Chapter 8
Success Stories and Key Takeaways
"As someone who’s navigated multiple M&A deals, I can confidently say that success hinges on preparation, alignment, and leadership. The companies that win in M&A are those that understand it’s not just about the deal but about integrating people, processes, and culture effectively." — David Schwimmer, CEO of London Stock Exchange Group
Chapter 8 of Mastering Mergers and Acquisitions explores the factors that drive success in M&A transactions, from effective leadership and decision-making to operational and cultural integration. Through real-world case studies and industry-specific insights, the chapter provides a comprehensive guide to leveraging strengths, mitigating risks, and achieving long-term value creation. It highlights critical success factors such as strategic alignment, technological synergies, and cultural compatibility, offering practical strategies for ensuring post-merger success in both digital and capital-intensive sectors./
8.1. Success Stories and Key Takeaways
In any merger or acquisition (M&A), the overarching goal is to create value, whether through expanding market reach, enhancing operational efficiency, or accelerating growth in strategic areas. However, not all M&A transactions are successful; many falter due to an inability to integrate disparate corporate cultures, misalignment of strategic objectives, or a failure to harness the synergies inherent in the deal. This section highlights two notable success stories—Disney's acquisition of Pixar and Facebook's acquisition of Instagram—which illustrate how focusing on cultural alignment, leveraging synergies, and maintaining a long-term vision can lead to the creation of sustainable value and growth.
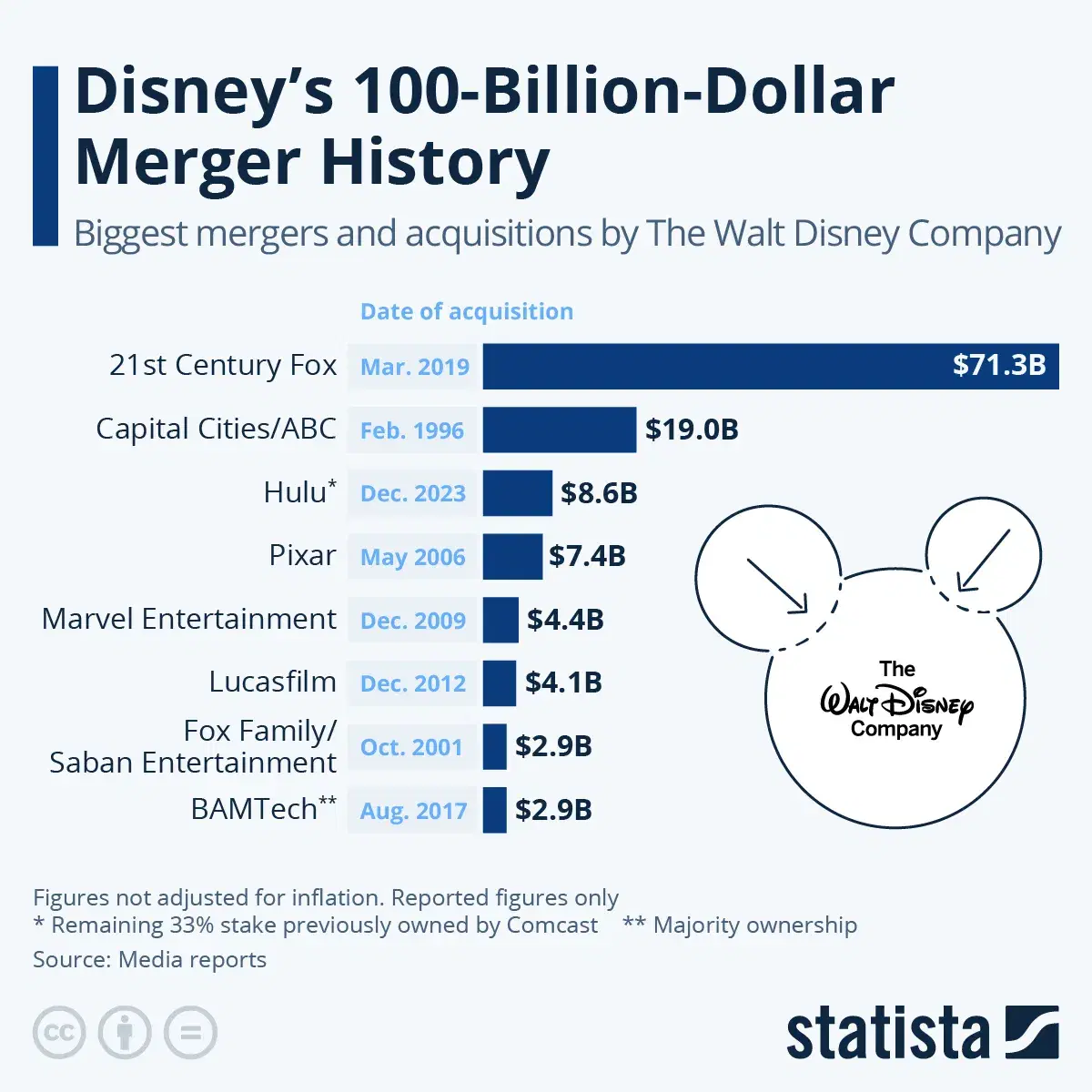
Figure 8.1: Disney 100B M&A History.
