Chapter 9
Key Elements of Post-Merger Integration Strategy
"Successful post-merger integration is about harmonizing the best of both worlds. By creating alignment across leadership, operations, and strategy, you can unlock synergies that fuel innovation and growth." — John Chambers, former CEO of Cisco Systems
Chapter 9 delves into the essential strategies for successfully integrating merged companies to create sustained growth. It covers the development of a comprehensive integration plan, setting priorities, aligning business processes and leadership, and managing cultural, operational, and technological synergies. The chapter also emphasizes the importance of sustaining corporate responsibility and monitoring progress to ensure long-term success, making it a blueprint for post-merger excellence.
9.1. Key Elements of Post-Merger Integration Strategy
The cornerstone of any successful post-merger integration is the establishment of a strategic vision. This vision acts as the guiding principle that sets the course for all integration efforts, ensuring that both companies involved in the merger are aligned on shared goals and ambitions. The strategic vision helps define what success looks like for the merged entity—whether it’s market expansion, financial growth, or innovation. Without a clear vision, integration efforts can become fragmented, with teams pursuing divergent objectives, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
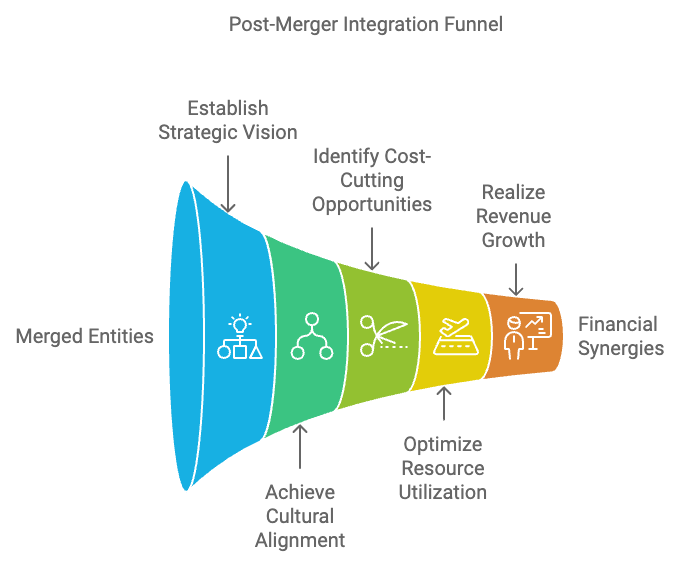
Figure 9.1: Post-merger activity funnel.
Crafting this vision requires a deep understanding of the strengths, synergies, and complementary capabilities of both organizations. For example, one company may bring technological innovation, while the other has a strong foothold in emerging markets. Identifying these synergies early on allows leadership to set a course for the combined entity that capitalizes on these unique advantages.
This vision not only serves as the North Star for decision-making but also communicates to employees, customers, and stakeholders the larger purpose behind the merger. By keeping the entire organization focused on achieving this shared vision, companies can navigate the complexities of integration with greater clarity and purpose. A well-defined strategic vision helps ensure that every aspect of the merger—from operational alignment to cultural integration—contributes toward realizing the full potential of the combined enterprise.
Mergers are not just about combining assets and processes; they involve the fusion of two often distinct organizational cultures. Achieving cultural alignment is one of the most challenging aspects of post-merger integration, yet it is critical for long-term success. Each company brings its own values, work styles, leadership philosophies, and interpersonal dynamics. When these cultural elements clash, it can result in employee disengagement, friction, and even the loss of top talent.
The importance of transparent communication cannot be overstated when managing cultural integration. Employees at all levels need to understand the rationale behind the merger, how it affects them, and how the new company’s culture will evolve. Without clear communication, employees may feel disconnected from the process, which can lead to decreased morale and productivity.
Leadership alignment is another key component. When senior leaders from both organizations are united in promoting a shared culture, it creates consistency in messaging and fosters a sense of unity. Leadership teams should actively model the behaviors and values they want the rest of the organization to adopt, signaling that the merged company’s culture is not just a top-down directive but a collaborative evolution.
Cultural integration also involves fostering a collaborative environment that embraces the best aspects of both organizations. This requires deliberate efforts to identify cultural strengths within each company and blend them in a way that supports the new organization’s goals. For instance, if one company is known for its innovation and agility, and the other for its operational discipline, the new culture should combine these strengths to create a more resilient and dynamic organization. Ultimately, successful cultural integration ensures that employees feel engaged, valued, and aligned with the company’s mission, leading to greater productivity and long-term retention.
One of the primary drivers of mergers and acquisitions is the promise of financial synergies—the ability to create value that exceeds the sum of the two companies as standalone entities. Realizing these synergies involves a combination of cost reduction, resource optimization, and revenue growth by leveraging the combined capabilities and assets of the newly formed company.
At the heart of financial synergy realization is the identification of cost-cutting opportunities. This often involves eliminating redundancies in areas such as IT systems, back-office functions, supply chains, and vendor contracts. Streamlining operations not only reduces operational costs but also improves efficiency, enabling the merged entity to operate more smoothly. However, care must be taken not to compromise on quality or disrupt essential functions during this cost-reduction process.
Beyond cutting costs, financial synergies are also about improving resource utilization. Merged companies often have overlapping resources that, if managed correctly, can be leveraged to increase efficiency and productivity. This may involve consolidating manufacturing facilities, optimizing workforce deployment, or pooling research and development efforts to create new products faster and more efficiently. Financial synergies also involve making better use of capital—whether through improving cash flow, reducing borrowing costs, or optimizing investment in growth areas.
Realizing revenue growth is another key aspect of financial synergy. This can be achieved by cross-selling products to the combined customer base, entering new markets, or offering bundled services that neither company could provide alone. The goal is to create value by exploiting the strengths of both companies and maximizing revenue-generating opportunities that did not exist pre-merger.
The challenge in realizing financial synergies lies in balancing short-term financial goals with long-term strategic objectives. While cost-cutting and operational efficiency can provide immediate gains, it’s important to ensure that these actions do not hinder the company’s long-term growth potential. Likewise, while revenue growth is a key objective, it requires thoughtful planning and execution to ensure that the combined company is positioned for sustainable success.
In summary, financial synergies are not just about cutting costs but about finding ways to create value through better use of resources and enhanced revenue-generating opportunities. The ability to realize these synergies is often what determines the financial success of a merger.
9.2. Developing a Comprehensive Integration Plan
The success of a post-merger integration largely depends on the early and thorough identification of all relevant stakeholders. This process involves recognizing and engaging both internal and external stakeholders who will be directly or indirectly affected by the merger. Internally, stakeholders include employees, leadership teams, and middle management, all of whom must be kept informed and aligned with the merger’s objectives. Each of these groups plays a critical role in ensuring that operations run smoothly, and their buy-in is essential for a successful integration.
