Chapter 19
Digital Transformation and M&A
"The convergence of digital transformation and M&A is creating unparalleled opportunities for companies to scale faster, innovate more deeply, and achieve operational synergies that were once unimaginable. AI, automation, and remote integration are the future of deal-making." — Julie Sweet, CEO, Accenture.
This chapter explores the critical role digital transformation plays in modern M&A processes. It highlights how AI and machine learning can enhance due diligence, how automation can streamline complex workflows, and how virtual integration techniques are reshaping the post-merger landscape. Companies that adopt these technologies and approaches can gain a significant edge in managing complex M&A transactions, ensuring successful integration, and driving long-term business growth in a digital-first world.
19.1. Introduction
As companies across industries adapt to the rapid pace of technological advancement, M&A has become a critical tool for acquiring the capabilities necessary to thrive in the digital era. Digital transformation is no longer an option but a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to maintain competitive advantage, enhance operational efficiency, and position themselves for long-term growth. In this context, M&A provides a direct path for acquiring the technological expertise, digital talent, and innovative business models that can accelerate digital transformation efforts.
At the core of this alignment between digital transformation and M&A is the recognition that traditional business models are increasingly being disrupted by digital technologies. Cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics are transforming how companies operate, interact with customers, and deliver value. For companies that are lagging in digital capabilities, acquiring firms with advanced technological infrastructure or innovative digital platforms can offer an expedited route to modernization. This is especially important in industries like finance, healthcare, and retail, where digital technologies are not only enhancing operational efficiency but also enabling entirely new business models centered around data-driven decision-making and customer-centric solutions.
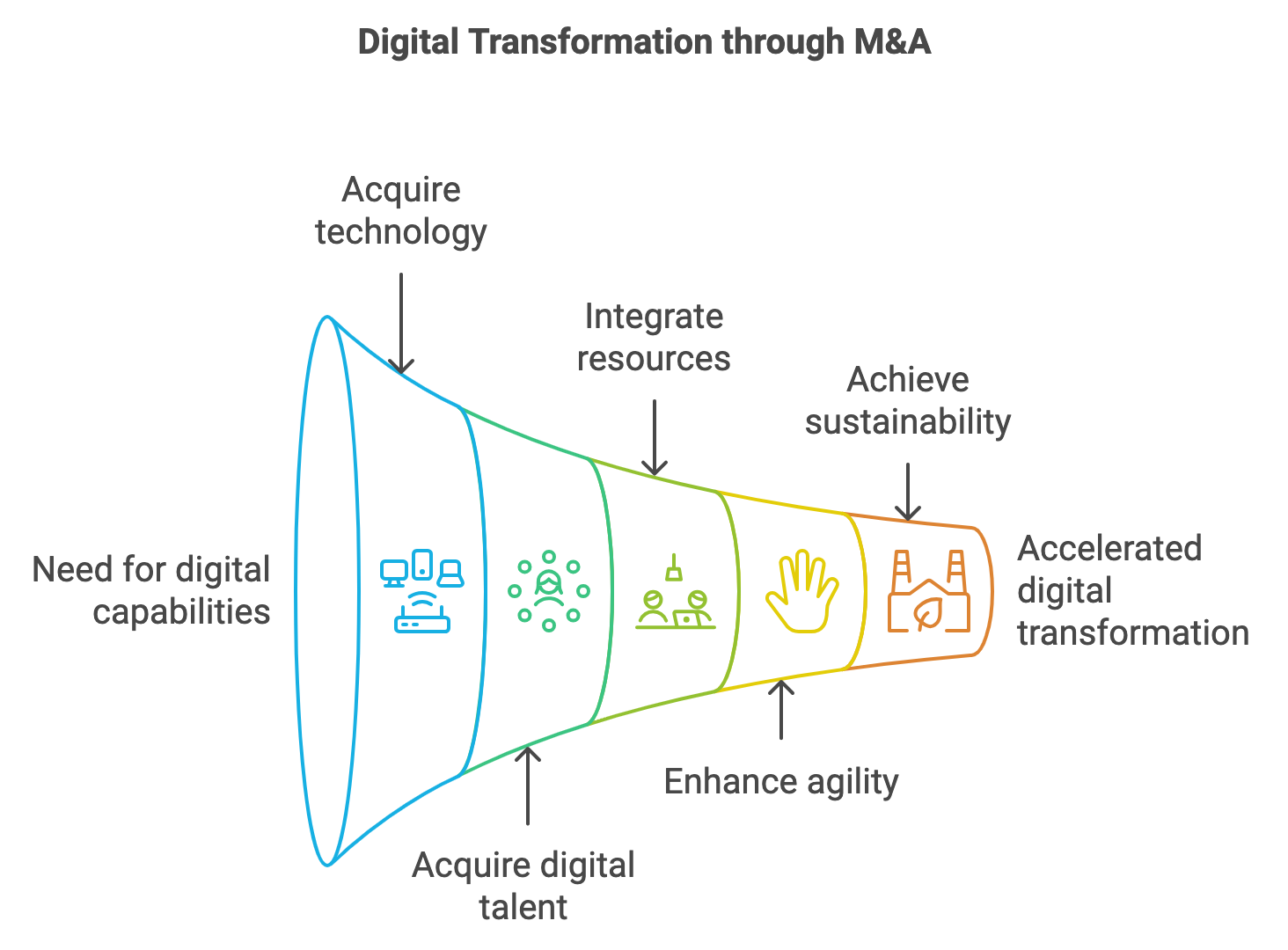
Figure 19.1: Funnel of digital transformation through M&A.
The strategic value of digital transformation in M&A lies in its ability to modernize legacy infrastructure. Many companies face the challenge of outdated IT systems and operational processes that are ill-suited for today’s fast-paced, digital-first world. Through M&A, companies can integrate modern technologies, such as cloud-based platforms, which offer greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure. Cloud computing, for instance, allows companies to move away from costly hardware and software investments, enabling them to streamline operations, reduce costs, and focus on innovation. Acquisitions of cloud-native companies or those with advanced digital platforms allow the acquiring firm to leapfrog years of development and implementation, ensuring a faster and more efficient digital transformation.
Moreover, digital transformation-driven M&A strategies are often focused on acquiring digital talent and expertise. In a landscape where technological capabilities are constantly evolving, having the right talent is essential to driving innovation and leveraging new technologies effectively. Companies that acquire firms with strong engineering, data science, and AI expertise can rapidly build up their digital capabilities. This approach is particularly relevant in industries where technological disruption is occurring at a rapid pace, and competition for top digital talent is fierce. By acquiring firms with specialized talent, companies can close the skills gap and better position themselves to leverage emerging technologies to their advantage.
