Chapter 16
Acquisition Programs and Competitive Benefits
"The ability to develop repeatable M&A processes and build strong internal capabilities gives companies a significant advantage in the market, allowing them to execute deals faster, more efficiently, and with greater impact." — Michael DeVito, Global Head of M&A, JPMorgan Chase.
This chapter explores how organizations can develop structured acquisition programs, build internal M&A capabilities, create repeatable processes, and leverage mergers and acquisitions to gain a competitive edge. It emphasizes the importance of a strategic approach to M&A, where success is driven by consistency, agility, and the ability to capitalize on market opportunities. Companies that effectively manage their M&A initiatives position themselves for sustained growth and long-term competitiveness in their industries.
16.1. Acquisition Programs and Competitive Benefits
The focus in this section is on how structured acquisition programs can be a powerful tool for organizations seeking to establish and maintain a competitive edge in their industries. A well-designed acquisition program allows companies to systematically identify and pursue M&A opportunities that align with their broader strategic goals, whether those goals are market expansion, operational efficiency, access to new technologies, or diversification. By taking a proactive approach to acquisitions, companies are better positioned to seize market opportunities, outpace competitors, and achieve sustained growth in a dynamic business landscape.
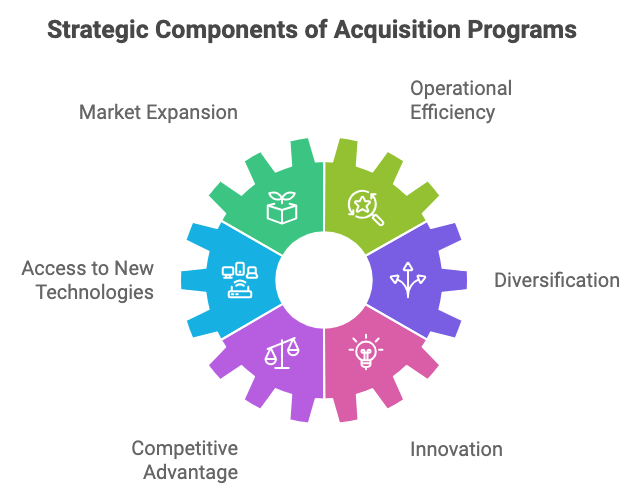
Figure 16.1: Key Strategic Components of a Structured Acquisition Program.
From an academic standpoint, acquisition programs are grounded in strategic management theories, particularly those related to resource-based views (RBV) and competitive advantage. These theories suggest that firms gain a competitive edge by acquiring and integrating valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable (VRIN) resources, such as intellectual property, cutting-edge technologies, or specialized human capital. A structured acquisition program enables companies to systematically scout for and acquire these strategic resources, thus enhancing their competitive position. The theory of dynamic capabilities also plays a role here, as it highlights the importance of an organization’s ability to adapt, integrate, and reconfigure internal and external competencies to respond to rapidly changing market conditions. Acquisition programs, therefore, serve as a mechanism for building and deploying these dynamic capabilities.
In practice, a comprehensive acquisition program is defined by its alignment with the organization’s long-term vision and growth strategy. Companies that excel in leveraging acquisitions as a competitive tool typically establish clear strategic objectives that guide their acquisition efforts. These objectives often include expanding into new geographic markets, acquiring innovative technologies, entering new industry verticals, or enhancing operational efficiency through economies of scale. For example, a technology firm might pursue acquisitions to gain access to emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) or blockchain, allowing it to stay ahead of the competition and accelerate innovation. Similarly, a retail company may focus on acquiring competitors in key geographic regions to rapidly scale its market presence and capture additional market share.
A key benefit of acquisition programs is the ability to achieve rapid market expansion, often faster than organic growth would allow. Academically, this aligns with theories of first-mover advantage, which suggest that companies that are quick to enter new markets or adopt new technologies can achieve a dominant position that is difficult for competitors to dislodge. Acquisition programs allow organizations to identify and capitalize on market opportunities swiftly, especially in fast-moving industries such as technology, healthcare, or consumer goods. For instance, by acquiring companies in high-growth markets, a firm can immediately gain access to new customer bases, distribution networks, and local expertise, significantly shortening the time it would take to build those capabilities from scratch.
In industry practice, companies that build successful acquisition programs often adopt a portfolio approach to M&A, viewing acquisitions not as isolated transactions but as part of a broader strategy to strengthen their competitive position. This portfolio approach ensures that each acquisition aligns with the company’s long-term goals and that synergies are realized across multiple areas, such as operations, marketing, and innovation. For example, when a global pharmaceutical company develops an acquisition program focused on acquiring biotech startups, it does so not only to diversify its product lines but also to build a robust pipeline of innovative therapies that will drive future growth. Each acquisition is carefully selected to complement the company’s existing capabilities, enhance its R&D efforts, and solidify its leadership position in the market.