Disney’s acquisition of Pixar in 2006 is widely regarded as a textbook example of a successful M&A, driven largely by Disney's ability to align its corporate culture with that of Pixar. At the time, Disney’s animation division was struggling creatively, having lost its innovative edge. Pixar, on the other hand, had revolutionized the animation industry with hits like Toy Story and Finding Nemo. The acquisition presented Disney with an opportunity to reinvigorate its animation division by harnessing Pixar’s talent and creativity. However, the key to the success of this deal was not just about bringing Pixar’s expertise into Disney but about how Disney approached the integration of the two companies.
Rather than imposing its corporate structure and culture on Pixar, Disney allowed Pixar’s leadership—particularly Steve Jobs, John Lasseter, and Ed Catmull—substantial creative autonomy. This decision to preserve Pixar's unique culture, while aligning the companies’ broader strategic objectives, was critical. Pixar retained its innovative spirit and its creative teams flourished under Disney’s broader distribution network, marketing resources, and financial backing. By giving Pixar the freedom to continue creating groundbreaking content, Disney not only revitalized its animation division but also produced a string of commercially successful and critically acclaimed films, such as Up, WALL-E, and Inside Out.
Cultural alignment is one of the most critical, yet often overlooked, factors in M&A success. While financial and operational synergies are essential, deals often falter because of cultural clashes between the acquirer and the target company. Disney’s acquisition of Pixar underscores the importance of recognizing and respecting the differences in corporate culture. Rather than forcing Pixar to conform to Disney’s way of doing business, Disney created a space where both cultures could coexist and complement each other. This allowed Pixar to continue its creative output without disruption, while Disney benefited from the innovation and creativity that Pixar brought to the table. The lesson here is that cultural compatibility can be as important as financial performance in determining the long-term success of an acquisition.
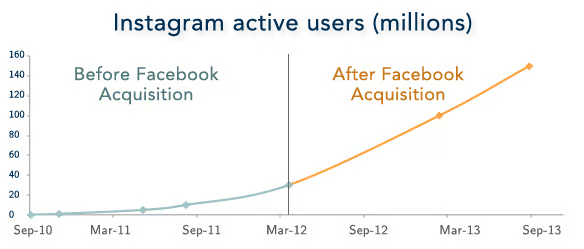
Figure 8.2: IG active users before and after FB acquisition.
In 2012, Facebook made headlines when it acquired Instagram for $1 billion—a staggering amount for a company that had just 13 employees and no significant revenue at the time. Many questioned the rationale behind the acquisition, but it soon became evident that Facebook’s decision was driven by its recognition of Instagram’s potential to complement its existing platform. Instagram brought something that Facebook lacked: a rapidly growing base of mobile-first users and a highly engaged community around photo-sharing, a trend that Facebook was looking to capitalize on.
The success of the acquisition was rooted in Facebook’s ability to leverage complementary synergies between the two platforms. Facebook provided Instagram with the financial resources and infrastructure necessary to scale, including advanced advertising technology and access to Facebook’s vast user base. In turn, Instagram’s visual-first, mobile-friendly platform helped Facebook diversify its product offerings and tap into a younger demographic that was increasingly shifting to mobile usage. By integrating Instagram into its ecosystem, Facebook was able to maintain Instagram’s independent brand identity while enhancing the platform’s capabilities through advertising tools and algorithms. As a result, Instagram has grown to become one of the world’s most influential social media platforms, boasting over a billion active users and contributing significantly to Facebook’s advertising revenue.
Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram highlights the importance of recognizing and maximizing synergies in an M&A transaction. Synergies are often the driving force behind M&A deals, whether they be operational, technological, or market-based. In this case, the complementary nature of the two platforms—Facebook’s focus on social connectivity and Instagram’s emphasis on visual storytelling—created opportunities for cross-platform innovation and revenue generation. By allowing Instagram to retain its core identity while integrating it into Facebook’s advertising ecosystem, both companies benefited from each other’s strengths. The lesson here is that the best M&A deals are those that enable both the acquirer and the target to leverage each other’s capabilities in ways that accelerate growth.