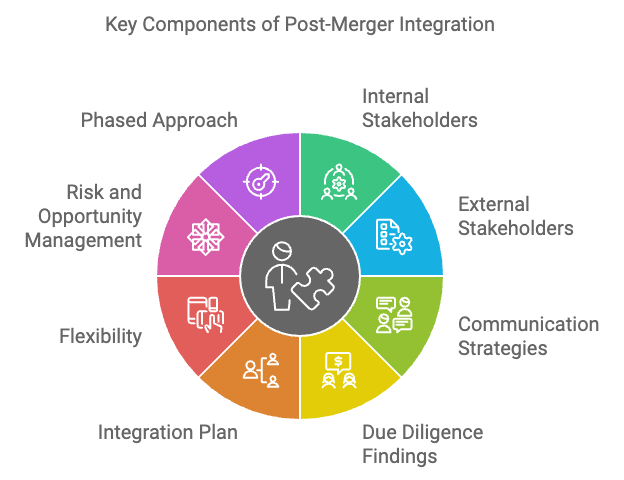
Figure 9.2: Key components of post-merger integration.
Externally, stakeholders encompass customers, business partners, investors, and regulators. For instance, customers need to feel reassured that the merger will not disrupt service or product delivery. Business partners must be aware of any changes in processes or expectations, while investors and regulators must be kept up-to-date on financial performance and compliance matters.
Fostering collaboration and communication with these stakeholders minimizes operational disruptions and helps ensure that the integration proceeds smoothly. Regular updates, stakeholder meetings, and clear communication channels are essential to keeping everyone aligned with the merger’s progress. By identifying stakeholder concerns early on, companies can proactively address potential challenges, reducing friction and building trust throughout the process.
Once stakeholders are identified, the next critical step is translating due diligence findings into actionable steps. During the pre-merger phase, due diligence uncovers essential details about both organizations, such as their financial health, operational structures, cultural dynamics, and potential risks. This data forms the foundation of the integration strategy and must be carefully analyzed to design a robust execution plan.
The integration plan should focus on mission-critical areas first, such as IT systems, financial reporting, and human resources. These areas are often the backbone of operations, and ensuring their continuity is essential for maintaining business stability. For example, merging two companies’ IT infrastructures can be complex, requiring detailed planning to prevent disruptions and ensure data security. Similarly, aligning financial systems ensures that both companies can produce unified financial reports and comply with regulatory requirements.
An effective transition from planning to execution requires maintaining flexibility. While initial due diligence provides a roadmap, the dynamic nature of integration may require ongoing adjustments as new information emerges. Companies must remain agile, ready to adapt their strategies to overcome unexpected obstacles or capitalize on emerging opportunities.
By focusing on key areas of risk, synergy, and opportunity, companies can develop integration strategies that not only ensure continuity but also drive growth. For example, uncovering complementary capabilities during due diligence can lead to operational improvements, while identifying potential risks enables the company to mitigate them early.
To manage the complexity of post-merger integration, companies should adopt a phased approach that establishes short-term, mid-term, and long-term goals. This approach provides structure and creates manageable checkpoints that allow for progress tracking and real-time adjustments.
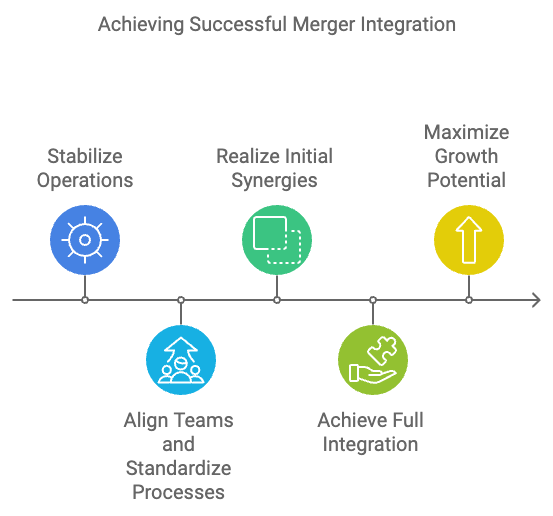
Figure 9.3: Process to achieve successful merger.
Short-term goals focus on immediate operational needs. For example, integrating IT systems, establishing clear financial reporting lines, and addressing immediate employee concerns should be prioritized. During this phase, it’s also important to stabilize business operations to prevent any negative impact on customers or partners.
Mid-term goals involve aligning teams, standardizing processes, and beginning to realize initial synergies. For instance, streamlining redundant departments, harmonizing workflows, and ensuring that KPIs are aligned across the merged entity can create efficiencies that improve productivity and reduce costs.
Long-term goals aim for full integration, including cultural alignment, brand unification, and strategic growth. This is where the real benefits of the merger are realized, as the two organizations fully merge their operational, cultural, and strategic objectives into one cohesive whole. At this stage, the focus shifts to maximizing growth potential, expanding market reach, and creating value through innovation.
By establishing these phases, the company can manage expectations both internally and externally, ensuring that progress is tracked at each step and that any necessary course corrections are made in real-time.
Mergers are inherently risky, with potential pitfalls in operational, financial, and cultural areas. To safeguard against these risks, companies must embed risk mitigation strategies into the integration plan from the outset.
Operational risks may arise from the complexity of merging IT systems, supply chains, or customer-facing operations. To mitigate these risks, companies should implement contingency plans, ensuring that backup systems are in place in case of any major disruptions. For example, when merging IT systems, careful data migration planning and testing should be performed to avoid downtime.
Financial risks include unexpected costs, misaligned budgets, or cash flow challenges. These can be mitigated by conducting thorough financial audits and maintaining strict control over budgets during the integration phase. Regular financial monitoring and forecasting also allow companies to stay ahead of potential financial risks.
Cultural risks arise from misalignments between the two companies’ values, leadership styles, or employee expectations. To mitigate these risks, companies should prioritize change management and communication strategies that promote transparency and address employee concerns early on. Leadership must be actively involved in driving the cultural integration, ensuring that both organizations’ cultures are respected while fostering a shared sense of purpose.
A key component of risk mitigation is securing leadership buy-in. Without the support of senior leaders from both organizations, the integration effort can falter. Leadership teams must be aligned on the integration strategy and ready to make swift decisions when challenges arise. Furthermore, maintaining operational flexibility allows the organization to adapt to unforeseen issues while keeping the integration on track.
Embedding risk management into the integration process ensures that companies can respond to unexpected challenges swiftly and effectively, keeping the integration on course and avoiding costly delays or inefficiencies. These strategies not only protect the business from immediate risks but also contribute to the long-term success of the merger by building resilience into the new organization.
9.3. Setting Integration Priorities and Timelines
One of the key steps in ensuring a smooth post-merger integration is prioritizing mission-critical functions at the very beginning of the process. These functions include finance, IT, HR, and supply chain management, which serve as the backbone of operational continuity. By addressing these areas early, companies can prevent significant disruptions that could otherwise destabilize the merged organization and create chaos for both internal and external stakeholders.