Acquisition programs also play a crucial role in fostering innovation. Academically, the connection between acquisitions and innovation is well-established, particularly in industries where technological disruption is common. By acquiring companies with innovative technologies or processes, organizations can accelerate their own innovation timelines and reduce the risks associated with in-house research and development. Moreover, acquisitions often bring in new talent, new ideas, and different perspectives, all of which can invigorate the acquiring company’s innovation efforts. In practice, companies that leverage acquisition programs for innovation often target startups or smaller firms that are pushing the boundaries of technology, enabling them to integrate these cutting-edge solutions into their existing operations. This can provide a significant competitive advantage, especially in industries where being at the forefront of technological change is critical for maintaining market leadership.
Another competitive benefit of acquisition programs is the ability to enhance operational efficiency. When companies acquire firms with complementary operational strengths—such as supply chain efficiencies, advanced manufacturing processes, or specialized human capital—they can integrate these strengths into their existing operations, achieving cost savings and improving overall productivity. Academically, this ties into the concept of operational synergies, where the combined entity is more efficient than the sum of its parts. For example, a company may acquire a competitor that operates at a lower cost structure, allowing the combined entity to achieve greater economies of scale. In practice, operational synergies often manifest in areas such as procurement, manufacturing, logistics, and human resources, where consolidation leads to reduced costs and improved efficiency.
Furthermore, acquisition programs can help companies consolidate industry leadership, giving them the ability to outmaneuver competitors and achieve greater market dominance. Academically, this can be seen in the lens of competitive strategy and industry consolidation, where larger firms acquire smaller competitors to build scale, reduce competition, and create barriers to entry for new market entrants. In practice, companies that adopt this approach often focus on acquiring rivals or complementary businesses in fragmented industries, where consolidation can lead to greater market power. For instance, a large financial services company might pursue an acquisition program aimed at consolidating regional banks, allowing it to create a national footprint and strengthen its position against larger, more established players.
Finally, one of the most strategic advantages of a well-structured acquisition program is the ability to align acquisitions with the company’s long-term vision and growth strategy. Academically, strategic alignment is key to successful M&A, as it ensures that the acquired company’s resources, capabilities, and market position complement the acquiring company’s objectives. Acquisition programs that are designed with this alignment in mind are more likely to succeed because they focus on deals that drive long-term value creation rather than short-term financial gains. In practice, companies that integrate acquisitions into their broader strategic plans are better equipped to realize synergies, avoid integration challenges, and maintain focus on their core business objectives.
In conclusion, a well-structured acquisition program offers numerous competitive benefits, from market expansion and operational efficiency to innovation and industry consolidation. By aligning acquisitions with strategic objectives and long-term vision, companies can use M&A as a powerful tool to strengthen their market position, outmaneuver competitors, and drive sustained growth. The academic foundations of acquisition programs—rooted in resource-based views, dynamic capabilities, and competitive strategy—underscore their importance as a mechanism for building and sustaining competitive advantage. In industry practice, acquisition programs allow companies to rapidly respond to market opportunities, leverage synergies, and maintain leadership in their respective sectors, ultimately positioning them for long-term success in a competitive global marketplace.
16.2. Building M&A Capabilities within the Organization
The focus in this section is on the essential role that developing strong in-house M&A capabilities plays in ensuring long-term success in the competitive mergers and acquisitions landscape. The ability to execute and manage acquisitions effectively requires more than just financial and legal acumen; it demands a comprehensive set of strategic, operational, and cultural skills that enable organizations to identify, evaluate, and integrate acquisition targets in a way that maximizes value creation. By building these capabilities internally, companies can enhance their agility in responding to market opportunities, reduce dependency on external advisors, and maintain greater control over the acquisition process from start to finish.
From an academic perspective, the development of M&A capabilities aligns with the broader concept of organizational capabilities, which highlights the importance of building internal competencies that allow firms to adapt, innovate, and sustain competitive advantages. In the context of M&A, this translates to the need for organizations to develop a holistic understanding of the acquisition process, including the ability to identify strategic targets, conduct thorough due diligence, and manage post-merger integration. These capabilities form the foundation for what scholars refer to as “acquisition competence”—the ability of a firm to consistently execute successful mergers and acquisitions over time. Acquisition competence goes beyond the technical aspects of deal-making; it also encompasses the softer, more strategic dimensions of M&A, such as aligning the transaction with the company’s long-term vision, fostering cultural integration, and managing leadership transitions.
In practice, building in-house M&A capabilities starts with assembling a dedicated M&A team that brings together expertise from various disciplines, including finance, law, operations, human resources, and strategy. This cross-functional approach ensures that all aspects of the acquisition are considered holistically, from the initial identification of potential targets to the final stages of integration. Financial and legal expertise are, of course, essential for navigating the complexities of deal structuring, regulatory compliance, and valuation. However, equally important is the ability to conduct strategic assessments of potential acquisition targets, evaluating not just their financial performance but also their strategic fit with the acquiring company’s long-term goals, market position, and operational capabilities.