Both Disney’s acquisition of Pixar and Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram were guided by a long-term vision that went beyond immediate financial gains. In Disney’s case, the acquisition of Pixar was about more than just improving the bottom line—it was a strategic move to rebuild its animation legacy and foster long-term creative innovation. Similarly, Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram was not motivated by short-term revenue prospects but by the potential for long-term growth through mobile engagement and visual content.
In both cases, the acquirers had a clear understanding of how the acquisition aligned with their broader strategic goals. Disney saw Pixar as the key to revitalizing its core business of storytelling and animation, while Facebook recognized that Instagram would enable it to capture new markets and user behaviors. This long-term perspective allowed both companies to focus on integration strategies that fostered growth and innovation rather than merely cutting costs or achieving immediate synergies.
Strategic Takeaway: Long-Term Vision A clear, long-term vision is critical for M&A success. Acquirers should approach M&A with a strategy that aligns with their overall business objectives and future growth aspirations, rather than focusing solely on short-term financial returns. This involves thinking beyond the immediate post-merger integration process and considering how the combined entities can create new growth opportunities over time. Companies that enter M&A deals with a long-term perspective are more likely to unlock value from the acquisition, ensuring that the transaction contributes to sustainable competitive advantage.
The success stories of Disney and Pixar, and Facebook and Instagram, provide valuable insights into what drives M&A success. The common thread in both cases is the emphasis on cultural alignment, leveraging synergies, and maintaining a long-term vision. Companies that prioritize these elements during the acquisition process are more likely to achieve their strategic objectives and create lasting value.
The key lesson is that successful M&A transactions require more than just financial due diligence and operational planning. Acquirers must also focus on softer factors, such as corporate culture and strategic alignment, to ensure that the deal creates value in the long run. By fostering an environment where synergies can thrive and growth can be accelerated, companies can unlock the full potential of the acquisition, achieving both short-term financial goals and long-term strategic objectives.
8.2. Critical Success Factors in M&A
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are inherently complex processes that require careful planning, thorough evaluation, and the alignment of multiple strategic objectives. Despite the appeal of achieving growth, market expansion, or operational efficiencies, many M&A deals fall short of their intended outcomes because they fail to address the critical factors that ensure long-term success. To improve the odds of success, acquirers must focus on several key elements that underpin the overall effectiveness of the transaction: strategic alignment, comprehensive due diligence, and post-merger integration planning. Each of these factors plays a vital role in ensuring that the acquisition creates sustained value, meets strategic goals, and avoids the pitfalls that often lead to failure.
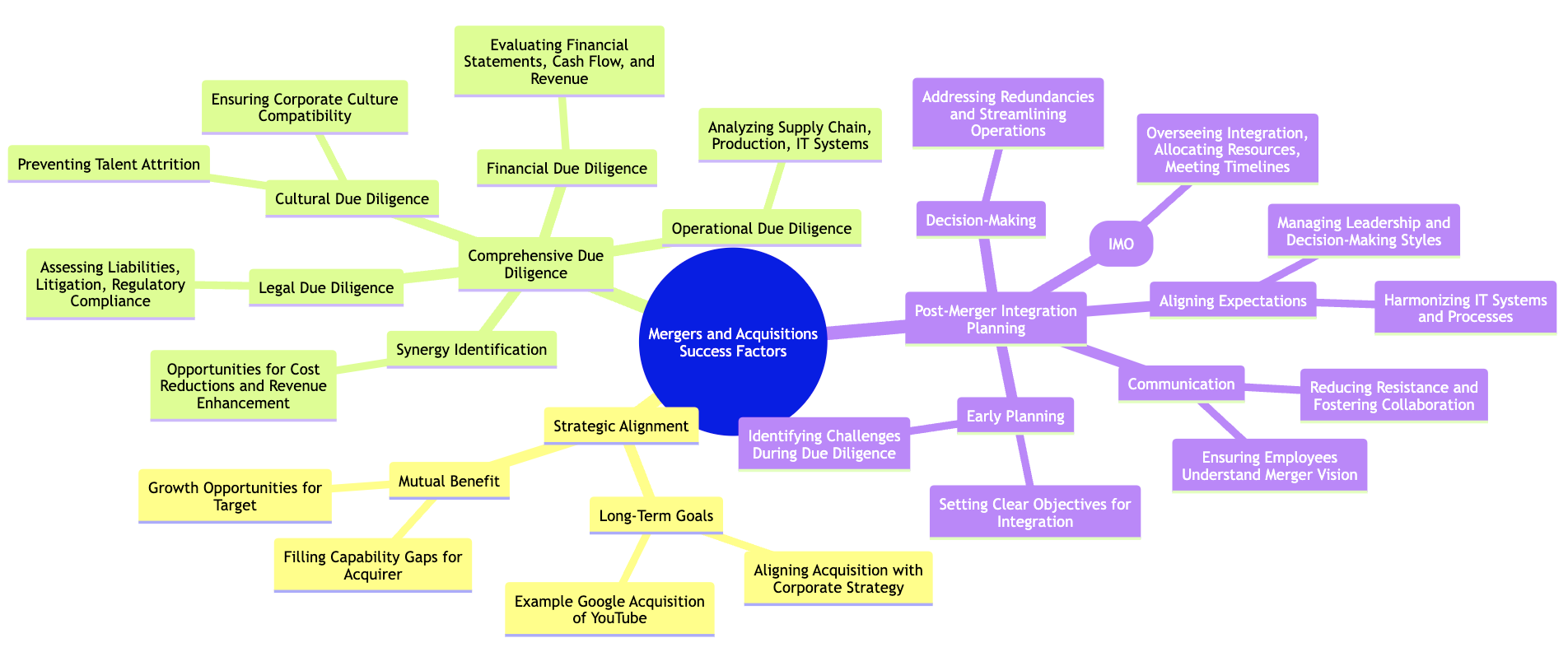
Figure 8.3: Landscape of success factors in M&A.
At the heart of every successful M&A transaction is strategic alignment—the degree to which the acquisition fits within the acquiring company’s long-term goals and business strategy. It is not enough for a deal to make financial sense in the short term; the acquisition must also serve the broader strategic vision of both the acquiring and target companies. When deals are well-aligned with corporate strategies, they have a greater chance of delivering meaningful value and achieving growth.
