to assess how well the target company aligns with global sustainability trends and to forecast potential long-term gains from enhanced operational efficiency, brand value, and access to new markets. Companies with robust ESG practices are often seen as lower-risk, more innovative, and more resilient in the face of changing market conditions, which can command a premium during deal negotiations.
Operational synergies, often a key driver in M&A, are also influenced by ESG factors. Companies that integrate ESG into their M&A strategies can realize synergies not only in traditional areas, such as cost savings or market expansion, but also in sustainable practices. For instance, combining two companies with complementary sustainability initiatives—such as renewable energy investments or sustainable supply chain management—can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced environmental impact. In some cases, ESG integration can help companies optimize resource usage, lower operational costs, and reduce regulatory risks, creating additional value for the merged entity.
Moreover, post-merger integration is another critical stage where ESG factors play a significant role. A company’s ability to successfully integrate ESG practices post-merger can determine the long-term success of the transaction. Merging two companies with differing ESG policies, for example, requires careful alignment to ensure that the new entity upholds consistent sustainability standards across its operations. This includes harmonizing corporate governance structures, ensuring that labor practices align with ESG goals, and integrating environmental management systems to maintain compliance with regulations and stakeholder expectations. Companies that succeed in embedding ESG principles throughout the post-merger integration process are better positioned to achieve long-term sustainability and financial performance, as well as build trust with employees, customers, and investors.
In terms of enhancing a company’s reputation, incorporating ESG into M&A is increasingly seen as a differentiating factor in competitive markets. Companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices can gain a significant edge over competitors. This differentiation is particularly important in industries where consumers and investors are placing greater emphasis on sustainability, such as consumer goods, technology, and financial services. Acquirers that proactively integrate ESG considerations into their M&A strategy can attract environmentally and socially conscious customers, enhance brand loyalty, and appeal to investors who prioritize long-term, sustainable growth.
The role of ESG in strengthening stakeholder trust cannot be overstated. Investors, regulators, customers, and employees are increasingly scrutinizing companies for their commitment to responsible business practices. Acquiring companies that fail to meet ESG standards can erode stakeholder confidence and lead to reputational damage. On the other hand, companies that prioritize ESG factors in their M&A strategy signal to stakeholders that they are committed to ethical, sustainable growth. This can result in increased investor confidence, easier access to capital, and stronger relationships with regulators and industry bodies. Furthermore, integrating ESG into M&A can also improve employee retention and engagement, as many employees today prefer to work for companies that are aligned with ethical and environmental values.
From an academic perspective, the integration of ESG into M&A strategy aligns with the principles of stakeholder theory, which emphasizes the importance of balancing the interests of various stakeholders—not just shareholders. This approach to business is increasingly viewed as a way to create long-term, sustainable value by considering the social and environmental impacts of corporate activities. The academic literature also highlights that companies with strong ESG performance tend to outperform their peers in terms of financial returns, stock performance, and risk management. In the context of M&A, this suggests that ESG integration can enhance not only the immediate value of the deal but also the long-term growth prospects of the merged entity.
In industry practice, companies that successfully integrate ESG into their M&A strategy are setting new benchmarks for how deals are evaluated and executed. For instance, companies like Unilever, Microsoft, and BlackRock have integrated ESG criteria into their M&A processes to ensure that acquisitions align with their sustainability goals. These companies are using ESG metrics to assess potential synergies, mitigate risks, and identify opportunities for innovation and value creation. In the case of Unilever, its focus on acquiring businesses with sustainable products and practices has helped the company strengthen its leadership position in the consumer goods sector while enhancing its brand reputation and market share.
In conclusion, incorporating ESG into M&A strategy is no longer optional but a critical component of achieving long-term success in today’s market. Companies that develop structured frameworks for assessing ESG-related risks and opportunities throughout the M&A lifecycle—from due diligence to post-merger integration—are better positioned to unlock value, realize synergies, and differentiate themselves in competitive markets. By embedding ESG into their M&A strategy, companies not only enhance their financial performance but also build stronger relationships with stakeholders, improve their reputation, and align their growth strategies with global sustainability trends. This holistic approach to M&A is essential for navigating the increasingly complex and interconnected business environment of the 21st century.
20.3. Impact of Climate Change Policies
As governments and international organizations implement policies aimed at mitigating climate change, companies must adapt their M&A strategies to account for the regulatory risks and opportunities associated with these evolving frameworks. Climate change policies, such as carbon pricing mechanisms, emissions reduction targets, and environmental reporting requirements, are reshaping the global business landscape, compelling companies to reassess the sustainability of their operations and investments.