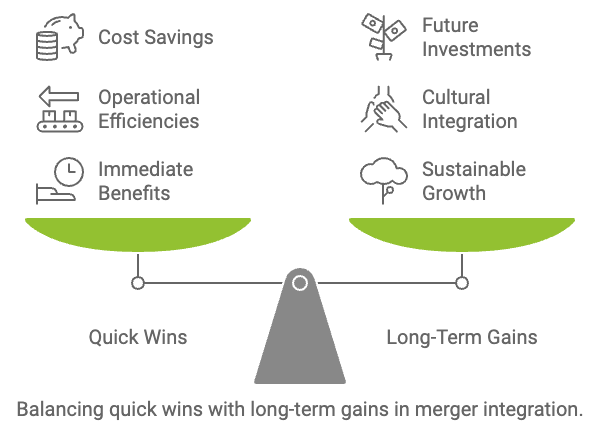
Figure 9.4: Balancing quick and long-term goals.
Finance must be aligned quickly to ensure that financial reporting and budget control are consistent across both organizations. A failure to integrate financial systems early on can result in inaccurate financial data, delays in reporting, and regulatory compliance issues, which could undermine investor confidence and the company’s ability to make informed decisions.
IT systems are another critical area that requires immediate attention. The merging of IT infrastructures is complex but essential for ensuring smooth data flow, operational efficiency, and cybersecurity. Ensuring that IT systems are consolidated and operational prevents interruptions in communications, customer service, and data processing, which are essential for business continuity.
HR integration is vital for managing employee transitions, aligning compensation and benefits structures, and maintaining morale. If HR functions are not prioritized, the merger can lead to confusion, dissatisfaction, and the potential loss of key talent. Quick stabilization of HR systems, such as payroll, benefits, and performance tracking, ensures that employees remain engaged and focused during the integration.
Supply chain management is the operational lifeline of many businesses. Early integration of supply chains minimizes the risk of disruptions that can lead to delays in product delivery, inventory issues, or customer dissatisfaction. Aligning supply chain processes helps maintain consistent operations and strengthens relationships with suppliers and customers alike.
By focusing on these mission-critical functions first, companies can ensure that the foundational aspects of the business are stable, reducing the risk of operational breakdowns and allowing for a smoother transition into the next phases of the integration.
A central challenge in any merger is balancing the need for speed with the importance of precision. Speed is crucial in minimizing the uncertainty that often accompanies a merger, as prolonged integration efforts can lead to employee disengagement, market uncertainty, and missed opportunities. Quick action reduces the time during which the organization operates in a state of limbo, allowing it to regain focus on strategic goals.
However, moving too quickly without sufficient attention to detail can result in long-term complications. Rushed decisions, especially in areas like system integration, financial reporting, or cultural alignment, can cause errors that may take years to rectify. For instance, poorly integrated IT systems may lead to costly downtimes or security breaches, while a lack of precision in aligning HR policies can foster resentment and disengagement among employees.
Leaders must strike a delicate balance between these two forces. Rapid integration is important to maintain momentum and reduce uncertainty, but each decision must be made with an understanding of its long-term impact on the organization. This balance can be achieved through careful planning, clear communication, and the use of phased integration strategies, which allow the company to move forward at a steady pace while ensuring quality and thoroughness in key areas. This dual focus allows the organization to maintain progress without sacrificing the stability and cohesion necessary for long-term success.
While long-term strategic objectives are the ultimate goal of any merger, identifying and achieving quick wins can play a crucial role in building momentum and confidence in the integration process. Quick wins are often found in areas such as cost savings, operational efficiencies, and process improvements, which can be realized within the first few months of the merger. These early successes not only demonstrate the value of the merger to employees, customers, and investors but also provide tangible evidence that the integration is on track.
For example, immediate cost savings can be achieved by eliminating redundancies in back-office functions such as IT, HR, or finance. Streamlining overlapping processes in these areas creates immediate financial benefits and helps build confidence among stakeholders. Similarly, early operational improvements, such as simplifying workflows or centralizing procurement, can boost efficiency and provide a sense of progress in the integration.
However, while quick wins are important, it is essential that they do not come at the expense of long-term gains. The danger of focusing too heavily on short-term victories is that it may lead to decisions that compromise the merger’s ultimate objectives, such as sustainable growth, cultural integration, or market expansion. The integration plan must lay the foundation for long-term success, including achieving full operational and cultural alignment, realizing financial synergies, and executing strategic growth initiatives.
Achieving this balance between quick wins and long-term gains requires strategic foresight. Leaders must ensure that the pursuit of immediate benefits is aligned with the broader goals of the merger and does not detract from the sustained value that the combined entity is expected to deliver. For example, while cost-cutting might provide early financial relief, it should not undermine the company’s ability to invest in future innovations or expand into new markets.
In summary, quick wins build immediate momentum, while long-term gains secure the future success of the merger. Both are essential to the integration process, but they must be carefully coordinated to ensure that the organization remains on a path to sustainable growth.
9.4. Alignment of Business Processes and Goals
One of the most critical elements in post-merger integration is the standardization of business processes across the merging organizations. Without a concerted effort to standardize, businesses often face operational inefficiencies, duplicated efforts, and conflicting workflows that can undermine the potential synergies of the merger. By creating unified processes, companies can eliminate redundancy, streamline operations, and achieve significant cost savings.
The standardization process often begins with a thorough review of the existing workflows, technologies, and methodologies employed by both organizations. This evaluation helps identify which processes are most efficient and scalable. The goal is to adopt the best practices from each company and then create a uniform set of procedures that can be implemented across the entire organization.
Technology standardization is a particularly important aspect. Merged companies often have different IT systems, software platforms, and operational tools. Harmonizing these technologies ensures that data flows seamlessly across departments, reduces overhead from maintaining multiple systems, and improves overall operational efficiency. For example, consolidating customer relationship management (CRM) systems or enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms can lead to more consistent reporting and improve decision-making processes.
Additionally, process standardization fosters scalability. By creating uniform workflows and systems, the organization is better equipped to handle growth, enter new markets, or scale operations without encountering bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Standardized processes provide a solid foundation for future innovation and expansion.
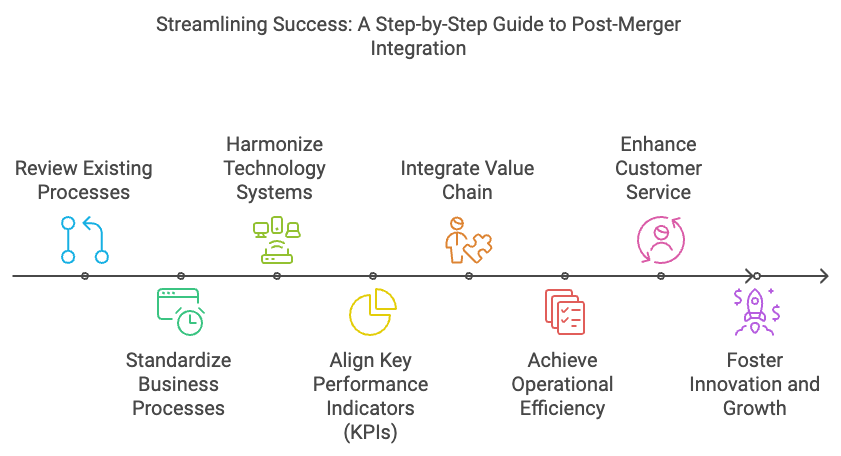
Figure 9.5: Streamlined process of post-merger activities.