A compelling example of this is Google’s acquisition of YouTube. In 2006, when Google acquired the then-nascent YouTube platform for $1.65 billion, many questioned the rationale behind the deal. At the time, YouTube was a relatively new player in the digital media space, with little revenue and uncertain profitability. However, Google recognized the immense strategic potential in video content as a complement to its existing dominance in search and advertising. The acquisition aligned with Google’s broader strategy of becoming a dominant player in digital media, extending its reach into video content while capitalizing on its core competencies in advertising and search algorithms. Fast forward to today, YouTube has become one of the most visited websites in the world, generating billions in advertising revenue and cementing Google’s role as a leader in online content.
Strategic alignment also plays a crucial role in ensuring that both companies can benefit from each other’s strengths. For the acquirer, the deal should fill gaps in its capabilities, expand its market reach, or provide access to new technologies or business models. For the target, the acquisition should provide opportunities for growth through access to new resources, infrastructure, or expertise. Without this alignment, even the most financially sound deal may falter if the two companies cannot combine their assets in a way that drives long-term value creation.
One of the most critical factors in M&A success is the thoroughness of the due diligence process. Due diligence involves a detailed and in-depth evaluation of the target company’s financial health, legal standing, operational efficiency, and cultural compatibility. A comprehensive due diligence process allows the acquirer to uncover potential risks, identify areas for synergy, and make informed decisions about the value of the acquisition. Without this level of scrutiny, acquirers can miss critical red flags that may later derail the transaction or erode its value.
Financial due diligence is often the first step and includes a deep dive into the target’s financial statements, cash flow, debt levels, and revenue streams. However, financial evaluation alone is not sufficient. Legal due diligence is equally important, as it ensures that the acquirer is aware of any potential liabilities, ongoing litigation, intellectual property disputes, or regulatory challenges that could pose risks post-acquisition. For example, when acquiring a company with global operations, regulatory compliance and legal liabilities in multiple jurisdictions can complicate integration and increase costs if not accounted for during due diligence.
Beyond financial and legal aspects, operational due diligence focuses on assessing the target’s capabilities, supply chain, production processes, and IT systems. This helps the acquirer determine whether the target company’s operations can be integrated smoothly and whether there are any operational inefficiencies that need to be addressed. Additionally, cultural due diligence has become increasingly important, as it examines the compatibility of corporate cultures between the two entities. Cultural mismatches can lead to friction, talent attrition, and difficulties in integrating teams, which can ultimately undermine the success of the deal.
The due diligence process not only serves to uncover risks but also helps identify opportunities for synergies. Acquirers can use the information gathered to develop strategies for achieving operational efficiencies, cost reductions, or revenue enhancements. The more thorough and well-rounded the due diligence process, the better equipped the acquirer is to make decisions that will maximize the value of the transaction.