One of the most significant ways climate change policies affect M&A decisions is through the introduction of carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems. These policies place a financial cost on carbon emissions, incentivizing companies to reduce their carbon footprint and shift toward cleaner technologies. For companies in carbon-intensive industries, such as oil and gas, chemicals, or heavy manufacturing, the regulatory burden associated with carbon pricing can have a profound impact on profitability. M&A activity in these sectors increasingly requires an in-depth analysis of the target company's carbon emissions profile and the potential financial liabilities associated with future carbon pricing regimes.
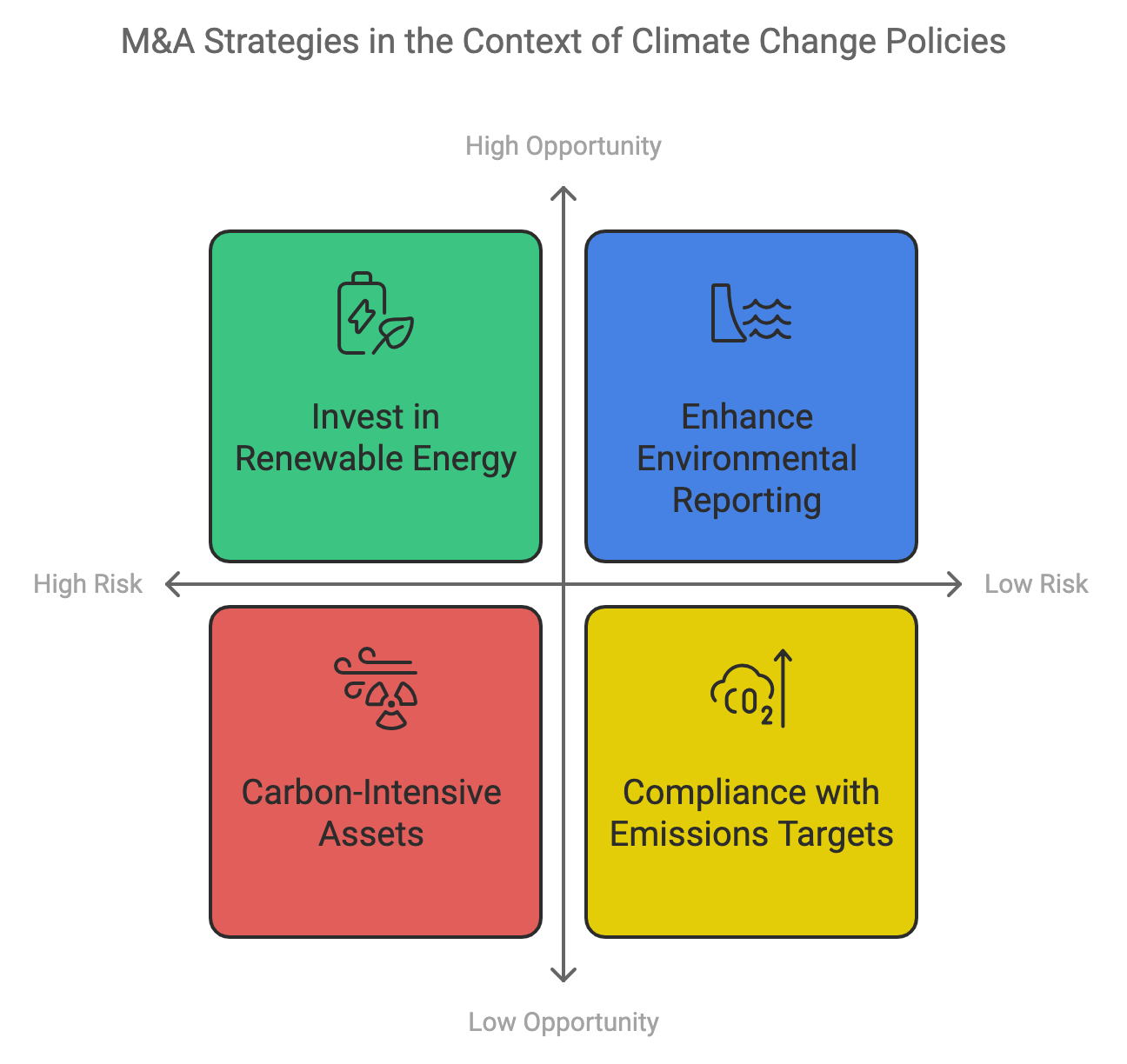
Figure 20.4: M&A strategies due to climate change policy.