One of the most critical aspects of digital transformation in the context of M&A is the ability to enhance a company’s agility. Digital transformation empowers companies to respond more rapidly to changes in the market, customer preferences, and competitive pressures. Through M&A, companies can acquire more agile organizational structures and digital operating models that support continuous innovation. For example, a company may acquire a startup that has developed a cutting-edge AI-powered customer service platform, enabling the acquiring firm to enhance its customer engagement strategies and improve overall responsiveness. The integration of such agile business models allows larger, more traditional companies to benefit from the speed and flexibility that smaller, digitally native firms often embody.
From an academic perspective, digital transformation in M&A can be analyzed through the lens of resource-based theory, which emphasizes the importance of acquiring valuable, rare, and inimitable resources to build competitive advantage. In the digital age, these resources increasingly include advanced technologies, proprietary algorithms, data analytics platforms, and digital ecosystems that enable companies to differentiate themselves in the marketplace. The strategic acquisition of these resources can enable companies to not only enhance their existing operations but also enter new markets, create innovative products and services, and build stronger customer relationships. The resource-based view underscores the importance of M&A as a tool for acquiring these intangible assets, which are often difficult or time-consuming to develop in-house.
Industry practices further highlight the importance of acquiring companies that are at the forefront of technological innovation. For example, major tech companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon have long used M&A to acquire startups and emerging tech firms with innovative solutions in AI, cloud computing, and data analytics. These acquisitions allow them to continuously evolve their product offerings, enhance their digital platforms, and maintain leadership in their respective industries. Similarly, traditional companies in sectors like automotive, manufacturing, and healthcare are increasingly using M&A to gain access to advanced digital technologies such as autonomous driving systems, IoT-enabled devices, and AI-driven diagnostic tools. These acquisitions help them stay competitive in a rapidly changing landscape and ensure they remain relevant in a digitally connected world.
In addition to technology acquisitions, M&A in the digital transformation context also focuses on acquiring new business models. Many traditional companies find themselves constrained by legacy business models that are not well-suited for the digital age. Acquiring companies with innovative digital-first business models—such as subscription-based services, platform ecosystems, or AI-driven marketplaces—can provide new revenue streams and improve customer engagement. For example, the acquisition of a digital subscription platform could enable a traditional media company to shift away from its reliance on advertising revenues and towards a more sustainable, recurring revenue model. These new business models are often underpinned by data and analytics, which allow companies to offer more personalized services and drive customer loyalty.
The integration of digital capabilities acquired through M&A also supports long-term sustainability goals. As environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations become more prominent, companies are increasingly seeking digital solutions that improve operational efficiency, reduce carbon footprints, and enable more sustainable practices. For instance, acquisitions in the energy sector might focus on digital technologies that enhance energy efficiency, optimize resource management, or enable more sustainable supply chains. In this sense, digital transformation through M&A not only drives business growth but also helps companies align with global sustainability goals, creating long-term value for both shareholders and society at large.
In conclusion, digital transformation is transforming the way companies approach mergers and acquisitions, offering new avenues for innovation, operational improvement, and competitive differentiation. By acquiring technological capabilities, digital talent, and innovative business models, companies can accelerate their digital transformation efforts and build the agility needed to thrive in a rapidly evolving market. M&A deals in the digital era are no longer just about consolidating market share or acquiring physical assets; they are about gaining access to the digital tools and expertise that enable long-term growth, operational efficiency, and sustainability. Through a well-aligned digital transformation and M&A strategy, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
19.2. Role of AI and Machine Learning in Due Diligence
Traditionally, due diligence has been a time-consuming and labor-intensive process, requiring teams of analysts, lawyers, and financial experts to comb through large volumes of data to assess the viability and risks associated with an acquisition. However, AI and ML technologies are revolutionizing this process by enhancing both the speed and accuracy of data analysis, allowing companies to make more informed and timely decisions.
At the heart of this transformation is the ability of AI and ML to process vast datasets with a level of speed and precision that far surpasses traditional methods. Due diligence in M&A requires the analysis of financial statements, legal contracts, operational data, and market trends—datasets that are often voluminous and complex. AI-driven tools can automatically sift through these documents, identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies that may be missed by human analysts. For example, AI can analyze years of financial data to spot inconsistencies or signs of financial distress, enabling companies to flag potential red flags before moving forward with a deal. This allows for a more granular and comprehensive understanding of the target company's financial health.
One of the most impactful applications of AI and ML in due diligence is in contract analysis. Traditionally, reviewing legal contracts is a labor-intensive task that involves parsing through dense legal language to identify risks, liabilities, and obligations. AI-driven natural language processing (NLP) tools have drastically improved this process by automating the review of contracts. These tools can quickly identify key clauses, such as change of control provisions, termination clauses, and indemnity obligations, ensuring that no critical risks are overlooked. This automation reduces the time needed for contract analysis from weeks or months to mere hours, improving the overall efficiency of the M&A process. Additionally, AI tools can highlight discrepancies between different versions of contracts, reducing the risk of misinterpretation or oversight.