The third critical success factor in M&A is post-merger integration planning, which begins long before the deal is finalized. The integration phase is where many M&A transactions stumble, as companies struggle to combine systems, processes, and cultures in a way that fosters synergy and minimizes disruption. A failure to plan for integration can lead to delays, operational inefficiencies, and even the loss of key talent. In the worst-case scenario, poor integration planning can erode the value of the deal entirely.
Integration planning should start early, ideally during the due diligence phase. This allows the acquirer to identify potential challenges and develop strategies to address them. One of the first steps in integration planning is setting clear objectives for the integration process. What are the primary goals—cost savings, operational synergies, market expansion? How will success be measured? Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) for the integration process helps ensure that the acquiring company stays on track and meets its goals.
Another important aspect of post-merger integration is aligning expectations between the two companies. Misaligned expectations can lead to confusion and conflict, especially when it comes to integrating core systems and processes. For example, when combining IT infrastructure, differences in technology platforms can create compatibility issues that delay integration and increase costs. Similarly, differences in management styles or decision-making processes can cause friction between leadership teams, slowing down the integration process.
Communication is also crucial during integration. Employees from both companies need to understand the vision for the merger and how it will affect their roles. Effective communication can help ease uncertainty, reduce resistance to change, and foster collaboration between teams. Many successful M&A transactions create an Integration Management Office (IMO) to oversee the entire integration process, ensuring that timelines are met, resources are allocated appropriately, and any challenges are addressed promptly.
In some cases, integration planning also involves making difficult decisions about redundancies or streamlining operations. While these decisions can be challenging, they are often necessary to achieve the cost synergies that are a major driver of many M&A deals. The key is to approach these decisions thoughtfully and transparently, balancing the need for efficiency with the goal of maintaining employee morale and minimizing disruption.
M&A success is never guaranteed, but companies that focus on strategic alignment, comprehensive due diligence, and post-merger integration planning are far more likely to achieve their desired outcomes. Strategic alignment ensures that the acquisition fits into the broader goals of both the acquiring and target companies, creating a foundation for long-term value creation. Comprehensive due diligence uncovers risks and identifies opportunities, allowing the acquirer to make informed decisions and avoid costly pitfalls. Finally, post-merger integration planning lays the groundwork for a seamless integration, ensuring that systems, processes, and cultures are combined in a way that fosters synergy and minimizes disruption. Together, these factors provide a roadmap for navigating the complexities of M&A and delivering a value-enhancing transaction.
8.3. Effective Leadership and Decision-Making
Leadership is one of the most critical determinants of success in mergers and acquisitions (M&A). The complexity of M&A transactions—ranging from strategic planning and negotiation to integration and cultural alignment—demands more than just technical acumen. Leaders must provide direction, manage uncertainty, and guide the organization through each stage of the M&A process. Their decisions, vision, and communication skills can make or break the success of a deal. This section examines how visionary leadership, change management, and agile decision-making contribute to the success of M&A transactions, with real-world examples that illustrate these principles in action.
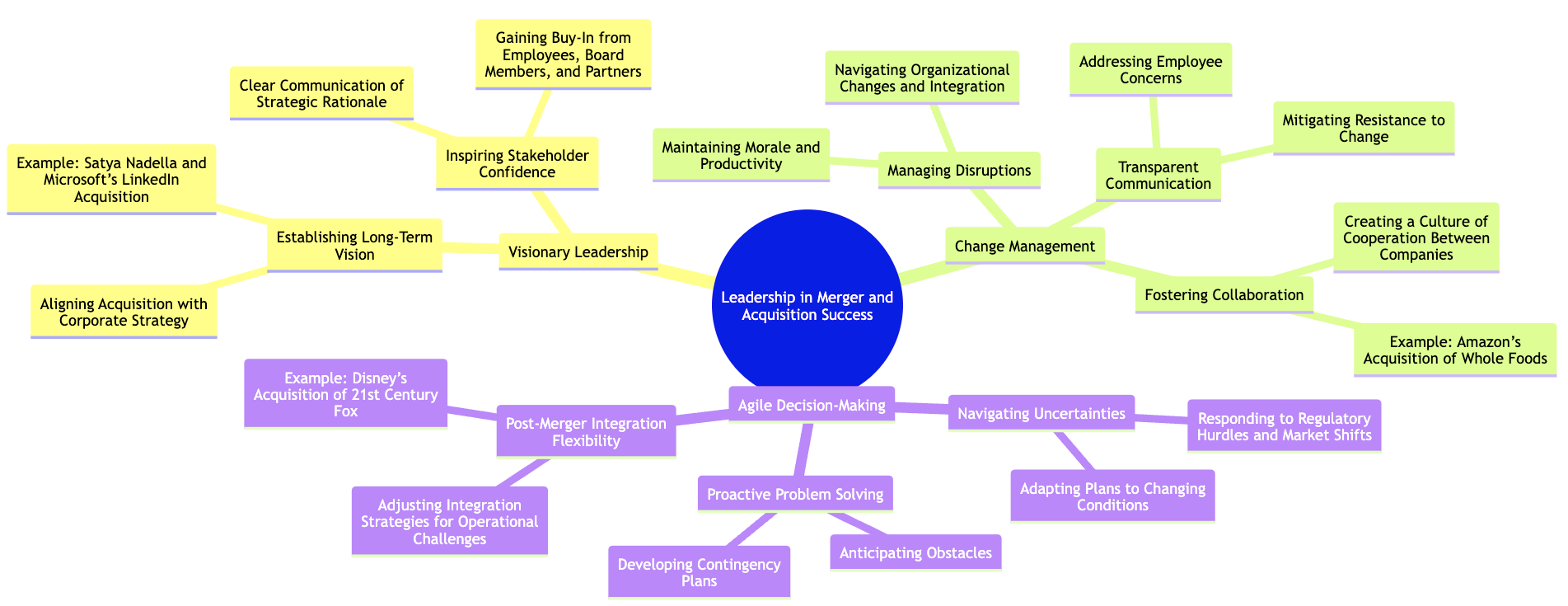
Figure 8.4: Key elements of effective leadership and decision making.