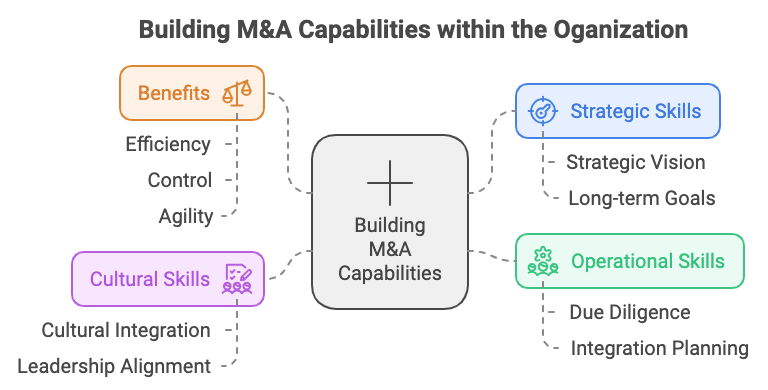
Figure 16.2: Key Aspects in Building In-house M&A Capabilities.
One of the key benefits of developing an in-house M&A team is that it allows companies to execute deals more efficiently and maintain better control over the process. In academic terms, this aligns with transaction cost economics, which suggests that firms can reduce costs and risks by internalizing critical functions rather than relying on external intermediaries. By building internal M&A expertise, companies reduce their dependence on investment banks, consultants, and legal advisors, gaining greater control over the timeline, cost, and strategic direction of each deal. Moreover, an internal M&A team is better positioned to develop deep organizational knowledge, allowing them to apply lessons learned from past deals to future transactions and to tailor the acquisition process to the specific needs and culture of the company.
In industry practice, companies that excel in M&A often develop specialized M&A teams or centers of excellence (CoEs) that focus solely on acquisitions and integrations. These teams are tasked with building a standardized approach to deal-making, ensuring consistency in how deals are evaluated, negotiated, and executed. This consistency is crucial for reducing execution risks and ensuring that all acquisitions are aligned with the company’s overarching strategy. For example, a multinational corporation with a strong M&A capability may have a dedicated integration team that focuses on ensuring smooth transitions during the post-merger phase, minimizing disruption to business operations and accelerating the realization of synergies. This capability allows the company to maintain focus on its core operations while efficiently absorbing new acquisitions into its structure.
Additionally, fostering a culture that supports M&A initiatives is critical for ensuring that these internal capabilities are utilized effectively. Academically, this ties into the concept of cultural integration, where successful mergers are often the result of not just technical and financial alignment but also the ability to integrate the cultures of the two organizations. An organizational culture that embraces M&A as a strategic tool for growth creates an environment where cross-functional collaboration, leadership alignment, and the development of M&A-specific skills are prioritized. Companies that encourage collaboration between finance, legal, operations, and human resources teams during the M&A process are better equipped to handle the complexities of integration, ensuring that synergies are captured and that the combined entity functions as a cohesive whole.
Leadership alignment is particularly important in building strong M&A capabilities. Academically, leadership plays a central role in setting the strategic direction for acquisitions and ensuring that all teams are aligned with the broader goals of the transaction. Effective leadership in M&A requires not only technical expertise but also the ability to manage change, communicate the vision for the acquisition, and ensure that all stakeholders are engaged throughout the process. In practice, companies that succeed in M&A often have leadership teams that are well-versed in both the strategic and operational aspects of deal-making, enabling them to guide their organizations through the complexities of mergers and acquisitions with confidence.
Moreover, organizations that invest in developing M&A-specific skills, such as negotiation, valuation, integration planning, and risk management, are better positioned to execute successful acquisitions. These skills are not only critical during the deal-making phase but also play a central role in the post-merger integration process, where the real value of the acquisition is realized. Academically, the post-merger phase is often where the greatest challenges—and opportunities—arise, as companies must integrate diverse cultures, systems, and processes to capture synergies. Companies with strong M&A capabilities are able to navigate these challenges more effectively, ensuring that value creation is sustained beyond the initial transaction.
Building M&A capabilities also enhances an organization’s agility and responsiveness to market opportunities. In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies that can quickly identify and act on acquisition opportunities are better positioned to stay ahead of competitors and capitalize on emerging trends. Academically, this aligns with theories of strategic agility, where organizations that can adapt and pivot their strategies in response to market changes are more likely to achieve long-term success. A robust M&A capability allows companies to move quickly when opportunities arise, ensuring that they can acquire valuable assets, enter new markets, or gain access to critical technologies before competitors do.
In practice, organizations with strong M&A capabilities often develop “playbooks” or standardized processes that guide each stage of the acquisition process, from initial target identification to post-merger integration. These playbooks incorporate best practices, lessons learned, and standardized templates that streamline the M&A process and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned. For example, a technology company with a mature M&A capability may develop a playbook that outlines specific criteria for evaluating potential tech acquisitions, such as intellectual property strength, talent acquisition potential, and market positioning. This playbook allows the company to assess potential targets quickly and consistently, ensuring that each deal aligns with its strategic goals and maximizes value creation.