For example, an acquiring company in the energy sector might need to evaluate the long-term financial impact of rising carbon prices on a target’s oil and gas assets. Companies that are heavily reliant on fossil fuel extraction may face escalating costs as carbon prices increase, diminishing the value of these assets over time. In contrast, acquisitions that focus on renewable energy sources—such as solar, wind, or hydrogen—can provide companies with strategic advantages by reducing exposure to carbon pricing risks. This shift in focus from traditional energy sources to cleaner technologies reflects the broader trend of decarbonization across the global economy, where investments in green energy and low-carbon technologies are seen as essential for long-term sustainability.
Emissions reduction targets, set by governments and international agreements like the Paris Agreement, are another critical factor shaping M&A strategies. These targets aim to limit global temperature rises by reducing greenhouse gas emissions across key industries. As these targets become more stringent, companies face increased pressure to decarbonize their operations, supply chains, and product offerings. In the context of M&A, acquiring companies must evaluate how well a target company is positioned to meet current and future emissions reduction requirements. Failure to align with emissions targets can lead to regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aviation, and energy, where emissions are a central concern.
Beyond compliance, companies that proactively pursue acquisitions aligned with emissions reduction goals can benefit from a first-mover advantage in the transition to a low-carbon economy. For example, automakers that acquire companies specializing in electric vehicle (EV) technology or battery manufacturing can accelerate their shift away from internal combustion engines, positioning themselves to meet future emissions standards and capture market share in the rapidly growing EV market. Similarly, companies in the energy sector that invest in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies or hydrogen production can play a leading role in the decarbonization of industrial processes, gaining a competitive edge as global demand for low-carbon solutions increases.
Environmental reporting mandates, which require companies to disclose their environmental performance and carbon emissions, are also influencing M&A strategies. These reporting requirements, which are becoming increasingly stringent in many regions, allow investors, regulators, and consumers to assess a company’s environmental impact and sustainability efforts. As a result, acquiring companies must evaluate not only the environmental performance of a target but also its ability to comply with reporting standards and improve transparency. Companies that fail to meet environmental disclosure requirements may face legal penalties, investor backlash, and reputational damage, all of which can undermine the value of an acquisition.
In contrast, companies with strong environmental reporting capabilities and a commitment to transparency are more likely to attract favorable attention from investors and stakeholders. As environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria play an increasingly important role in investment decisions, companies that prioritize sustainability reporting are better positioned to secure capital and enhance their market reputation. In the M&A context, acquiring firms with robust environmental reporting practices can also strengthen the acquiring company’s overall ESG profile, making the combined entity more attractive to socially conscious investors.
The impact of climate change policies on M&A is not limited to regulatory risks; it also presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth. Companies that proactively invest in green energy, carbon reduction technologies, and sustainable innovations can position themselves as leaders in the transition to a low-carbon economy. For example, renewable energy projects, energy efficiency solutions, and sustainable infrastructure investments offer substantial growth potential as governments and businesses seek to reduce their environmental footprint. Acquiring companies that are developing these technologies or integrating them into their operations can provide acquirers with access to new markets, revenue streams, and innovation capabilities.
From an academic perspective, the integration of climate change policies into M&A strategies aligns with the broader concept of corporate resilience. As climate risks become more prominent, companies that are adaptable and forward-thinking in their approach to climate change are more likely to thrive in an increasingly uncertain global environment. Research suggests that companies that prioritize sustainability and align their strategies with climate change goals tend to outperform their peers financially over the long term. This is particularly true for companies that invest in low-carbon technologies, as these investments position them to benefit from the global shift toward sustainability and decarbonization.
In industry practice, companies across sectors are already integrating climate change considerations into their M&A strategies. Major corporations in the energy, transportation, and manufacturing sectors are increasingly prioritizing acquisitions that support their sustainability goals. For example, oil and gas companies are diversifying their portfolios by acquiring renewable energy assets and technologies that reduce carbon emissions. Similarly, companies in the automotive industry are acquiring electric vehicle technology companies and battery manufacturers to accelerate their transition to low-emissions transportation. This shift reflects the growing recognition that climate change policies are not just a regulatory burden but also a strategic opportunity to innovate, reduce risk, and capitalize on emerging trends.