However, the challenge in process standardization is balancing the need for uniformity with the necessity to remain adaptable. While it’s important to create consistency, it’s equally critical that the merged organization retains the flexibility to adjust processes as market conditions change or new technologies emerge.
Another crucial aspect of aligning business processes post-merger is the harmonization of key performance indicators (KPIs). KPIs are vital tools that help the organization measure success, monitor performance, and ensure that both entities are working toward the same strategic goals. Without alignment, different parts of the merged organization may prioritize conflicting objectives, leading to inefficiencies and misaligned efforts.
In the context of a merger, KPIs must be redefined to reflect the new, combined organization's goals. This means establishing a unified set of KPIs across critical business areas such as finance, operations, sales, and human resources. For instance, finance KPIs may include profitability, cash flow, and return on investment (ROI), while operational KPIs could focus on productivity, efficiency, and cost savings. By unifying these metrics, leadership can gain a clear, holistic view of the company's progress.
Aligning KPIs also helps in identifying issues early. If one part of the organization is underperforming, harmonized KPIs allow for early detection and provide a framework for taking corrective actions. For example, if operational efficiency is lagging behind in one division, leadership can pinpoint the exact cause through aligned KPIs and adjust strategies accordingly.
Moreover, harmonized KPIs facilitate cross-functional collaboration. When all departments and teams are working towards the same set of measurable goals, it becomes easier to coordinate efforts, reduce silos, and foster a unified approach to achieving the company’s broader objectives. This alignment ensures that the entire organization is pulling in the same direction, leading to more efficient operations and a higher likelihood of achieving long-term success.
The success of a merger is deeply tied to the seamless integration of the value chain, which encompasses supply chains, customer relationships, and operational workflows. The value chain is the interconnected series of activities that contribute to delivering a product or service to the end customer, and integrating these processes is essential for maintaining the merged entity's competitive advantage.
Supply chain integration is one of the most complex yet impactful aspects of the value chain. Merged companies often have overlapping suppliers, distribution channels, or procurement processes. A comprehensive integration of the supply chain can reduce overhead costs, improve inventory management, and ensure that materials and products move efficiently through the organization. Consolidating supplier relationships, for example, can lead to better pricing, improved negotiation power, and more reliable delivery schedules.
Another key aspect is integrating customer relationships. Post-merger, the combined organization must ensure that its approach to customer service is unified and consistent. Whether the merger involves complementary or overlapping customer bases, aligning sales strategies and customer service processes is crucial to maintaining strong customer loyalty and satisfaction. For instance, integrating CRM systems can provide a 360-degree view of customer interactions, enabling personalized service and improving response times.
Additionally, value chain integration helps in optimizing operational workflows. By streamlining production processes, reducing redundancies, and aligning internal teams, the organization can achieve greater productivity and better allocation of resources. An integrated value chain also facilitates more effective communication between departments, from procurement to production to sales, ensuring that all functions are aligned in delivering value to customers.
Ultimately, successful value chain integration enhances responsiveness. The merged company becomes more agile, better equipped to respond to market changes, customer demands, and competitive pressures. This agility provides a competitive edge, allowing the organization to capitalize on opportunities and address challenges swiftly and effectively.
Conclusion: Aligning business processes and goals in a post-merger environment is essential for creating operational efficiency and achieving long-term success. By focusing on process standardization, harmonization of KPIs, and value chain integration, companies can streamline operations, improve decision-making, and create a cohesive organization that is well-positioned for growth and innovation. These efforts not only reduce costs but also enhance customer service, improve productivity, and lay the groundwork for future expansion.
9.5. Employee and Leadership Alignment
At the heart of a successful post-merger integration lies leadership integration, which is crucial for ensuring that the newly merged organization can execute its shared vision and strategy effectively. Merging two organizations means bringing together leadership teams that may have different management styles, decision-making processes, and strategic priorities. To achieve success, it is essential to create a unified leadership team that aligns both organizations around the common goals of the merger.
The unified leadership team must demonstrate transparency and decisiveness from the very beginning of the integration. Clear and decisive actions from leadership help build trust among employees and stakeholders, who are often navigating uncertainty during a merger. Trust is critical in maintaining stability during times of change, as it encourages employees to follow the new direction of the company and fosters confidence in the future success of the combined organization.
Moreover, leadership integration ensures that the merger's vision cascades throughout the organization. If leadership teams are not aligned, there is a risk of sending mixed messages to employees, creating confusion and disengagement. A cohesive leadership group can champion a clear, unified message that reinforces the company’s strategic objectives and helps employees understand their role in achieving the new organization's success.
A successful leadership integration plan involves selecting leaders from both entities who embody the best qualities of each organization. It also requires defining new roles and responsibilities to reflect the combined company's needs, ensuring that leaders have the authority and mandate to drive the integration process forward.
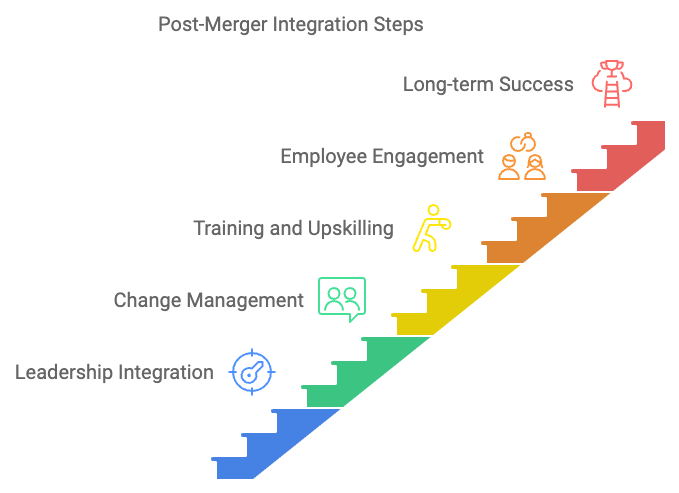
Figure 9.6: Integration process of post-merger activities.
One of the most challenging aspects of any merger is change management, as employees across both organizations often face uncertainty about their roles, future responsibilities, and how the merger will impact their daily work. Employees may fear layoffs, leadership changes, or shifts in company culture, all of which can cause anxiety, reduce morale, and lower productivity.
To mitigate these concerns, a robust communication plan is essential. Effective communication during a merger involves providing clear, consistent, and transparent updates to employees throughout the integration process. This ensures that employees are not left in the dark, reducing speculation and rumor, which can quickly spiral and create distrust.
Transparent communication should address key employee concerns, such as changes in reporting structures, potential adjustments to benefits or compensation, and shifts in organizational priorities. Keeping employees informed not only builds trust but also maintains morale by ensuring they understand how they fit into the newly merged organization.
Beyond communication, change management must involve carefully planned employee transition strategies. This includes helping employees adjust to new workflows, leadership structures, and organizational priorities. For example, employees may need to adapt to different work cultures or reporting hierarchies, and this can cause stress if not managed properly. A strong change management process provides support, resources, and guidance to help employees navigate these transitions with minimal disruption to their productivity and engagement.