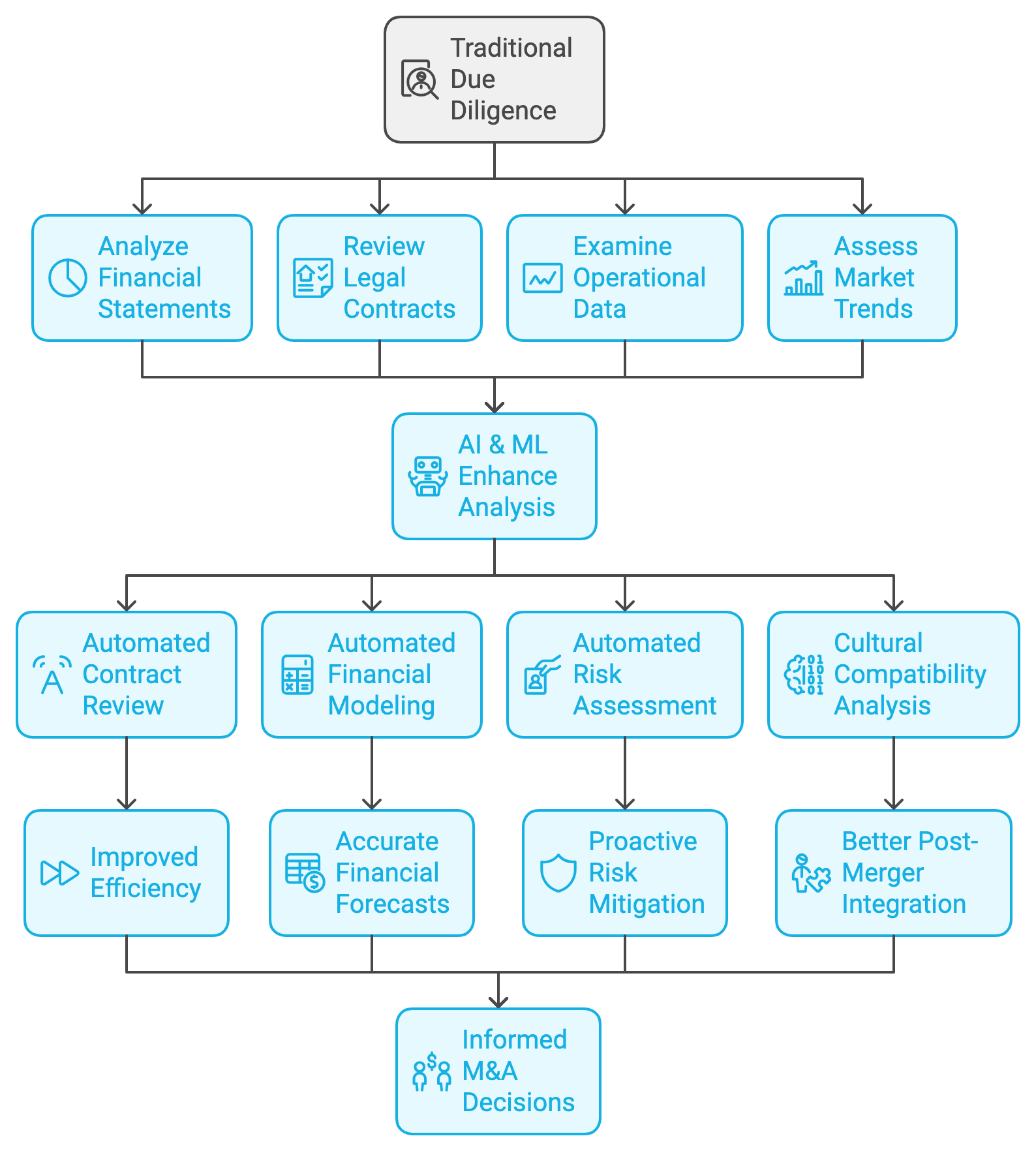
Figure 19.2: Traditional vs AI/ML based analysis in M&A process.
AI and ML are also transforming financial modeling during due diligence. M&A decisions are often based on projections of future revenue, profitability, and cash flows, which require complex financial models. AI-powered tools can automate the creation of these models by analyzing historical data, identifying trends, and predicting future financial performance. Machine learning algorithms, in particular, are well-suited for identifying patterns in large datasets and making predictions based on those patterns. For example, ML models can assess the likelihood of a target company meeting its future revenue targets based on historical performance, market conditions, and economic trends. This capability enables more accurate and data-driven financial forecasts, which are critical for evaluating the long-term value of an acquisition.
Risk assessment is another area where AI and ML are having a profound impact. In M&A, identifying and mitigating risks is essential to the success of the deal. AI-driven tools can automate risk assessments by analyzing various sources of data, including regulatory filings, news reports, and social media, to identify potential risks related to legal compliance, environmental issues, or reputational damage. For instance, AI can flag instances of non-compliance with industry regulations or detect early signs of litigation risk based on past legal cases. This automated risk detection allows acquiring companies to address potential liabilities proactively, thereby minimizing exposure to unforeseen risks.
Beyond financial and legal analysis, AI and ML can also play a role in assessing less tangible aspects of due diligence, such as cultural compatibility and market fit. Acquisitions often fail not because of financial or operational issues, but due to poor alignment between the acquiring and target companies' cultures. AI tools that analyze internal communications, employee feedback, and organizational structures can provide insights into the cultural dynamics of the target company. By analyzing patterns in communication styles, decision-making processes, and employee sentiment, AI can help assess whether the two organizations are likely to integrate successfully post-merger. Similarly, machine learning algorithms can evaluate market fit by analyzing market trends, consumer sentiment, and competitive positioning, helping companies gauge how well the target company’s products or services align with market demands.
In academic discussions, the role of AI and ML in M&A due diligence is often framed within the broader context of digital transformation. The use of these technologies represents a shift from traditional manual processes to more automated, data-driven decision-making frameworks. The academic literature highlights that AI and ML can significantly reduce the time and resources required for due diligence while improving the accuracy of risk assessments and financial projections. Additionally, research suggests that AI-enabled due diligence can lead to better post-merger integration outcomes, as the insights generated by AI tools can help identify potential areas of conflict or misalignment early in the process.
In practice, companies across industries are increasingly adopting AI and ML tools to streamline their due diligence processes. Large consulting firms and investment banks are leveraging AI to enhance their M&A advisory services, offering clients faster and more accurate insights into potential deals. For example, AI-driven platforms like Kira Systems and Leverton use machine learning algorithms to automate document review, significantly speeding up the due diligence process. These platforms are capable of extracting key data points from thousands of contracts, reducing human error and ensuring that important details are not overlooked.
Moreover, AI and ML tools are being used to enhance cybersecurity due diligence. With the growing importance of data security in M&A transactions, especially in sectors like healthcare and finance, acquiring companies must assess the cybersecurity posture of the target company. AI-driven cybersecurity tools can analyze network traffic, detect vulnerabilities, and assess the risk of data breaches, providing a comprehensive view of the target company's cybersecurity risks. This is particularly important given the increasing frequency of cyberattacks and data breaches, which can have significant financial and reputational consequences for acquiring companies.
In conclusion, AI and machine learning are transforming the due diligence process in mergers and acquisitions by automating complex tasks, improving data analysis, and enhancing risk assessment. These technologies enable companies to conduct more thorough and accurate due diligence in a fraction of the time required by traditional methods. From contract analysis and financial modeling to risk detection and cultural assessments, AI and ML provide real-time insights that help companies make more informed decisions during the M&A process. As digital transformation continues to shape the business landscape, AI-driven due diligence is becoming an essential tool for companies seeking to gain a competitive edge in the increasingly complex world of mergers and acquisitions.