In conclusion, building robust M&A capabilities within an organization is critical for long-term success in the competitive M&A landscape. These capabilities encompass not only the financial and legal expertise required to execute deals but also the strategic vision, leadership alignment, and cross-functional collaboration needed to ensure that acquisitions deliver value. By developing an in-house M&A team with specialized knowledge, companies can execute deals more efficiently, reduce reliance on external advisors, and maintain better control over the acquisition process. Furthermore, fostering a culture that supports M&A initiatives ensures that organizations remain agile and responsive to market opportunities, capturing synergies, mitigating risks, and driving value creation through well-executed acquisitions. In both academic theory and industry practice, companies with strong M&A capabilities are better positioned to navigate the complexities of deal-making and to achieve sustained growth and competitive advantage through mergers and acquisitions.
16.3. Developing Repeatable M&A Processes
Organizations that consistently succeed in acquiring and integrating new businesses typically follow a disciplined, repeatable approach that enables them to reduce complexity, enhance efficiency, and minimize the risks associated with M&A activities. By standardizing each phase of the acquisition process—target identification, synergy evaluation, due diligence, negotiation, and post-merger integration—companies can achieve greater consistency in their results, shorten their learning curve, and drive more predictable outcomes. This strategic approach is essential for maintaining long-term success in a highly competitive M&A landscape.
From an academic perspective, the development of repeatable M&A processes can be tied to organizational learning and process standardization theories. Organizations that are successful in M&A often build these capabilities through a process of continuous learning, where they refine their methods based on past experiences. This is akin to the concept of double-loop learning, where organizations do not merely adjust their actions in response to feedback but also re-examine and adjust the underlying assumptions and processes driving those actions. In M&A, this means that companies constantly evaluate the effectiveness of their acquisition strategies, integration frameworks, and due diligence methodologies to ensure that each successive deal is handled more efficiently and with fewer risks. Over time, this continuous refinement leads to the creation of a standardized, repeatable process that can be applied across multiple transactions, allowing the company to replicate successful outcomes.
In practice, developing a repeatable M&A process begins with creating standardized frameworks for each stage of the acquisition lifecycle. This includes clear criteria for identifying and evaluating potential acquisition targets, structured approaches to conducting due diligence, standardized templates for financial modeling and synergy analysis, and a robust integration playbook that guides post-merger activities. Standardization of these processes reduces the variability and unpredictability that can often derail M&A transactions. For example, a company that standardizes its due diligence process will be able to evaluate potential risks and opportunities in a consistent, thorough manner across different transactions, minimizing the likelihood of overlooking critical issues such as regulatory compliance or cultural misalignment.
One of the key benefits of repeatable M&A processes is the reduction of complexity. Academically, this can be linked to the theory of complexity management, which suggests that organizations that develop standardized processes for handling complex activities can manage them more effectively. In the context of M&A, repeatable processes break down the acquisition into clear, manageable steps, making it easier for cross-functional teams to collaborate and execute the deal efficiently. For instance, by having a standardized process for evaluating synergies, companies can ensure that they are consistently assessing how potential acquisitions will add value—whether through cost savings, revenue growth, or operational efficiencies. This structured approach helps reduce the cognitive and operational overload that often comes with managing the intricacies of M&A transactions.
In industry practice, companies with successful M&A track records often rely on playbooks that outline repeatable processes for every stage of the acquisition. These playbooks serve as a repository of best practices, lessons learned, and standardized templates that can be used across multiple deals. For example, a company that has developed a repeatable process for post-merger integration will have a clear roadmap for integrating systems, aligning organizational structures, and managing cultural differences, ensuring that synergies are captured quickly and effectively. This reduces the risk of post-merger value erosion, where integration challenges can undermine the financial and operational benefits of the acquisition. In sectors like technology or pharmaceuticals, where acquisitions are frequent and critical for maintaining competitive advantage, having a repeatable process ensures that companies can execute deals at speed while minimizing execution risks.
Another important advantage of developing repeatable M&A processes is the ability to shorten the learning curve. Academically, this aligns with the learning curve theory, which posits that organizations become more efficient at tasks as they repeat them over time. In M&A, where each transaction presents unique challenges, organizations that refine and standardize their processes are able to build a cumulative body of knowledge that allows them to handle future deals with greater speed and confidence. This learning curve effect is especially valuable in industries where acquisition activity is high, and companies must be able to move quickly to seize opportunities. By applying a consistent, repeatable process, companies can reduce the time spent on each transaction, allowing them to capitalize on market opportunities more rapidly than competitors.
Repeatable processes also contribute to greater predictability in outcomes. Academically, this concept ties into risk management theories, where standardized processes are seen as a way to reduce variability and uncertainty in complex operations. In M&A, variability in process execution can lead to inconsistent results, such as failing to capture synergies, overlooking due diligence risks, or struggling with post-merger integration challenges. By developing a repeatable process, companies create a framework that ensures a consistent level of rigor and discipline is applied to every deal, reducing the likelihood of costly mistakes and enhancing the predictability of outcomes. This predictability is critical for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring that M&A activity contributes to long-term value creation.