Effective change management also ensures that key talent is retained during the integration process. The uncertainty of a merger can sometimes lead to the loss of high-performing employees if they feel their role in the new organization is unclear or undervalued. Proactively managing these transitions helps retain critical talent by offering reassurance, career development opportunities, and demonstrating the value they bring to the new entity.
Post-merger integration often involves significant changes to operational structures, systems, and processes. Employees from both organizations may need new skills or knowledge to operate effectively within the merged entity. Therefore, training and upskilling are vital components of the integration process.
A comprehensive training plan ensures that employees are equipped to navigate new systems—whether that involves using new software, adapting to different workflows, or learning about the new organizational culture. Providing these learning opportunities early in the integration process reduces friction and helps employees adapt more smoothly, which is essential for maintaining productivity and ensuring a seamless transition.
Training programs should be tailored to meet the needs of different departments and roles. For example, IT staff may require specialized training to integrate different technologies or maintain cybersecurity standards, while sales teams may need guidance on how to cross-sell products or services from both organizations. Tailoring these programs ensures that the right skills are developed where they are most needed, empowering employees to succeed in their new environment.
Beyond immediate needs, upskilling also serves as a long-term investment in the merged company’s workforce. Offering employees opportunities for professional development fosters loyalty, enhances employee engagement, and contributes to building a more capable, resilient workforce. Upskilling helps ensure that the organization is better positioned to meet future challenges, adopt new technologies, and seize emerging opportunities.
Moreover, training programs send a powerful message to employees that the company is committed to their growth and success, which can help to alleviate concerns about job security and career progression in the post-merger environment.
Conclusion: Aligning employees and leadership is a critical element of post-merger integration. By focusing on leadership integration, change management, and training and upskilling, companies can ensure that both organizations are unified, employees are engaged, and the new entity is equipped to operate effectively and efficiently. Transparent leadership, well-executed change management, and a commitment to employee development build a strong foundation for long-term success in the post-merger organization.
9.6. IT and Data Integration
One of the most critical aspects of post-merger integration is the consolidation of IT systems, which forms the backbone of operational success for the merged entity. Integrating the IT infrastructure of two organizations is essential for ensuring that all data, processes, and communication channels are aligned and fully functional. Without a well-planned IT consolidation strategy, organizations risk inefficiencies, data silos, and operational disruptions that could jeopardize the overall success of the merger.
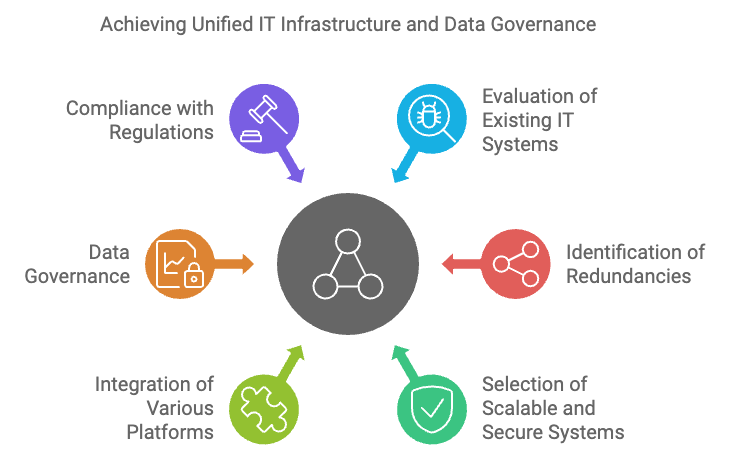
Figure 9.7: Unified IT infra and data governance.
The goal of systems consolidation is to create a unified IT infrastructure that supports seamless data flow, compatibility across platforms, and efficient management of shared resources. This involves evaluating the existing IT systems of both organizations, identifying redundancies, and deciding which systems to retain, integrate, or phase out. The focus should be on adopting the most scalable, secure, and efficient systems while minimizing overlap.
For instance, when merging two different enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems or customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, companies must ensure that the chosen solution integrates well with all other functions, such as finance, HR, and supply chain management. This integration allows for real-time data sharing, which is critical for decision-making and maintaining operational efficiency across departments.
Reducing redundancies is a key benefit of IT systems consolidation. Merged companies often have overlapping technologies and platforms, such as email servers, data storage systems, and cybersecurity protocols. Eliminating redundant systems reduces costs and streamlines operations, ensuring that the merged entity can work more efficiently and avoid unnecessary duplication of efforts.
Another essential consideration in systems consolidation is security. IT systems integration must prioritize secure data handling to protect sensitive information during the transition process. This is especially important when consolidating customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. Any lapse in data security could lead to breaches, loss of trust, and significant legal or financial consequences. Therefore, companies must conduct thorough risk assessments and implement robust security measures to safeguard the integration process.
Finally, systems consolidation provides the merged entity with a cohesive technological foundation that allows for greater agility and scalability in the future. By standardizing IT systems and ensuring compatibility, the company is better positioned to implement new technologies, streamline operations, and pursue growth opportunities with a unified and efficient IT infrastructure.
Alongside systems consolidation, data governance is a crucial element of IT and data integration. Mergers involve the combining of vast amounts of data from two distinct organizations, and without proper governance, this data can become a liability rather than an asset. Effective data governance ensures that the merged company maintains data privacy, security, and regulatory compliance throughout the integration process.
Data privacy is particularly important when handling personal information, whether it’s customer data, employee records, or sensitive business information. Companies must ensure that data is handled in accordance with global privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to significant legal penalties and reputational damage.
To establish strong data governance, the merged entity must first conduct a comprehensive audit of its data assets. This audit identifies what data is being stored, where it resides, and how it is being used. The goal is to gain full visibility into the data landscape and understand any potential risks, such as data duplication, outdated information, or unsecured access points. Once the data audit is complete, the company can develop a data governance framework that sets the policies and procedures for managing and protecting data moving forward.
This framework should outline data security protocols, including encryption, access controls, and data retention policies. Ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data reduces the risk of internal breaches, while encryption protects data in transit or at rest. Additionally, companies should establish clear protocols for data retention and deletion to avoid unnecessary storage of outdated or irrelevant data, which can increase security risks and incur additional costs.
In highly regulated industries such as finance or healthcare, strong data governance is even more critical. These industries are subject to strict compliance requirements, including HIPAA for healthcare or the Sarbanes-Oxley Act for financial institutions. Missteps in data governance can lead to legal and financial repercussions, such as fines, audits, or lawsuits. Therefore, companies in these sectors must ensure that their data governance practices are fully aligned with industry regulations.
Finally, data governance plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity of data used for decision-making. Merged entities rely heavily on data to inform their strategic direction, allocate resources, and assess performance. Without proper data governance, there is a risk of poor data quality, which can lead to inaccurate reporting and misguided decision-making. Implementing rigorous data quality controls ensures that the data used by the organization is accurate, complete, and reliable.