19.3. Automation of M&A Processes
Traditionally, M&A transactions have been labor-intensive, requiring significant human involvement in tasks such as document management, data entry, compliance verification, and integration planning. These processes are time-consuming, prone to human error, and can significantly slow down deal execution. However, with the advent of robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and other digital tools, companies are increasingly automating these repetitive tasks, allowing M&A teams to focus on more strategic and value-adding activities.
Automation, in the context of M&A, addresses several key challenges. One of the most prominent areas where automation adds value is document management. M&A transactions generate massive amounts of documentation, including contracts, financial statements, regulatory filings, and due diligence reports. Traditionally, managing this documentation required manual sorting, reviewing, and categorizing, which was not only time-consuming but also susceptible to human error. With automation, RPA and AI-powered tools can streamline the document management process by automatically organizing, tagging, and categorizing large volumes of documents. These tools can also apply machine learning algorithms to extract key information, identify discrepancies, and flag potential risks, thereby reducing the need for manual intervention and improving overall accuracy.
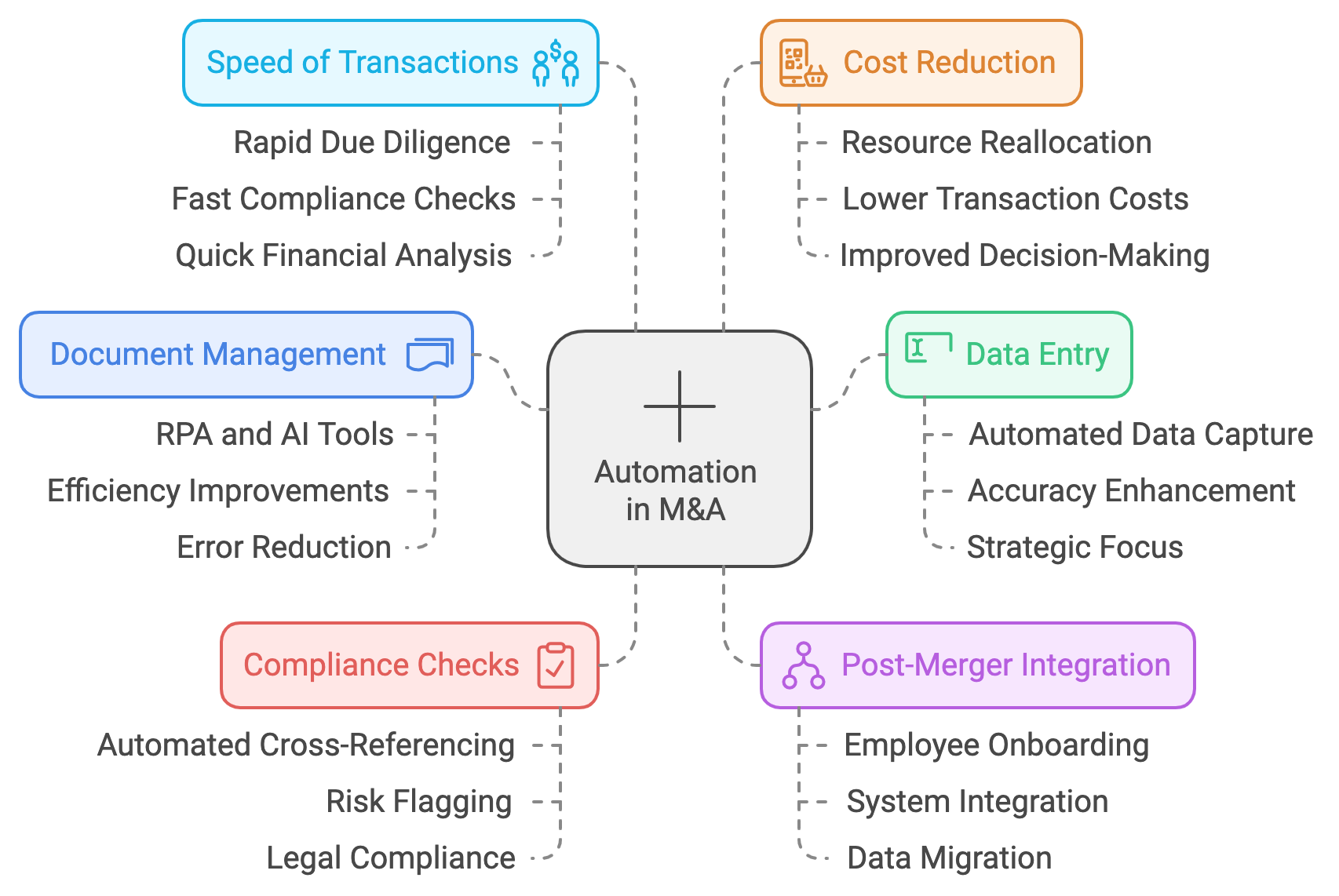
Figure 19.3: Scopes of automation in M&A process.
Data entry is another area where automation is making a significant impact. In M&A, large amounts of financial, operational, and market data must be entered into various systems to assess the target company’s performance and value. Manual data entry is prone to errors, especially when dealing with complex datasets. RPA can automate this process by capturing data from multiple sources and inputting it into relevant systems with minimal human oversight. This not only improves the speed of data processing but also enhances the accuracy of the data, reducing the likelihood of costly mistakes during the transaction. Automating data entry tasks also frees up M&A teams to focus on analyzing the data and deriving actionable insights, rather than spending time on manual data handling.
Compliance checks are another critical area where automation is playing an increasingly important role. The regulatory landscape for M&A transactions is complex, and companies must ensure that they comply with all relevant laws and regulations, such as antitrust laws, industry-specific regulations, and environmental standards. Manual compliance checks are labor-intensive and can lead to delays in the transaction process. Automation tools can streamline compliance by automatically cross-referencing documents and data against regulatory requirements. For example, AI-powered tools can analyze contracts to ensure they meet legal and regulatory standards, flagging any non-compliance or risks for further review. This reduces the time and effort required for compliance checks and ensures that the transaction adheres to all legal requirements.
One of the most significant benefits of automation in M&A is its role in post-merger integration (PMI) workflows. Integrating two companies after a merger is often one of the most challenging aspects of the M&A process, as it involves aligning systems, processes, and cultures. PMI can be a lengthy and complex process, requiring coordination across multiple departments such as finance, IT, human resources, and operations. Automation can help streamline this process by automating routine tasks such as employee onboarding, system integration, and data migration. For instance, RPA can be used to automate the transfer of employee data from the target company’s HR system to the acquiring company’s system, ensuring that the transition is smooth and error-free. Similarly, automation tools can facilitate the integration of financial systems by automatically reconciling accounts and transferring financial data, thereby reducing the risk of errors and speeding up the integration process.