In industry practice, companies that develop repeatable M&A processes also benefit from improved transparency and accountability. A structured, repeatable process makes it easier for teams across the organization to understand their roles and responsibilities in the acquisition process. This cross-functional alignment ensures that financial, legal, operational, and cultural considerations are all addressed systematically, reducing the potential for gaps or miscommunications that could derail the transaction. For example, a repeatable process for due diligence ensures that all relevant stakeholders—such as finance, legal, and human resources—are involved in assessing the target company’s risks and opportunities, providing a more comprehensive view of the transaction. This transparency also fosters accountability, as each team is aware of its responsibilities and can be held accountable for delivering on its part of the process.
Additionally, repeatable M&A processes improve collaboration and alignment with the company’s strategic goals. Academically, this ties into the concept of strategic alignment, where organizations ensure that all activities—such as acquisitions—are closely linked to their long-term objectives. A repeatable process helps ensure that each acquisition is evaluated through the lens of the company’s broader strategic goals, ensuring that the transaction aligns with the company’s vision for growth, market positioning, and operational capabilities. For example, if a company’s strategic goal is to expand into new geographic markets, a repeatable M&A process will include standardized criteria for assessing market entry potential, regulatory risks, and local competitive dynamics, ensuring that every acquisition supports the company’s long-term objectives.
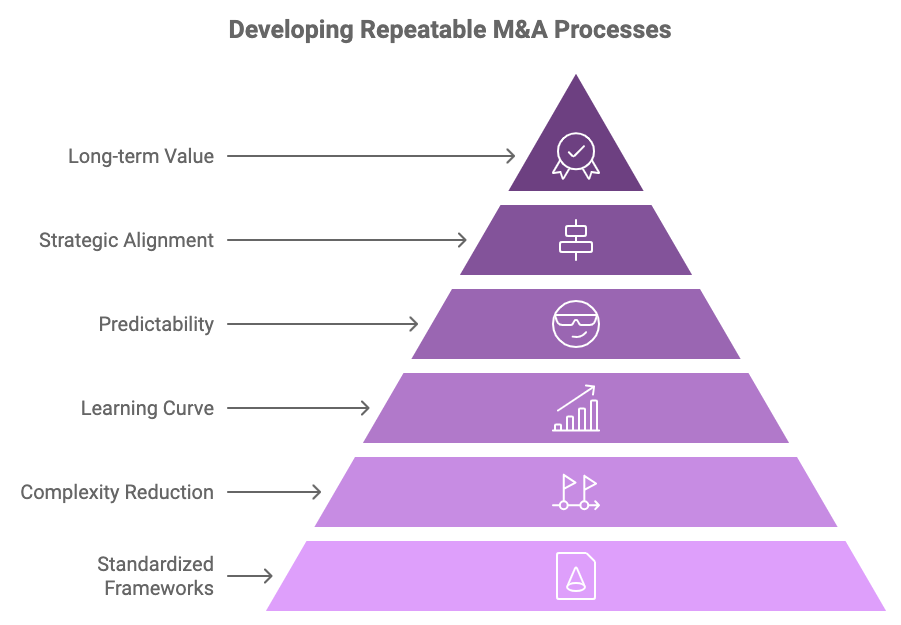
Figure 16.3: Essential Stages in Developing Successful Repeatable M&A Process.
Ultimately, developing repeatable M&A processes not only enhances efficiency and reduces risk but also drives long-term value creation. Companies that standardize their acquisition processes are better positioned to replicate successful outcomes and avoid repeating past mistakes. This cumulative learning process ensures that each transaction builds on the knowledge gained from previous deals, creating a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement. In both academic theory and industry practice, repeatable processes are a hallmark of M&A excellence, providing companies with the tools they need to navigate the complexities of acquisitions with greater confidence and consistency.
In conclusion, developing repeatable M&A processes is critical for organizations seeking to succeed consistently in acquiring and integrating new businesses. These processes reduce complexity, enhance efficiency, and minimize risk, allowing companies to replicate successful outcomes and achieve greater predictability in future deals. By standardizing each phase of the acquisition process and fostering cross-functional collaboration, organizations can align their M&A activities with their strategic goals, ensuring that acquisitions drive long-term value creation. Whether viewed through the lens of academic theories of organizational learning, risk management, or process standardization, or through industry best practices, repeatable M&A processes are a cornerstone of sustained success in the competitive world of mergers and acquisitions.
16.4. Leveraging M&A for Competitive Advantage
Acquisitions allow organizations to enhance their market position, access new capabilities, and accelerate growth by integrating complementary assets, technologies, or customer bases. However, the real competitive advantage comes not just from the act of acquiring but from the ability to fully integrate and exploit the synergies that these deals present. This requires a deliberate focus on leadership, integration planning, and the strategic alignment of the acquired assets with the acquiring company’s long-term goals.