Conclusion: IT and data integration are fundamental components of a successful merger. Through systems consolidation, companies can create a unified, secure, and efficient IT infrastructure that supports seamless operations and reduces redundancies. Data governance ensures that the merged organization maintains the highest standards of data privacy, security, and regulatory compliance, particularly in industries where regulatory oversight is strict. Together, systems consolidation and data governance provide the technological and data integrity necessary for the merged company to operate efficiently, scale effectively, and thrive in the long term.
9.7. Customer and Market Focus Post-Merger
Mergers often generate uncertainty among customers, who may question how the new company will impact the products or services they rely on. If not managed carefully, this uncertainty can lead to customer attrition and damage to the company’s brand. As such, retaining customer confidence is one of the most critical aspects of post-merger integration. Companies must take a proactive approach in communicating with their customers, ensuring they are informed about the benefits of the merger and reassured that there will be no disruption to the quality of service they receive.
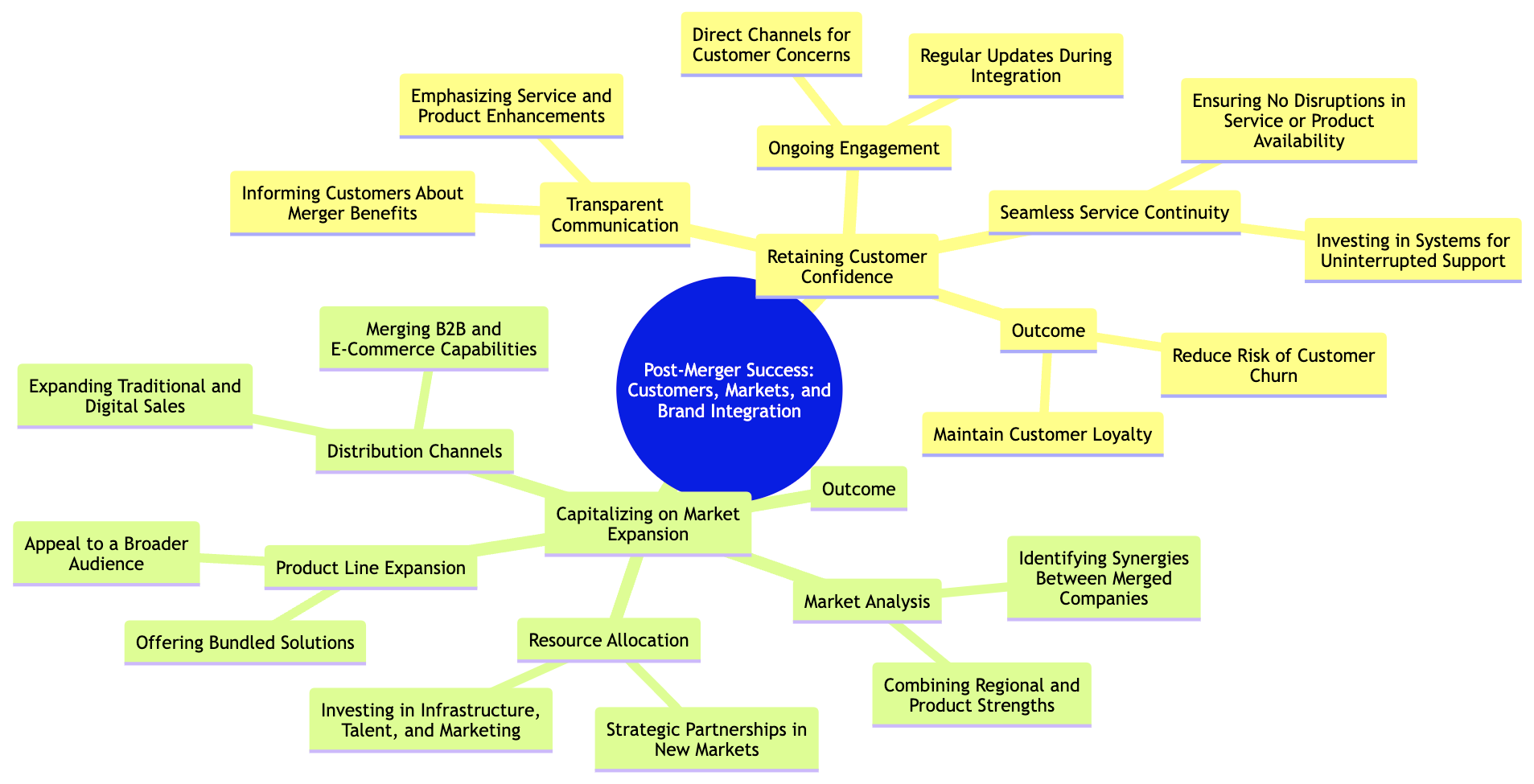
Figure 9.8: Customer and market focus post-merger.
To maintain confidence, companies need to engage in transparent communication. Customers should understand how the merger enhances the company’s ability to serve them better, whether through expanded product offerings, improved service capabilities, or stronger support infrastructure. Messaging should focus on the value the merger brings to the customer, such as access to more innovative solutions or broader service networks.
This communication should be consistent and ongoing, not just a one-time announcement. It is essential to provide regular updates during the integration process, so customers feel informed and valued. Additionally, companies should offer direct channels for customers to address any concerns or ask questions, whether through customer service teams, account managers, or digital platforms.
Ensuring seamless service continuity is equally important. Any disruptions in product availability, support, or customer service during the integration process can undermine the company’s efforts to build trust. Investing in systems and processes that guarantee uninterrupted service is key to reducing the risk of customer churn.
By focusing on proactive communication and delivering uninterrupted service, companies can successfully retain customer loyalty and minimize disruptions during the post-merger transition.
One of the most significant strategic advantages of a merger is the potential for market expansion. By combining the assets, customer bases, and distribution networks of two organizations, the merged company can extend its reach into new markets, deepen penetration in existing ones, and introduce complementary products or services. Identifying these opportunities early in the integration process allows the company to execute on them swiftly and gain a competitive edge.
The first step in leveraging market expansion opportunities is to perform a comprehensive market analysis that identifies synergies between the merging companies. For example, one company may have a strong presence in a particular region or customer segment, while the other may excel in offering products that have complementary demand in that same market. By combining these strengths, the merged entity can unlock new revenue streams.
Additionally, merging companies often have complementary distribution channels that can be used to deliver a broader range of products and services to customers. For instance, if one company specializes in B2B sales and the other has a strong e-commerce platform, combining these channels can provide access to both traditional and digital sales avenues, thereby expanding the company’s market presence.
Product line expansion is another key benefit. If the merged companies offer complementary or adjacent products, they can create bundled solutions that appeal to a wider audience. This not only enhances the value proposition for existing customers but also attracts new customers who are looking for comprehensive solutions.
Effective market expansion also requires a focused strategy for resource allocation. Companies must ensure that they have the necessary infrastructure, talent, and capital to support growth in new markets. This may involve investing in local teams, developing new marketing campaigns, or enhancing logistics capabilities. Strategic partnerships with local entities can also help the company navigate new markets more effectively.
By capitalizing on market expansion opportunities, companies can enhance their market share, strengthen their competitive position, and accelerate revenue growth.