Moreover, private equity firms and institutional investors are placing greater emphasis on climate-related risks and opportunities when evaluating potential acquisitions. As more investors incorporate ESG criteria into their decision-making processes, climate change policies are becoming a critical factor in deal negotiations and valuations. Companies that are better positioned to meet climate change regulations or that offer sustainable solutions are more likely to command a premium in the M&A market, while those that are exposed to carbon-intensive operations may see their valuations decline.
In conclusion, climate change policies are reshaping the M&A landscape, particularly in industries that are heavily reliant on carbon-intensive operations. Carbon pricing, emissions reduction targets, and environmental reporting mandates are influencing how companies evaluate potential acquisitions, leading to greater scrutiny of regulatory risks and opportunities. Companies that proactively address these challenges by acquiring green energy assets, investing in carbon reduction technologies, and enhancing their environmental reporting capabilities can future-proof their portfolios and position themselves as leaders in the transition to a low-carbon economy. By integrating climate change considerations into their M&A strategies, companies can mitigate risks, unlock new growth opportunities, and strengthen their long-term sustainability and financial performance.
20.4. Stakeholder Expectations and Transparency
This last section examines how the demand for greater transparency around Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) issues is influencing mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Stakeholders—including investors, customers, employees, and regulators—are increasingly scrutinizing how companies address ESG concerns, particularly during significant transactions like mergers and acquisitions. In this context, transparency becomes a critical factor in maintaining trust, securing regulatory approvals, and enhancing a company's reputation post-merger. Companies that fail to meet stakeholder expectations regarding ESG transparency risk damaging their credibility, while those that embrace it can unlock long-term value and foster stronger relationships with their key audiences.
One of the key drivers of this increased demand for ESG transparency is the growing awareness of sustainability issues and responsible corporate behavior. Investors are placing greater emphasis on ESG metrics when evaluating potential acquisitions, as they recognize that these factors can have a material impact on long-term financial performance. Customers are also becoming more discerning, preferring to engage with brands that prioritize sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical governance. Employees, particularly in younger generations, are seeking to work for companies that align with their values, placing pressure on organizations to demonstrate a commitment to ESG principles. In this environment, transparency is no longer a secondary consideration; it is central to the success of M&A transactions.
Figure 20.5: ESG transparency in M&A.
To meet these expectations, companies must develop clear and effective ESG communication strategies, particularly during the due diligence and post-merger integration phases. These strategies should include detailed reporting frameworks that disclose key information about the company’s environmental impact, social responsibility initiatives, and governance practices. During an M&A transaction, stakeholders expect transparency not only about financial performance but also about how the deal aligns with broader ESG goals. For example, investors may want to know how the acquiring company plans to address environmental risks, improve labor practices, or enhance governance structures after the merger. Customers and employees, on the other hand, may seek reassurance that the combined entity will uphold the same ethical standards and commitments to sustainability as before.
Incorporating transparency into the M&A process begins with robust ESG reporting. Companies must ensure that they have the necessary systems and processes in place to collect, analyze, and disclose ESG data in a clear and consistent manner. This requires not only internal capabilities but also alignment with global reporting standards, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). By adhering to these standards, companies can provide stakeholders with a comprehensive and comparable view of their ESG performance, facilitating more informed decision-making. Additionally, these frameworks offer guidance on how to report material ESG issues, ensuring that companies focus on the most relevant and impactful areas of their business.
Transparency in disclosing environmental impacts is particularly important in industries that are highly scrutinized for their carbon emissions, resource usage, and waste management practices. In the context of M&A, stakeholders want to understand how the acquisition will impact the combined company’s environmental footprint. For example, if a company in the energy or manufacturing sector is acquiring a business with significant environmental risks, such as high levels of pollution or resource depletion, stakeholders will expect to see detailed plans for mitigating these risks. This includes disclosing carbon reduction strategies, energy efficiency improvements, and investments in sustainable technologies. Companies that are transparent about their environmental challenges and proactive in addressing them are more likely to maintain stakeholder trust and avoid reputational damage.
Social responsibility initiatives are another critical area where transparency is essential. Stakeholders increasingly expect companies to demonstrate their commitment to ethical labor practices, diversity and inclusion, community engagement, and human rights. During M&A, companies must communicate how the transaction will impact employees, suppliers, and local communities. For instance, if the acquisition involves significant changes to the workforce, such as layoffs or restructuring, transparency about how these changes will be managed is key to maintaining employee morale and avoiding negative publicity. Similarly, stakeholders may want to know how the combined entity will uphold diversity and inclusion standards, particularly if one of the companies involved has a strong track record in this area.