Another key advantage of automation in M&A is its ability to improve the overall speed of transactions. M&A deals are often time-sensitive, with companies seeking to close deals quickly to capitalize on market opportunities or mitigate risks. Manual processes can slow down deal execution, leading to missed opportunities and increased transaction costs. Automation tools help reduce these delays by accelerating tasks that would otherwise require significant human intervention. For example, RPA can process large volumes of data in a fraction of the time it would take a human team to do the same, allowing M&A teams to move through due diligence, compliance checks, and financial analysis more rapidly. This speed not only improves deal execution but also enables companies to respond more quickly to market dynamics and competitive pressures.
Cost reduction is another important benefit of automation in M&A. Traditional M&A processes are resource-intensive, requiring large teams of professionals to manage tasks such as due diligence, contract review, and integration planning. Automation can significantly reduce the need for manual labor, resulting in lower transaction costs. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, companies can reallocate resources to higher-value activities, such as strategic planning, negotiation, and relationship management. This not only improves the cost-efficiency of the M&A process but also enhances the overall quality of decision-making, as teams can focus on analyzing data and crafting strategies rather than performing administrative tasks.
Academic discussions around automation in M&A emphasize the importance of leveraging digital technologies to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Research suggests that automation enables companies to make more data-driven decisions by providing real-time insights and reducing the risk of human error. The integration of AI and RPA in M&A processes allows companies to process large volumes of data quickly and accurately, facilitating better risk assessment and more informed decision-making. Additionally, automation tools can help identify synergies between the acquiring and target companies by analyzing operational data, customer trends, and market positioning. This enables companies to maximize the value of the acquisition by focusing on areas where the greatest synergies can be achieved.
Industry practices further underscore the growing importance of automation in M&A. Many companies are adopting automation tools to streamline their M&A processes and improve transaction outcomes. For example, global financial institutions and consulting firms are increasingly using RPA and AI to automate due diligence tasks, allowing them to manage large, complex transactions with greater efficiency. By automating tasks such as contract analysis, financial modeling, and compliance checks, these firms can reduce the time and cost associated with each deal, while improving the accuracy and reliability of their analyses.
In conclusion, automation is playing a transformative role in the M&A process by enhancing efficiency, reducing human error, and improving the speed of transactions. Through the use of technologies like RPA, AI, and other digital tools, companies can automate repetitive tasks such as document management, data entry, and compliance checks, allowing M&A teams to focus on more strategic activities. Automation not only accelerates the transaction process but also reduces costs and improves the accuracy of decision-making. As digital transformation continues to reshape the M&A landscape, automation will become an increasingly important tool for companies seeking to optimize their M&A strategies and achieve better outcomes in an increasingly competitive and fast-paced environment.
19.4. Virtual and Remote Integration Techniques
As the pandemic disrupted traditional in-person integration processes, companies turned to virtual platforms and digital tools to manage the complexities of M&A without physical proximity. This shift has reshaped how post-merger integration (PMI) is conducted, offering both opportunities and challenges for companies navigating the integration of assets, operations, and teams across different geographies.
Before the pandemic, M&A integration was largely dependent on face-to-face interactions, where teams would come together to conduct due diligence, finalize deal negotiations, and execute post-merger plans. The pandemic, however, imposed travel restrictions and necessitated remote work, compelling companies to adopt virtual integration techniques to maintain business continuity. Tools like virtual data rooms (VDRs), cloud-based collaboration platforms, and remote communication systems have since become integral to M&A activities, from the initial stages of due diligence to the complex phases of post-merger integration.
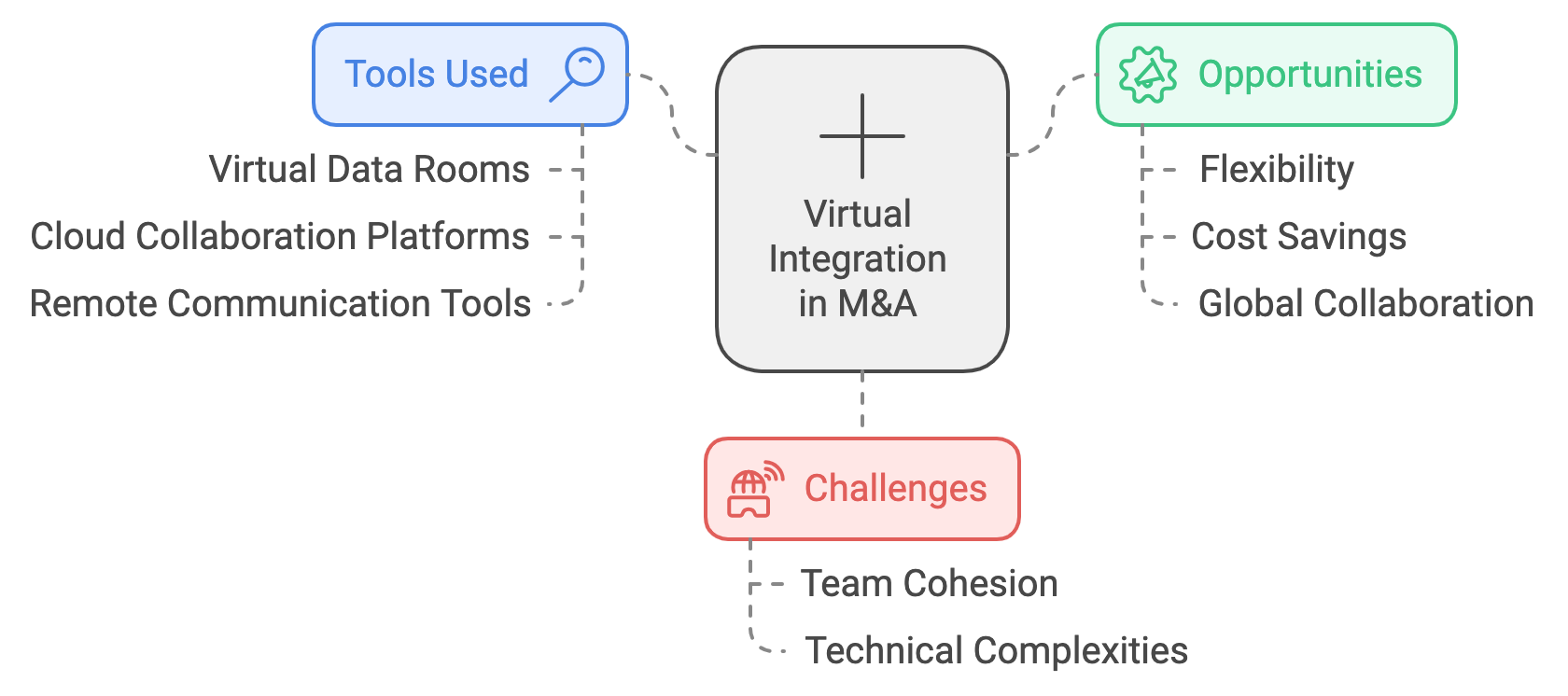
Figure 19.4: Virtual Integration in M&A process.