The successful integration of brands post-merger is essential for presenting a consistent and unified message to the market. A well-executed brand integration strategy ensures that the new company can leverage the strengths of its legacy brands while creating a cohesive identity that resonates with customers, partners, and investors.
The first step in brand integration is conducting an in-depth analysis of both companies’ brands, including their market perception, brand equity, and strategic positioning. This analysis helps determine whether it is advantageous to retain both brands, adopt a single brand identity, or create an entirely new brand. The decision should be based on how each brand is perceived in the market and how much value is attached to each brand’s reputation.
For example, in cases where both companies have strong, well-established brands, maintaining dual brands may be the most effective strategy. This allows the merged company to preserve the customer loyalty and brand equity built over time. In other cases, where one brand has significantly more market recognition or strategic importance, adopting a single brand may create a clearer and more powerful market presence.
In some situations, creating an entirely new brand can symbolize a fresh start and represent the combined strengths of the merged entity. However, this approach carries risks, as it may require significant investment in rebranding efforts, marketing campaigns, and customer education. A new brand identity should only be pursued if it aligns with the company’s long-term strategic goals and offers distinct advantages in market positioning.
Regardless of the approach, the key to brand integration is ensuring that the new or combined brand reflects a consistent message across all customer touchpoints. This involves aligning the brand’s values, tone, visual identity, and communication strategy with the company’s overall mission and vision. Consistency helps maintain customer trust and loyalty, as it reassures them that the quality and experience they expect from the brand will remain intact.
Brand integration also involves a gradual transition plan. Companies must communicate changes to the brand in a way that respects customer sentiment and minimizes confusion. For instance, if a brand name is being retired, the transition should include clear messaging about how the products and services will continue to deliver the same or better quality under the new brand.
In summary, a well-thought-out brand integration strategy is essential for ensuring that the merged company presents a strong, unified identity in the marketplace. This strategy reinforces customer loyalty, enhances market positioning, and supports long-term business growth.
Conclusion: Post-merger, maintaining a focus on customers and markets is vital for ensuring the continued success of the combined company. By retaining customer confidence through clear communication and seamless service, capitalizing on market expansion opportunities, and implementing a strategic brand integration plan, companies can strengthen their market presence, deepen customer loyalty, and set the foundation for long-term growth. These actions not only preserve existing relationships but also unlock new opportunities for revenue generation and competitive advantage.
9.8. Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility
Mergers present a unique opportunity to reassess and integrate sustainability practices across both organizations. The combined entity can leverage its new scale, resources, and expertise to implement long-term sustainability initiatives that not only improve operational efficiency but also enhance the company’s environmental and social impact.
Focusing on sustainability during the integration process enables companies to reduce operational costs, particularly by optimizing resource usage, minimizing waste, and improving energy efficiency. For instance, companies can combine supply chains to reduce environmental impact, streamline logistics, and consolidate production facilities to lower energy consumption. Sustainable practices such as recycling, reducing emissions, and adopting renewable energy sources can be woven into the fabric of the new organization’s operations.
Furthermore, integrating sustainability across the merged entity helps create a strong reputation for social responsibility. Consumers and investors are increasingly favoring companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, and by embracing this during the merger, the new organization can build trust and loyalty among stakeholders. This reputation not only enhances customer relationships but also attracts talent who are motivated by working for a purpose-driven organization.
Figure 9.9: Sustainability and CSR in post-merger.
By focusing on long-term sustainability, the merged company can not only contribute to environmental goals but also strengthen its competitive position. Businesses that prioritize sustainability often experience increased innovation, improved risk management, and better alignment with regulatory requirements—factors that drive long-term success and resilience.
In addition to sustainability efforts, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) must be a priority for the newly merged entity. Aligning CSR strategies from both companies ensures a unified approach that enhances the organization's contribution to society and the environment, while reinforcing public trust. A successful CSR integration requires a clear understanding of the values and initiatives of both organizations, and a plan for how these efforts can be combined to achieve a greater social impact.
CSR alignment involves evaluating and potentially expanding the scope of the company’s philanthropic efforts, diversity and inclusion initiatives, community engagement, and environmental commitments. For example, if one company has a strong history of community outreach, while the other excels in sustainability efforts, the combined entity can build a robust CSR strategy that capitalizes on these strengths.
A unified approach to CSR also enhances the merged company’s brand equity. Stakeholders, including customers, employees, and investors, are increasingly looking to support companies that take responsibility for their impact on society. A strong, cohesive CSR strategy helps the organization stand out in the marketplace as a responsible and ethical business.
Moreover, CSR efforts should not be limited to external activities; internal policies promoting employee well-being, workplace diversity, and ethical business practices also play a critical role in shaping the company’s culture and public image.
Tracking post-merger performance metrics is essential for measuring the success of the integration and ensuring the new entity remains on course toward its strategic objectives. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established across multiple dimensions, including financial metrics, operational efficiency, employee engagement, and customer retention.
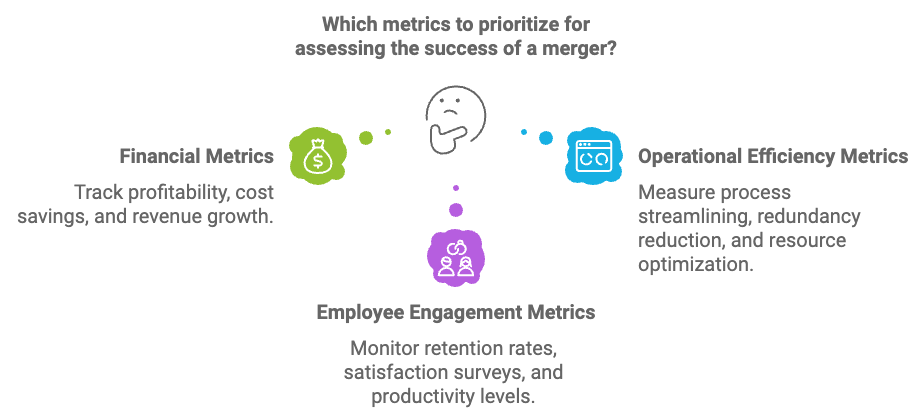
Figure 9.10: How to define success metrics to prioritize in post-merger.
Financial metrics such as profitability, cost savings, and revenue growth provide a snapshot of the merger’s financial impact. For instance, tracking synergies realized from cost-cutting initiatives or new revenue streams from cross-selling products can help assess whether the merger is delivering on its financial promises.
Operational efficiency metrics should measure how well the integrated company is streamlining processes, reducing redundancies, and optimizing resource allocation. These metrics might include production lead times, supply chain efficiency, or IT system performance, ensuring that the operational backbone of the company is functioning effectively.
Employee engagement metrics—such as retention rates, satisfaction surveys, and productivity levels—are critical to ensuring that the workforce remains motivated and aligned with the company’s goals. High engagement levels indicate that employees are adapting well to the changes brought by the merger, while low engagement may signal areas where additional support is needed.
Lastly, customer retention metrics help gauge whether the company is successfully maintaining relationships with its existing customer base and delivering on service promises. Monitoring customer satisfaction scores, churn rates, and net promoter scores (NPS) provides valuable insights into how well the merged entity is performing in the market.