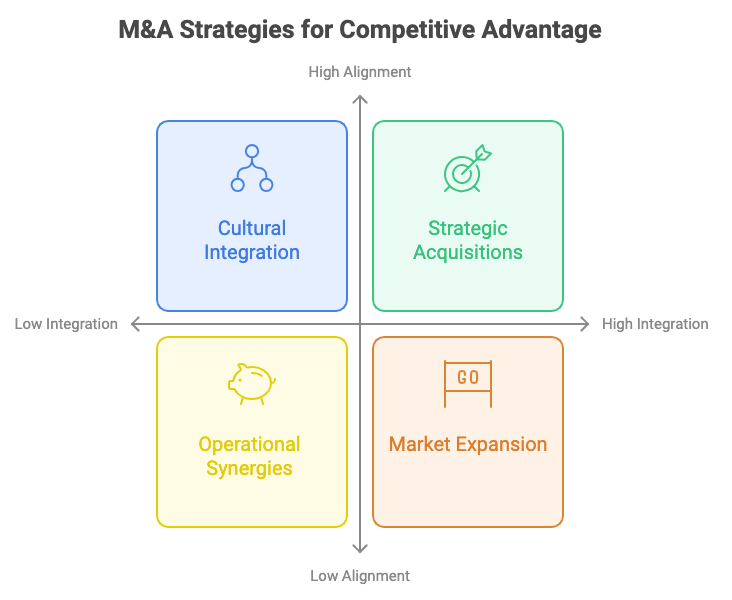
Figure 16.4: M&A Strategies Framework to Achieve Competitive Advantage.
From an academic perspective, the role of M&A in achieving competitive advantage is often viewed through the lens of resource-based theory (RBT), which posits that firms gain a competitive edge by acquiring and leveraging valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable (VRIN) resources. In the context of M&A, these resources could include proprietary technologies, intellectual property, customer relationships, or specialized human capital. The key to gaining a sustainable competitive advantage through M&A is not simply acquiring these assets but effectively integrating them into the organization in a way that amplifies their value. Companies that excel in this regard often follow structured post-merger integration (PMI) processes that ensure the swift realization of synergies, minimize disruption, and create a unified organization that is stronger than the sum of its parts.
In practice, M&A provides companies with several strategic avenues for competitive advantage, including market expansion, innovation acceleration, and operational efficiency. One of the most powerful ways in which M&A can drive competitive advantage is by enabling companies to enter new geographic markets or industry segments quickly. For example, a global consumer goods company might acquire a regional player with strong brand recognition and distribution networks, allowing the acquirer to instantly establish a foothold in a new market without the time and cost required to build that presence organically. This strategic use of acquisitions is supported by academic theories of market entry and competitive strategy, where first-mover advantages or rapid expansion can help firms outpace competitors.
Innovation is another area where M&A can deliver competitive advantage. Academically, innovation is often a key driver of sustained competitive advantage, particularly in industries where technological advancements occur rapidly. By acquiring firms with cutting-edge technologies, patents, or research capabilities, companies can accelerate their own innovation timelines and enhance their product offerings. For example, a large tech company might acquire a smaller startup working on breakthrough AI algorithms, integrating these technologies into its broader product portfolio and gaining a technological lead over competitors. The acquisition not only boosts the company’s innovation capabilities but also positions it as a leader in emerging technology spaces, enabling it to maintain or even strengthen its market position. In industry practice, companies that leverage M&A for innovation often focus on acquiring startups or smaller firms that bring novel capabilities and fresh perspectives to the table, allowing them to stay at the forefront of technological change.
Operational efficiency and economies of scale are also major competitive advantages that can be realized through M&A. Academically, this concept is rooted in the theory of economies of scale, where firms achieve cost advantages by increasing the scale of their operations. When companies merge or acquire competitors, they often gain efficiencies by consolidating production facilities, optimizing supply chains, or leveraging shared infrastructure. For example, a manufacturing company may acquire a competitor and consolidate their production processes, allowing the combined entity to operate at a lower cost structure, thereby improving profitability. These operational synergies not only provide cost savings but also improve the company’s ability to compete on price or reinvest savings into growth initiatives. In practice, companies that execute M&A deals with a focus on operational efficiencies often achieve significant cost savings and improved profit margins, which in turn strengthens their competitive position in the marketplace.
However, the ability to capture these competitive benefits hinges on the company’s ability to integrate the acquired assets seamlessly and effectively. A key challenge in M&A is that the anticipated synergies often fail to materialize due to poor integration planning or execution. Academically, the post-merger integration phase is widely regarded as the most critical determinant of M&A success. Successful integration requires strong leadership, clear communication, and a structured plan for aligning the operations, cultures, and systems of the two companies. Without a well-executed integration plan, even the most strategically sound acquisition can result in value erosion, employee disengagement, or operational disruptions.
In practice, companies that succeed in post-merger integration typically develop detailed integration playbooks that outline the steps for realizing synergies, aligning leadership teams, and maintaining business continuity. These playbooks often include specific strategies for cultural integration, which is frequently one of the most challenging aspects of M&A. For instance, companies might conduct cultural assessments during the due diligence phase to identify potential areas of conflict and develop strategies for fostering alignment between the merging entities. By addressing cultural integration proactively, companies reduce the risk of internal friction and ensure that the combined entity operates cohesively, driving long-term competitive advantage.