Virtual data rooms are now a cornerstone of modern M&A transactions, facilitating the secure sharing and review of sensitive information among parties in a deal. These virtual environments provide a secure platform for conducting due diligence remotely, enabling buyers and sellers to access key documents, financial statements, legal contracts, and operational data without the need for physical exchanges. Virtual data rooms also enhance transparency, allowing real-time collaboration between stakeholders across different time zones and regions. This increased accessibility has not only accelerated the due diligence process but also ensured that critical deal information remains confidential and secure through advanced encryption and access control protocols.
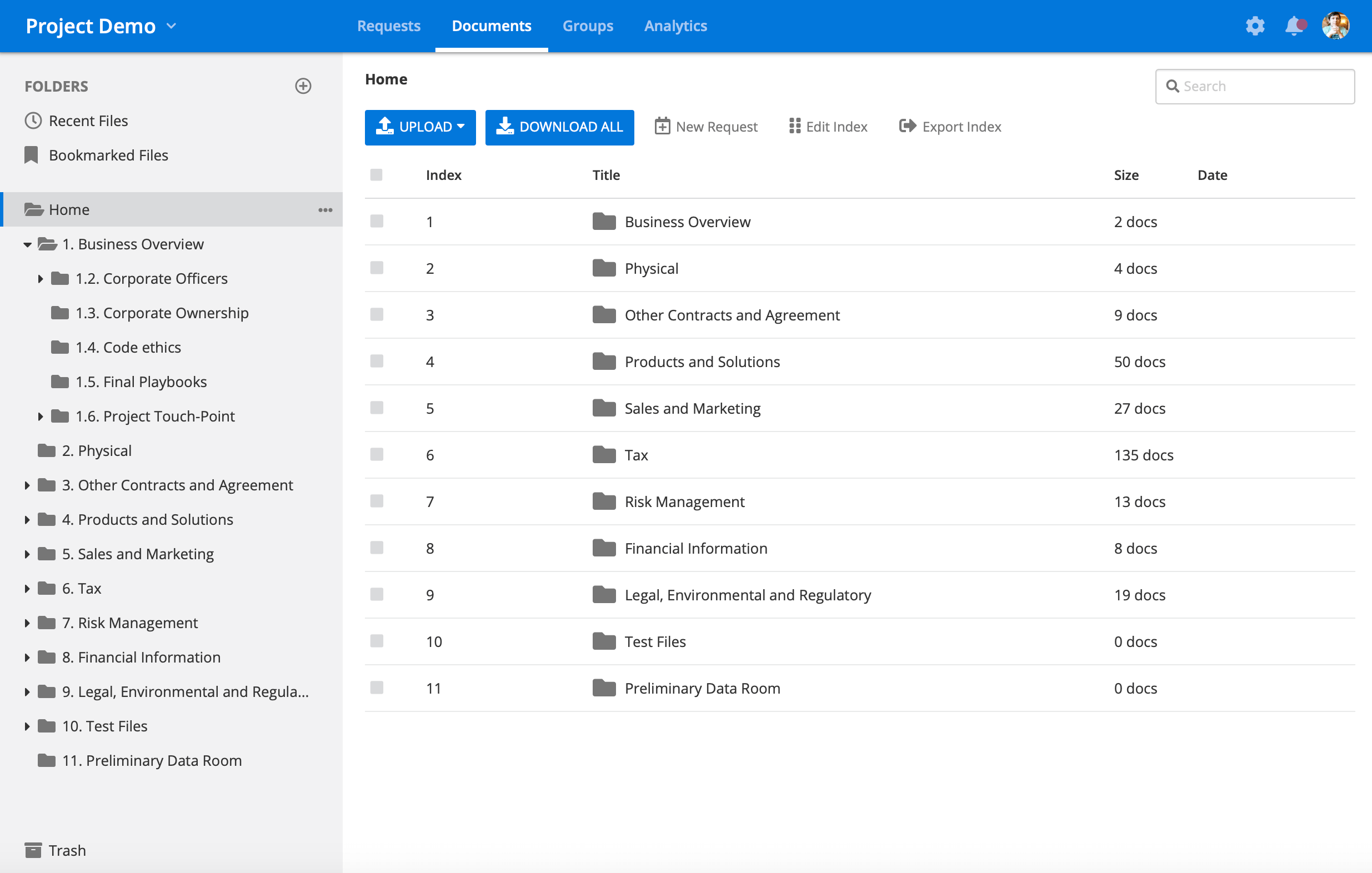
Figure 19.5: Example of cloud-based VDR tool.
Cloud collaboration platforms, such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Google Workspace, have also played a pivotal role in virtual integration, enabling teams to collaborate seamlessly despite being physically dispersed. These platforms offer real-time document sharing, version control, and communication capabilities, which are essential for coordinating the complex workflows involved in post-merger integration. The ability to access documents, financial models, and project plans from any location allows teams to maintain productivity and alignment throughout the integration process. Moreover, cloud platforms support asynchronous communication, enabling teams in different time zones to work efficiently without the delays associated with traditional in-person meetings or manual document exchanges.
Remote communication tools, including video conferencing platforms like Zoom and Webex, have further enhanced the integration process by allowing virtual meetings and discussions between executives, integration teams, and stakeholders. These tools provide a vital alternative to face-to-face meetings, ensuring that strategic decisions, cultural alignment discussions, and operational planning can continue without interruption. Additionally, the shift to virtual meetings has introduced greater flexibility into the M&A process, reducing the need for costly and time-consuming travel while enabling more frequent touchpoints between geographically dispersed teams.
While virtual integration techniques offer many advantages, they also present unique challenges that companies must address to ensure successful post-merger outcomes. One of the primary challenges is maintaining team cohesion and cultural alignment when teams are physically separated. Culture is a critical factor in the success of any M&A transaction, and virtual integration can make it more difficult to foster the interpersonal relationships and trust that are often built through in-person interactions. Without the benefit of shared physical spaces and spontaneous conversations, companies must take deliberate steps to facilitate communication and collaboration across teams. This may involve organizing more frequent virtual check-ins, creating informal virtual spaces for social interaction, and implementing strategies to ensure that employees feel connected to the broader organizational vision.