Regular monitoring of these metrics allows leadership to make informed decisions and adjust strategies as necessary to keep the integration on track.
Establishing feedback loops is crucial for gathering insights from employees, customers, and other stakeholders throughout the post-merger integration process. Feedback mechanisms provide real-time information that can be used to address concerns, adjust plans, and refine strategies based on the needs and perceptions of those most affected by the merger.
Figure 9.10: Elements of feedbacks in post-merger integration.
Employee feedback can be gathered through surveys, focus groups, and regular check-ins to gauge morale, understand challenges, and assess how well employees are adapting to the new organizational structure. Employee input can help identify potential bottlenecks or areas of concern before they become larger issues, allowing leadership to make proactive adjustments.
Customer feedback is equally important, especially in understanding how the merger is perceived externally. Surveys, direct conversations, or online feedback can reveal whether customers are satisfied with the level of service and if they perceive any improvement or disruption due to the merger. Addressing customer concerns swiftly helps maintain confidence and loyalty during the transition.
Stakeholder feedback from partners, suppliers, and investors can also provide valuable insights. These groups may offer perspectives on how the merger is impacting the broader business ecosystem, and their input can help the company navigate external pressures while strengthening key relationships.
By creating formal and informal channels for feedback, companies can remain agile and responsive during the integration process, ensuring that any challenges are addressed quickly and that the company remains aligned with stakeholder expectations.
Mergers are inherently complex, and unforeseen challenges are bound to arise. It is essential for the merged entity to maintain agility and remain open to course corrections based on real-time data and feedback. Flexibility is key to overcoming obstacles and adjusting strategies as the integration unfolds.
When issues are identified—whether through performance metrics, feedback loops, or operational disruptions—leadership must be willing to make adjustments to the integration plan. This could involve re-evaluating timelines, reallocating resources, or revising certain operational strategies to better align with the company's evolving needs. For example, if customer feedback suggests that service disruptions are occurring, the company may need to prioritize system integrations or communication channels that address these concerns.
Course correction also involves strategic re-evaluation. As the integration progresses, new opportunities or risks may emerge that were not initially anticipated. The ability to pivot and take advantage of these opportunities, or mitigate risks, ensures that the merger remains successful in the long term.
By maintaining an adaptive mindset, the company can stay focused on its ultimate goals while navigating the inevitable complexities of a merger. This approach not only helps resolve immediate issues but also strengthens the organization’s resilience, ensuring it remains competitive and agile in a rapidly changing business environment.
Conclusion: Ensuring sustainability and corporate responsibility are integrated into post-merger strategies lays the foundation for long-term success and public trust. By focusing on long-term sustainability planning and aligning CSR efforts, companies can enhance their operational efficiency and social impact. Moreover, monitoring progress through performance metrics, establishing feedback loops, and remaining open to course corrections ensures that the integration stays on track and adapts to challenges, driving continuous improvement and ensuring the merged entity's success in the long run.
9.9. Conclusion
Post-merger integration is critical to unlocking the potential value of any merger or acquisition. By strategically aligning cultures, business processes, and leadership while prioritizing financial synergies and stakeholder engagement, companies can realize both short-term wins and long-term growth. The ability to maintain focus on both operational efficiency and sustainable corporate responsibility ensures that the integration not only drives growth but also strengthens the company's market position.
9.9.1. Further Learning with GenAI
Here’s a refined set of robust and comprehensive prompts that will encourage deeper and more advanced insights from ChatGPT:
Analyze the most critical elements in developing a successful post-merger integration strategy, focusing on how these elements differ across industries such as technology, healthcare, and finance. What factors contribute to the success or failure of these strategies in each context?
Examine cultural alignment in post-merger environments. What are the advanced techniques for identifying potential cultural conflicts before the merger, and how can companies effectively foster a unified culture that promotes innovation and growth post-merger?
Explore the process of realizing financial synergies post-merger, focusing on advanced methods of cost optimization, revenue enhancement, and capital structure realignment. How can companies utilize predictive analytics to model these outcomes?
Discuss how companies can translate comprehensive due diligence findings into a multi-phased, actionable integration plan. Highlight the strategic importance of integrating both operational and strategic aspects across diverse business units.
What are the key phases of integration in M&A, and how should they be structured to ensure smooth operational continuity and long-term growth? Discuss the use of project management methodologies like Agile or Six Sigma in managing these phases.
Examine the strategic balance between speed and precision in setting integration priorities post-merger. How can companies use real-time data analytics to dynamically adjust timelines while minimizing risks and maximizing operational efficiency?
How can organizations identify "quick wins" during the post-merger integration process without compromising long-term strategic goals? Provide examples of industries where short-term victories have either bolstered or undermined the merger's overall success.
Provide advanced methods for aligning KPIs across merged entities to ensure synergy and performance tracking. How can AI-driven performance management systems enhance real-time alignment and adaptive decision-making?
Discuss the challenges and advanced strategies for process standardization in post-merger integration. What role does process automation play in harmonizing workflows, and how can companies balance customization with standardization?
Evaluate the leadership challenges faced during post-merger integration. How can the creation of cross-functional leadership teams ensure a smooth transition? Provide insights into successful leadership structures from high-profile M&A cases.
What are the most effective change management strategies for navigating employee transitions in M&A? Discuss the use of AI-driven communication platforms for real-time engagement and morale boosting during the integration process.
Explore the complexities of IT and data system integration during post-merger processes. What are the advanced strategies for managing large-scale digital transformations, and how do companies ensure that cybersecurity and regulatory compliance are maintained throughout?
What role does data governance play in post-merger IT integration, and how can companies implement advanced AI and machine learning techniques to harmonize data structures while ensuring regulatory compliance?
What strategic actions can companies take to retain customer confidence during a post-merger period of transition? Analyze how personalized customer experience platforms can help reduce churn and maintain brand loyalty.
How can M&A create opportunities for market expansion? Discuss advanced analytical techniques to identify and seize expansion opportunities across different regions and product lines, considering case studies of successful global M&A expansions.
What strategic considerations should companies make when developing a unified branding strategy after a merger? How can companies balance brand equity, consumer perception, and market positioning during the rebranding process?
Analyze how sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) can be effectively integrated into post-merger strategies. How can companies leverage sustainability as a competitive advantage in M&A scenarios, particularly in environmentally regulated industries?
Identify the most effective metrics for monitoring the success of post-merger integration. How can predictive analytics and AI-driven tools provide real-time insights into integration success across finance, operations, and human resources?
How can companies create advanced feedback mechanisms during post-merger integration that incorporate machine learning models to analyze employee, customer, and stakeholder sentiment, driving continuous improvement in strategic decision-making?
What are the most common pitfalls in post-merger integration, especially in highly regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals or financial services? How can companies proactively mitigate these risks through advanced regulatory compliance strategies and technology integration?
These refined prompts should elicit advanced, detailed, and nuanced responses from AI, addressing various facets of post-merger integration in a way that provides deep insights into strategy, operations, and leadership challenges.
Comments