Governance practices are the third pillar of ESG transparency, and they play a crucial role in shaping stakeholder perceptions of an M&A deal. Good governance is essential for ensuring accountability, ethical decision-making, and regulatory compliance. During M&A, stakeholders expect companies to disclose how governance structures will be integrated and strengthened post-merger. This includes providing clarity on board composition, executive compensation practices, anti-corruption measures, and overall corporate governance frameworks. Transparent governance reporting helps reassure investors and regulators that the combined entity will operate with integrity and adhere to the highest ethical standards, reducing the risk of legal or reputational issues arising from poor governance practices.
In addition to meeting stakeholder expectations, transparency in ESG reporting can also facilitate regulatory approvals. M&A deals often require the approval of regulatory bodies, particularly when they involve large-scale transactions or occur in industries with significant environmental or social impacts. Regulators are increasingly considering ESG factors when evaluating deals, and companies that demonstrate a commitment to transparency and sustainability are more likely to receive favorable outcomes. By proactively addressing potential regulatory concerns, such as environmental compliance or labor rights, companies can streamline the approval process and avoid costly delays or challenges.
Moreover, transparent ESG communication can enhance a company’s brand reputation post-merger. A successful merger or acquisition is not just about financial performance; it is also about how the company is perceived by its stakeholders. Companies that are open and honest about their ESG goals and progress are more likely to build trust with customers, investors, employees, and the broader public. This trust can translate into stronger brand loyalty, higher employee retention, and increased investor confidence, all of which contribute to long-term value creation. Conversely, companies that lack transparency or fail to meet stakeholder expectations regarding ESG commitments may suffer reputational damage, leading to customer attrition, investor divestment, and challenges in attracting top talent.
Academically, transparency in ESG reporting is closely linked to the concept of corporate social responsibility (CSR) and stakeholder theory, which emphasize the importance of addressing the needs and expectations of a broad range of stakeholders. Research has shown that companies with high levels of ESG transparency tend to perform better financially over the long term, as they are better equipped to manage risks, build stakeholder trust, and capitalize on emerging sustainability trends. From an academic perspective, ESG transparency is not just a compliance requirement; it is a strategic tool for building resilient, sustainable businesses that are aligned with societal and environmental goals.
In industry practice, leading companies are setting new standards for ESG transparency in the M&A process. For example, large corporations such as Unilever and Nestlé have integrated ESG considerations into their M&A strategies, providing detailed disclosures on how each transaction aligns with their sustainability goals. These companies have implemented comprehensive ESG reporting frameworks that allow them to communicate their progress on environmental, social, and governance issues to stakeholders in a clear and measurable way. By doing so, they have strengthened their brand reputation, enhanced investor confidence, and positioned themselves as leaders in responsible business practices.
In conclusion, meeting stakeholder expectations for ESG transparency is essential for the success of M&A transactions in today’s business environment. Companies must develop clear ESG communication strategies and reporting frameworks to provide stakeholders with the information they need to assess the environmental, social, and governance implications of a deal. By prioritizing transparency in disclosing environmental impacts, social responsibility initiatives, and governance practices, companies can build trust, secure regulatory approval, and enhance their brand reputation post-merger. Moreover, robust ESG commitments not only mitigate risks but also drive long-term value creation, positioning companies for success in an increasingly competitive and sustainability-focused market.
20.5. Conclusion
Chapter 20 highlights the growing importance of sustainability and ESG factors in M&A transactions, demonstrating how companies can integrate these elements into their strategic decision-making. By incorporating ESG considerations into M&A processes—from due diligence through to integration—companies can mitigate risks, meet regulatory requirements, and unlock new opportunities for sustainable growth. Climate change policies, stakeholder expectations, and the demand for transparency are redefining success in M&A, making it critical for companies to align their acquisitions with sustainable and responsible business practices.
20.5.1. Further Learning with GenAI
The following prompts encourage comprehensive, strategic thinking about the integration of ESG and sustainability into M&A processes. They focus on key areas like risk mitigation, climate policies, stakeholder transparency, and the long-term value of sustainable acquisitions.
How can companies integrate sustainability and ESG factors into their M&A strategy to mitigate risks and unlock long-term value, while aligning with global efforts toward sustainability? Explore how ESG factors can influence M&A deal structuring, valuation, and integration to drive both financial performance and sustainability outcomes.
What are the best practices for conducting ESG due diligence during M&A, and how can companies assess potential risks related to environmental sustainability, social impact, and corporate governance? Discuss frameworks for assessing ESG risks and opportunities and their influence on the success of mergers and acquisitions.