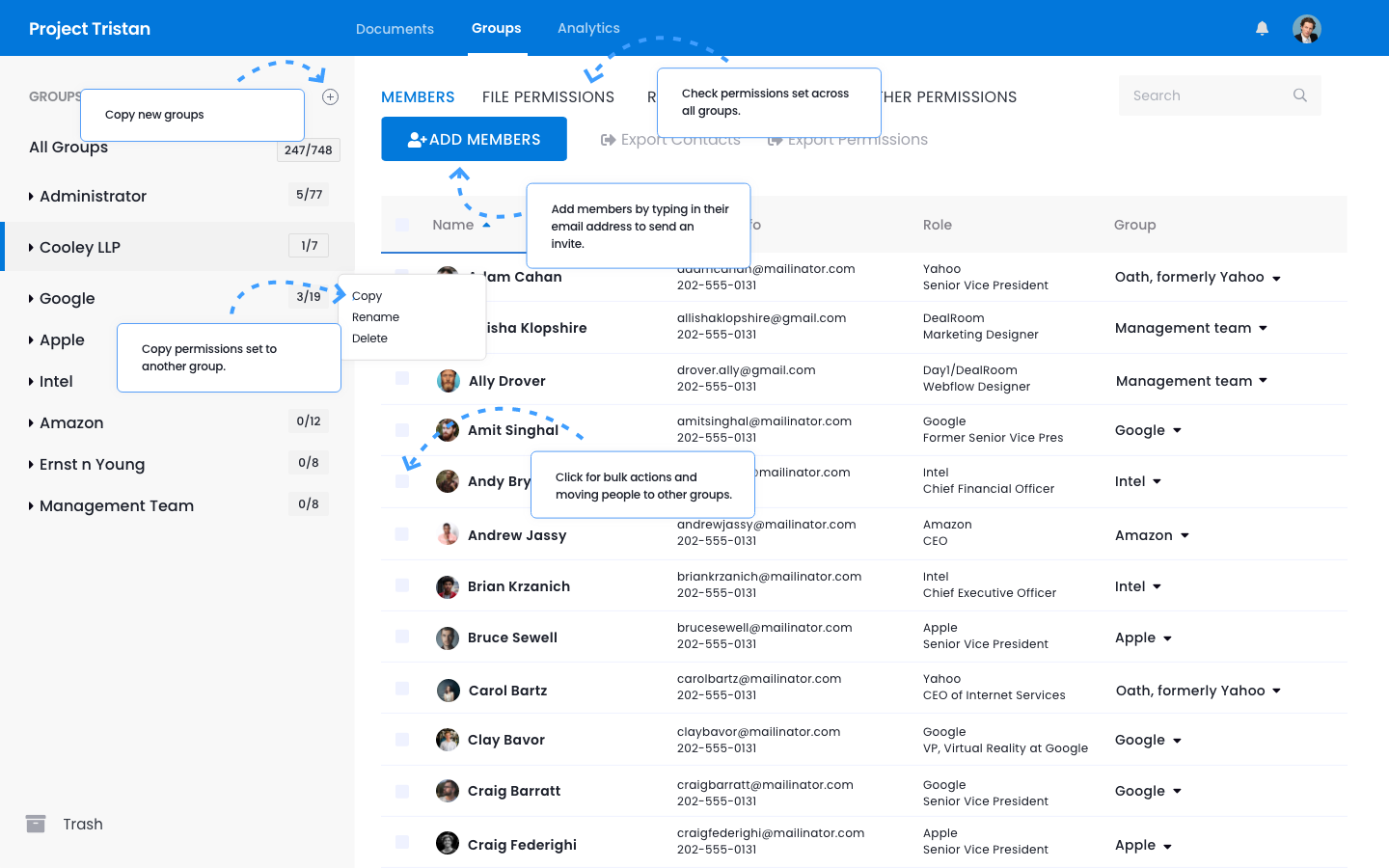
Figure 19.6: Team cohesion and alignment in VDR (eq. Sharepoint solution).
Another challenge is managing the technical complexities of virtual integration. While digital tools provide powerful capabilities for collaboration, they also require robust IT infrastructure, cybersecurity measures, and data governance protocols. Companies must ensure that their cloud platforms, virtual data rooms, and communication tools are fully integrated, secure, and scalable to handle the demands of the integration process. This includes addressing potential issues related to data privacy, regulatory compliance, and access control, particularly when integrating teams and assets across different countries with varying legal requirements. Failure to establish a secure and efficient digital infrastructure can lead to data breaches, miscommunication, and operational delays, undermining the success of the integration.
Despite these challenges, the shift to virtual and remote integration presents significant opportunities for companies to rethink and modernize their integration strategies. One of the most notable benefits is the increased flexibility and agility that virtual tools provide. Remote integration enables companies to tap into a global talent pool, allowing them to assemble integration teams from multiple regions without being constrained by geographic limitations. This global reach not only enhances the diversity and expertise of the integration team but also enables faster decision-making and execution by leveraging the capabilities of a geographically dispersed workforce. Moreover, virtual integration allows companies to scale their integration efforts more easily, adjusting the size and scope of integration teams as needed without the logistical constraints of physical proximity.
Additionally, virtual integration techniques can lead to cost savings by reducing travel expenses, office space requirements, and other overhead costs associated with traditional in-person integration. By leveraging digital tools for document management, communication, and collaboration, companies can streamline their operations and reduce the time and resources needed to complete the integration process. This cost-efficiency is particularly valuable in M&A transactions, where controlling integration costs is critical to maximizing the value of the deal.
Academically, the rise of virtual and remote integration techniques aligns with broader trends in digital transformation and the future of work. Research highlights that remote collaboration can increase efficiency and productivity when supported by the right technologies and organizational practices. Virtual integration not only enables companies to overcome the constraints of physical distance but also encourages more flexible and adaptive approaches to managing complex M&A transactions. Scholars have noted that virtual integration allows for more continuous and iterative integration processes, where teams can adjust their strategies in real-time based on the evolving needs of the business and the market.
Industry practices demonstrate that companies across sectors are increasingly embracing virtual integration as a long-term strategy, even as pandemic-related restrictions ease. The financial services, technology, and healthcare industries, in particular, have seen a surge in the use of virtual tools for M&A integration, as these industries rely heavily on knowledge work and digital collaboration. Companies that have successfully navigated the shift to virtual integration have reported increased speed and efficiency in their integration efforts, as well as improved employee engagement and satisfaction through the use of flexible work arrangements. As remote work becomes more ingrained in the corporate culture, virtual integration is likely to remain a central component of M&A strategies, offering companies the ability to adapt to a rapidly changing business environment.