At the outset of any M&A deal, leaders must establish a clear, long-term vision for how the acquisition fits into the overall corporate strategy. Visionary leadership is not just about closing the deal; it’s about understanding the strategic implications of the acquisition and how it aligns with the company’s growth objectives. The leader’s role is to articulate this vision in a way that inspires confidence and ensures that all stakeholders, from board members to employees, understand the strategic rationale behind the deal.
A prime example of visionary leadership in M&A is Satya Nadella’s role in Microsoft’s acquisition of LinkedIn. When Microsoft acquired LinkedIn in 2016 for $26.2 billion, Nadella had a clear vision of how the acquisition would create new synergies between LinkedIn’s vast professional network and Microsoft’s enterprise-focused cloud services. He recognized that LinkedIn’s data on professionals and companies could integrate seamlessly with Microsoft’s offerings like Office 365 and Dynamics 365, enabling a more personalized and data-driven experience for business users. This vision went beyond simply acquiring a profitable social network; it was about integrating LinkedIn’s capabilities into Microsoft’s broader strategy of digital transformation and enterprise growth.
Nadella’s visionary approach ensured that the acquisition wasn’t just viewed as a standalone transaction but as a core component of Microsoft’s future. By clearly communicating how LinkedIn would enhance Microsoft’s existing products and create new value for customers, Nadella was able to gain widespread buy-in, both internally and externally. This long-term perspective is crucial for M&A success because it aligns the deal with broader business goals, ensuring that the acquisition is more than just a short-term financial maneuver.
Mergers and acquisitions are inherently disruptive. They often involve significant organizational changes, from restructuring teams to integrating systems and processes. Effective leaders must not only manage these disruptions but actively guide both organizations through the transformation process. This requires a deep understanding of change management—the ability to address employee concerns, navigate resistance, and ensure that the integration process proceeds smoothly.
One of the biggest challenges during M&A is maintaining morale and productivity while the two organizations are brought together. Employees often fear job redundancies, cultural clashes, and shifts in leadership priorities. Leaders must engage in transparent communication to mitigate these fears and ensure that all stakeholders remain aligned with the company’s vision. This means clearly explaining the goals of the acquisition, how it will impact employees, and what steps are being taken to integrate the two companies without causing unnecessary disruption.
Effective leaders also know how to engage key stakeholders, from employees and customers to investors and partners, in the change process. They ensure that everyone understands their role in the post-merger organization and how the acquisition will benefit them in the long run. One of the most important aspects of change management is fostering a culture of collaboration. Leaders must create an environment where employees from both companies feel valued and are encouraged to contribute their ideas and skills to the success of the merger.
A strong example of change management in M&A is Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods in 2017. Amazon’s leadership, led by Jeff Bezos, knew that integrating a traditional brick-and-mortar retailer into an e-commerce giant would be a challenging process. Whole Foods employees were used to a very different corporate culture than Amazon’s, and there were concerns about how the acquisition would affect Whole Foods’ brand and values. Amazon’s leadership addressed these concerns by maintaining Whole Foods’ existing management team and brand identity while slowly integrating Amazon’s technology and logistics capabilities into the company’s operations. This measured approach allowed Amazon to avoid major disruptions while gradually transforming Whole Foods into a more efficient, tech-enabled retailer.