Strong leadership is also crucial in leveraging M&A for competitive advantage. Academically, leadership plays a critical role in setting the strategic vision for the acquisition and ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned with the company’s goals. In M&A, leaders must navigate complex challenges, such as managing change, communicating the rationale for the acquisition, and ensuring that both the acquirer and the acquired entity are working toward the same objectives. Effective leaders in M&A are those who can balance the technical and strategic aspects of the deal with the softer, human elements—such as managing talent retention, addressing cultural integration, and ensuring employee engagement throughout the integration process. In practice, companies that excel in M&A often have leadership teams that are highly skilled in both strategic execution and change management, enabling them to drive the integration process smoothly and capture the full value of the acquisition.
Finally, competitive advantage from M&A is often realized through the strategic alignment of acquisitions with the company’s long-term vision and growth strategy. Academically, strategic alignment is a critical success factor in M&A, ensuring that acquisitions are not just opportunistic transactions but part of a broader plan for long-term value creation. When companies approach M&A with a clear understanding of how each acquisition fits into their overall strategic objectives, they are better positioned to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the deal. For example, a healthcare company with a strategic goal of becoming a leader in digital health might acquire several tech-focused firms to build a comprehensive portfolio of digital health solutions. Each acquisition is part of a deliberate plan to dominate the digital health space, allowing the company to outmaneuver competitors and create a lasting competitive edge.
In practice, companies that leverage M&A for strategic advantage often develop acquisition programs that are closely aligned with their growth plans. These programs enable them to systematically target acquisitions that will enhance their core capabilities, expand their market presence, or diversify their product offerings in ways that support their long-term objectives. By maintaining strategic discipline in their M&A activities, these companies avoid the pitfalls of “deal chasing” and ensure that each acquisition contributes meaningfully to their competitive advantage.
In conclusion, mergers and acquisitions are powerful tools for gaining competitive advantage, but only when approached with a strategic mindset and executed with precision. Companies that leverage M&A to acquire complementary capabilities, innovative technologies, or strong market positions can enhance their product offerings, expand into new markets, and achieve operational efficiencies that give them a distinct edge over competitors. However, the true competitive advantage comes from the ability to integrate these acquisitions effectively, realizing synergies that translate into increased profitability, market share, and long-term value creation. With strong leadership, a clear integration plan, and a focus on strategic alignment, M&A becomes a key driver of sustained competitive advantage in today’s complex and fast-moving business environment.
16.5. Conclusion
Chapter 16 highlights the strategic role of mergers and acquisitions in building competitive advantage through structured acquisition programs, strong in-house M&A capabilities, repeatable processes, and effective execution. By developing these elements, companies can consistently identify and execute value-creating deals, ensuring long-term growth and sustainability. The chapter underscores that successful M&A is not just about completing transactions but about creating a competitive edge that drives the organization’s strategic goals.
16.5.1. Further Learning with GenAI
The following prompts encourage deep strategic thinking and analysis around building M&A capabilities, structuring acquisition programs, developing repeatable processes, and leveraging M&A as a competitive advantage. They are designed to generate comprehensive insights into how organizations can optimize their approach to M&A for long-term success.
How can organizations design a comprehensive acquisition program that aligns with their long-term strategic goals, market positioning, and innovation objectives, and how can they ensure this program delivers sustainable competitive advantages over time? Explore the integration of strategic planning, market analysis, and growth forecasting in creating acquisition programs that continually adapt to changing market conditions and business objectives.
What are the critical components of a successful acquisition program, including market intelligence, target identification, financial modeling, and post-merger integration, and how can companies structure these components for repeatable success across multiple acquisitions? Analyze how each component, from pre-deal assessment to integration, contributes to the overall success of an acquisition program and how continuous refinement enhances long-term effectiveness.
How can companies leverage acquisition programs to strategically expand into new markets, geographies, or industries, and what role does comprehensive market analysis and competitive benchmarking play in identifying the right opportunities for growth? Discuss methods for identifying growth markets, evaluating potential synergies, and mitigating risks associated with entering new sectors, while ensuring acquisitions align with long-term strategic goals.
What are the best practices for building and scaling in-house M&A capabilities, including talent development, cross-functional collaboration, and strategic alignment, to ensure successful deal execution and value creation? Explore how companies can develop internal teams with specialized skills in valuation, negotiation, integration, and governance, reducing reliance on external advisors and fostering in-house expertise.
How can leadership foster a culture that supports and prioritizes M&A initiatives, ensuring that cross-functional teams, including finance, legal, operations, and HR, work collaboratively to align acquisition activities with broader corporate strategies? Examine the role of leadership in setting a clear M&A vision, building organizational alignment, and creating a collaborative environment that supports deal execution and post-merger success.