In conclusion, virtual and remote integration techniques are reshaping the M&A landscape by enabling companies to integrate assets, operations, and teams without the constraints of physical proximity. Virtual data rooms, cloud collaboration platforms, and remote communication tools have become essential for conducting M&A activities, from due diligence to post-merger integration. While the shift to virtual integration presents challenges, such as maintaining cultural alignment and managing technical complexities, it also offers significant opportunities for increased flexibility, cost savings, and global collaboration. As companies continue to embrace digital transformation, virtual integration is poised to play an increasingly important role in driving successful M&A outcomes in the post-pandemic world.
19.5. Conclusion
Chapter 19 demonstrates how digital transformation is impacting the entire M&A lifecycle—from due diligence to post-merger integration. By leveraging AI, automation, and virtual integration techniques, companies can drive more efficient, cost-effective, and strategically aligned M&A processes. Digital tools and technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for growth, sustainability, and competitive advantage in a fast-evolving market. As M&A moves deeper into the digital age, companies that embrace these technologies will be better equipped to handle the complexities of modern business deals and unlock long-term value.
19.5.1. Further Learning with GenAI
The following prompts encourage an in-depth exploration of the intersection between digital transformation and M&A, focusing on AI, automation, and remote integration to streamline processes and create long-term value. Each prompt is designed to provide comprehensive insights into how companies can harness digital tools to optimize M&A outcomes.
How can companies align digital transformation goals with M&A strategies to maximize growth, operational efficiency, and long-term value creation? Discuss how M&A can serve as a vehicle for acquiring digital capabilities and how digital transformation enhances deal-making outcomes.
What are the key digital transformation drivers in M&A, and how can companies evaluate acquisition targets based on their technological capabilities, digital maturity, and innovation potential? Explore how companies assess a target’s digital transformation readiness and align acquisitions with future digital strategies.
How can AI and machine learning be applied during due diligence to improve accuracy, identify hidden risks, and provide deeper insights into a target company’s financial, legal, and operational health? Analyze the role of AI in automating due diligence tasks such as financial analysis, contract review, and compliance checks.
What specific areas of M&A due diligence benefit the most from AI-driven analysis, and how can AI help detect red flags related to financial discrepancies, legal liabilities, or operational inefficiencies? Explore how AI helps uncover hidden risks and identifies early warnings that traditional due diligence may miss.
How can machine learning models improve the precision of predictive analytics during M&A, providing more accurate forecasts about the future performance and market positioning of the target company? Discuss the use of ML algorithms for predicting post-merger outcomes, including revenue growth, market share, and profitability.
What are the key advantages of automating M&A processes such as data collection, compliance management, and post-merger integration, and how does automation reduce the risk of human error? Analyze how automation improves the efficiency, speed, and accuracy of M&A transactions by eliminating repetitive manual tasks.
How can robotic process automation (RPA) streamline tasks like document management, financial reporting, and regulatory compliance during M&A, allowing companies to focus on high-value strategic decisions? Discuss the role of RPA in reducing time spent on administrative tasks and enabling faster deal execution.
What challenges do companies face when integrating automation into their M&A processes, and how can these challenges be overcome to achieve faster, more efficient deal-making? Explore barriers to adopting automation and strategies for successful implementation across the M&A lifecycle.
How can companies leverage AI and automation to optimize post-merger integration, ensuring that operational, financial, and cultural synergies are realized more quickly and effectively? Discuss how AI and automation streamline integration processes such as HR, IT, and finance integration to unlock synergies.
What role do virtual data rooms, cloud collaboration platforms, and remote communication tools play in the digital transformation of M&A, and how do they facilitate seamless virtual due diligence? Examine the impact of virtual collaboration tools in enabling efficient, secure M&A transactions across geographically dispersed teams.
How has the shift to virtual and remote integration techniques reshaped the post-merger landscape, and what best practices can companies follow to ensure successful remote integration of assets, operations, and teams? Explore how companies can manage cultural and operational integration remotely without sacrificing efficiency or team cohesion.
What are the potential risks and challenges associated with virtual M&A processes, such as cybersecurity vulnerabilities or communication gaps, and how can companies mitigate these risks? Discuss the importance of cybersecurity and communication strategies in maintaining security and alignment during virtual deals.
How can companies maintain a sense of team cohesion and shared purpose during virtual post-merger integration, especially when integrating geographically dispersed teams with different corporate cultures? Explore strategies for virtual team-building and maintaining alignment during remote integration efforts.
How can AI-driven sentiment analysis and predictive analytics be used to assess cultural compatibility between merging companies, providing insights into potential cultural integration challenges? Discuss the use of AI tools to evaluate and predict cultural fit during the integration phase.
What role do digital transformation technologies such as cloud computing and data analytics play in accelerating post-merger integration, and how can they support the scalability of newly combined entities? Examine how cloud-based platforms and data analytics tools facilitate faster integration and scalability post-merger.
How can companies evaluate the digital maturity of an acquisition target, and what key metrics should they track to determine whether the target is aligned with their broader digital transformation goals? Discuss metrics such as technology stack compatibility, digital talent, and innovation capabilities for assessing digital maturity.
How can companies build a robust digital transformation roadmap that integrates AI, automation, and data analytics into their M&A strategy to drive long-term innovation and competitive advantage? Explore how a digital transformation roadmap can support M&A strategies focused on technological leadership and innovation.
What role do AI-powered decision support systems play in M&A deal structuring, and how can they improve deal outcomes by providing real-time insights into market conditions and deal economics? Analyze the impact of AI-powered tools in making data-driven decisions during M&A deal structuring.
How can companies use digital dashboards and real-time analytics to monitor post-merger integration progress, ensuring that key performance indicators (KPIs) are tracked and adjusted dynamically? Discuss the use of digital tools to continuously monitor integration milestones and ensure KPIs align with strategic goals.
How can digital transformation enable companies to build a more agile M&A strategy, allowing them to respond quickly to emerging market opportunities and integrate acquisitions more efficiently?
Explore how digital tools and agile processes support faster, more adaptive M&A strategies in a rapidly evolving market.
The prompts offer a focused, one-sentence approach while encouraging a comprehensive exploration of digital transformation's role in M&A, particularly through AI, automation, and virtual processes.
Comments