The M&A process is rarely linear. Deals often face unexpected challenges, from regulatory hurdles to market shifts, that require swift and decisive action. Leaders must be able to navigate these uncertainties with agile decision-making—the ability to assess new information, pivot when necessary, and make decisions that keep the deal on track. Agility is essential for adapting to the fluid nature of M&A transactions, where timelines, priorities, and even the scope of the deal can change rapidly.
Agile leaders are not only reactive but also proactive. They anticipate potential obstacles and develop contingency plans to address them. For example, during due diligence, leaders may uncover unforeseen liabilities, such as regulatory compliance issues or cultural mismatches, that could derail the deal. Rather than abandoning the acquisition, agile leaders find ways to mitigate these risks, whether through renegotiation or by developing strategies to address the issues post-merger.
Agile decision-making is also crucial during the post-merger integration phase. As companies work to combine their operations, new challenges often arise that require leaders to make quick, informed decisions. For instance, integrating technology systems can be fraught with complexity, especially when the two companies use different platforms. Leaders must be able to pivot from the original plan if they encounter compatibility issues, developing alternative solutions that ensure the integration process continues without major delays.
An example of agile decision-making in M&A can be seen in Disney’s acquisition of 21st Century Fox. The acquisition, which was finalized in 2019, faced significant regulatory scrutiny, particularly around concerns that the merger would reduce competition in the entertainment industry. Disney’s leadership, led by CEO Bob Iger, navigated these challenges by making strategic concessions, such as selling off certain assets (including Fox’s regional sports networks) to satisfy antitrust regulators. Iger’s ability to adapt to regulatory demands without compromising the core value of the deal demonstrated the importance of agility in managing complex M&A transactions.
Leadership is the cornerstone of any successful M&A transaction. Visionary leaders set the strategic direction, ensuring that the acquisition aligns with the company’s long-term goals. Effective change management enables leaders to guide their organizations through the disruptions that accompany mergers, maintaining morale and productivity while facilitating a smooth transition. Agile decision-making allows leaders to navigate the inevitable uncertainties that arise during the M&A process, ensuring that the deal stays on track and achieves its desired outcomes.
In short, M&A success is not just about technical expertise or financial acumen—it requires leaders who can see the bigger picture, communicate effectively, and make decisions with both flexibility and conviction. By focusing on these aspects of leadership, companies can significantly increase their chances of executing a successful M&A deal that delivers long-term value.
8.4. Leveraging Strengths and Capabilities
In mergers and acquisitions (M&A), the ultimate goal is to create value by combining the strengths and capabilities of both the acquiring and target companies. However, simply merging two organizations does not automatically result in success. The real challenge lies in the ability of the acquirer to leverage complementary resources—such as intellectual property, proprietary technologies, operational expertise, and human capital—to gain a competitive advantage. This section explores the critical importance of identifying and integrating these strengths in a way that maximizes synergies and drives long-term growth. By doing so, companies can turn M&A transactions into powerful drivers of innovation, market expansion, and sustained business success.