What specific skills and expertise should organizations cultivate within their M&A teams to navigate complex deal structures, conduct thorough due diligence, and manage the risks associated with acquisitions, particularly in high-stakes or cross-border transactions? Analyze the importance of specialized knowledge in legal compliance, cross-border regulatory issues, financial modeling, and cultural integration in building a high-performing M&A team.
What are the key steps involved in developing a repeatable, scalable M&A process, and how can companies standardize critical elements—such as target screening, financial valuation, and integration planning—while maintaining flexibility to adapt to different types of deals? Explore the balance between creating a standardized process for efficiency and maintaining the adaptability to respond to unique deal-specific challenges, such as market conditions or target industry.
How can organizations refine and enhance their M&A processes over time by capturing lessons learned from previous transactions, integrating new technologies, and continuously improving governance and decision-making frameworks? Discuss how continuous improvement mechanisms, driven by post-deal audits, feedback loops, and technology adoption, can ensure that M&A processes evolve and remain effective in a dynamic business environment.
What role does knowledge management play in creating repeatable, successful M&A processes, and how can companies effectively capture, store, and disseminate lessons learned and best practices from past deals to optimize future acquisitions? Examine how knowledge management systems can institutionalize learning, ensuring that key insights are transferred across teams and applied to future deals, creating cumulative expertise and organizational agility.
How can organizations balance the need for standardized M&A processes with the flexibility required to respond to varying deal types, industries, and market dynamics, ensuring both efficiency and adaptability in deal execution? Explore strategies for creating modular M&A frameworks that allow organizations to customize deal processes while retaining core efficiency drivers across acquisitions.
What are the most common challenges organizations face when developing and implementing repeatable M&A processes, such as resistance to standardization, cultural differences, or inconsistent governance, and how can these challenges be overcome? Analyze case studies of companies that have successfully overcome internal and external barriers to creating scalable, efficient M&A processes, and discuss the strategic value of addressing these challenges early.
How can companies leverage M&A as a key strategic tool for building competitive advantage, particularly in fast-moving or disruptive industries, and what role do innovation, technological integration, and operational efficiencies play in maximizing acquisition value? Examine the role of acquiring innovative technologies, intellectual property, or high-growth startups in strengthening a company’s market position and driving long-term competitive advantage.
What are the critical factors that determine whether a company’s M&A strategy will generate a sustainable competitive advantage, and how can leadership ensure that acquisitions are integrated in ways that enhance the firm’s strategic positioning in its industry? Explore how leadership can align M&A with broader corporate goals such as digital transformation, customer experience enhancement, and operational excellence to ensure lasting competitive gains.
How can companies identify and acquire targets that offer complementary capabilities, innovative technologies, or strategic synergies, ensuring that the acquisition strengthens their competitive position in existing or emerging markets? Analyze the process of identifying synergistic acquisitions, conducting a thorough strategic fit analysis, and ensuring that the acquired company aligns with long-term growth objectives.
What strategies can companies employ to ensure the seamless integration of acquired assets, technologies, and teams, while preserving the strengths of the acquired entity and maximizing synergies across all functional areas? Discuss best practices for integration planning and execution, including early stakeholder involvement, clear communication strategies, and maintaining operational continuity during post-merger transitions.
How can organizations develop a long-term M&A roadmap that anticipates future market trends, emerging technologies, and competitive threats, ensuring that the acquisition strategy remains aligned with both near-term and future growth objectives? Explore how companies can use scenario planning, market trend analysis, and innovation forecasting to create an M&A strategy that positions them for continued success amid industry shifts.
What role does leadership alignment, transparency, and communication play in ensuring the successful execution of M&A deals, particularly in building trust and collaboration between the merging entities and driving alignment on strategic goals? Discuss the importance of leadership in driving the cultural integration of newly acquired entities and how clear communication can mitigate risks, such as employee disengagement or misalignment on integration objectives.
How can companies use advanced data analytics, AI, and other cutting-edge technologies to enhance their M&A capabilities, particularly in areas like target identification, due diligence, valuation, and post-merger integration tracking? Examine the role of technology in optimizing each phase of the M&A lifecycle, from predictive analytics for target screening to AI-driven financial modeling and integration performance monitoring.
How can companies effectively measure the long-term success of their M&A activities, using financial, operational, market, and cultural metrics to ensure that acquisition programs consistently generate value and contribute to competitive advantage? Analyze how a balanced scorecard approach, integrating both quantitative and qualitative metrics, can provide a comprehensive view of M&A success, ensuring alignment with long-term business objectives.
What lessons can companies learn from failed or underperforming acquisitions, and how can these insights be used to refine acquisition programs, improve decision-making frameworks, and develop more resilient M&A processes? Explore how post-deal analysis, root cause assessments, and ongoing process refinement can turn the challenges of failed deals into learning opportunities, strengthening future M&A outcomes.
The prompts encourage deep exploration of how companies can strategically develop and refine acquisition programs, build internal M&A capabilities, leverage repeatable processes, and use M&A as a tool for long-term competitive advantage. Each prompt is designed to foster comprehensive thinking about optimizing M&A activities in the context of evolving business environments.
Comments