How can companies quantify the financial impact of ESG factors during M&A, such as the cost of environmental liabilities, potential social risks, or governance challenges? Analyze methods for incorporating ESG metrics into financial models to evaluate the long-term financial and non-financial value of an acquisition.
What role do climate change policies, such as carbon pricing and emissions regulations, play in shaping M&A strategy, particularly in carbon-intensive industries? Explore the impact of climate policies on deal selection, valuation, and integration strategies in industries affected by environmental regulations.
How can companies identify M&A opportunities that align with global climate goals, such as acquiring clean energy assets, carbon reduction technologies, or businesses focused on sustainability innovation? Discuss strategies for targeting acquisitions that support a company’s sustainability agenda and future-proof its business model.
What steps should companies take to ensure that they are compliant with evolving environmental regulations and policies in the post-merger integration phase? Analyze how companies can develop a compliance roadmap for newly acquired entities to align with national and international environmental standards.
How can companies use ESG as a differentiator in competitive M&A markets, and what role does ESG play in enhancing a company’s reputation, stakeholder trust, and brand equity? Discuss how a strong ESG profile can increase a company’s attractiveness in M&A markets and contribute to long-term value creation.
How can companies balance short-term financial gains with long-term sustainability objectives in M&A transactions, particularly when acquiring assets with potential environmental or social risks? Explore strategies for integrating ESG goals into deal assessments to achieve both financial and sustainability targets.
What are the most effective ways for companies to integrate ESG frameworks into post-merger integration, ensuring that the newly combined entity adheres to sustainable and ethical practices? Analyze how companies can harmonize ESG policies, governance structures, and reporting practices after a merger.
How can companies assess the materiality of ESG factors in different industries, and how does this impact deal selection, due diligence, and post-merger integration strategies? Discuss how companies can tailor their ESG approach to the specific risks and opportunities in industries such as energy, tech, or consumer goods.
What role does transparency play in ESG-related M&A, and how can companies develop clear communication strategies to meet stakeholder expectations on sustainability and governance? Explore how companies can improve stakeholder engagement by disclosing ESG practices, risks, and impacts throughout the M&A process.
How can companies develop robust ESG reporting frameworks post-merger to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and meet investor demands for transparency? Discuss best practices for creating comprehensive ESG reports that satisfy regulators and enhance investor confidence post-merger.
What challenges do companies face when incorporating ESG factors into cross-border M&A, particularly with differing environmental and governance standards across jurisdictions? Analyze how companies can navigate varying ESG regulations and stakeholder expectations in international mergers.
How can companies use M&A to accelerate their transition to a low-carbon economy, and what role does acquiring sustainable technologies and assets play in this strategy? Discuss how companies can align their M&A strategy with the transition to renewable energy and sustainability-driven innovation.
What are the key ESG factors that companies should prioritize in industries most affected by climate change, and how can they mitigate risks during the M&A process? Explore how companies in sectors like energy, agriculture, or manufacturing can evaluate and mitigate climate-related risks in M&A.
How can companies ensure that ESG considerations are aligned with their broader corporate strategy and goals during M&A, rather than being treated as a standalone initiative? Discuss how to embed ESG into the overall corporate strategy to create synergies between M&A transactions and long-term business objectives.
What role do institutional investors play in driving the integration of ESG factors in M&A, and how can companies align their acquisition strategy with investor expectations for sustainability and governance? Explore how institutional investors influence M&A decision-making and ESG performance, and how companies can meet these expectations.
How can companies assess the governance structures of target companies during M&A, ensuring alignment with best practices in transparency, board diversity, and executive accountability? Analyze how governance due diligence can impact deal valuation and post-merger integration success, especially in terms of leadership and corporate governance practices.
What are the emerging trends in ESG-driven M&A, such as the rise of green finance and sustainability-linked acquisitions, and how can companies position themselves to capitalize on these trends? Discuss how green finance, sustainability bonds, and ESG-focused funds are shaping M&A activity and creating new opportunities for growth.
How can companies create long-term value by integrating ESG into their M&A strategy, focusing on stakeholder engagement, regulatory compliance, and sustainable business practices post-merger? Explore the ways companies can drive long-term success by embedding ESG into every stage of the M&A lifecycle, from target selection to integration.
These prompts promote strategic reflection on the integration of ESG in M&A, encouraging concise yet comprehensive consideration of sustainability in deal-making.
Comments