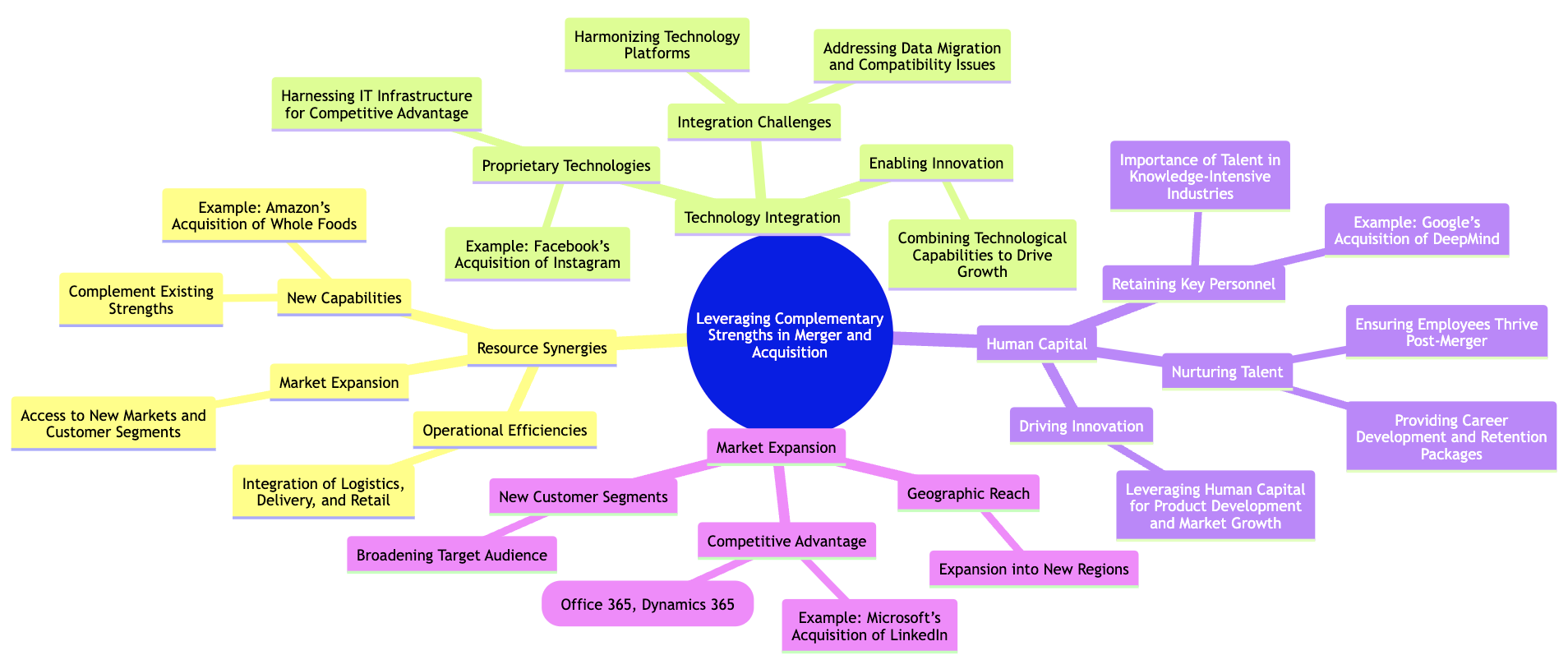
Figure 8.5: Leveraging Complementary Strengths in Merger and Acquisition
One of the primary reasons companies pursue M&A is to gain access to new capabilities that complement their existing strengths. Successful M&A transactions are often characterized by resource synergies, where the assets of the target company enhance the acquirer’s ability to compete in the market. These synergies can take many forms, such as operational efficiencies, access to new technologies, or expansion into new markets.
A notable example of leveraging resource synergies is Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods in 2017. By acquiring Whole Foods, Amazon gained access to a vast network of physical retail stores, which complemented its already dominant position in e-commerce. Amazon, known for its advanced logistics, technology, and delivery infrastructure, was able to integrate these strengths with Whole Foods' established customer base and expertise in premium grocery retail. This merger allowed Amazon to significantly expand its footprint in the grocery sector while introducing innovative services like grocery delivery through its Prime Now platform. The acquisition was not just about gaining stores—it was about enhancing Amazon's logistical capabilities and leveraging Whole Foods' brand equity to provide a seamless online-offline retail experience.
This example illustrates that M&A deals are most successful when they enable the acquirer to gain new capabilities or bolster existing ones. Resource synergies offer the potential for both operational efficiency and market differentiation, but only if the acquirer can effectively integrate these assets. A key takeaway from Amazon’s strategy is the importance of having a clear plan for how these resources will be utilized post-merger to create new growth opportunities.
In the modern business landscape, technology is often one of the most valuable assets in any M&A deal. The ability to harness proprietary technologies or IT infrastructure can significantly enhance an acquirer’s competitive position. However, technological integration is also one of the most challenging aspects of post-merger integration. Without a detailed plan to harmonize technology platforms, companies risk operational disruptions, increased costs, and missed opportunities for synergy.
One of the most successful examples of leveraging technological synergies is Facebook’s acquisition of Instagram in 2012. At the time of the acquisition, Instagram was a fast-growing mobile app with a highly engaged user base, but it had limited infrastructure and monetization capabilities. Facebook, on the other hand, had robust data infrastructure, sophisticated advertising technology, and a vast user base. By integrating Instagram into its technology ecosystem, Facebook was able to enhance Instagram’s platform while maintaining its distinct brand identity. Facebook provided Instagram with the resources and infrastructure it needed to scale, such as advanced data analytics and advertising tools, which helped Instagram grow exponentially without disrupting its core user experience. Today, Instagram contributes significantly to Facebook’s advertising revenue, demonstrating the power of harmonizing technology platforms to unlock new revenue streams.
For companies engaging in M&A, successful technology integration requires a strategic plan that addresses potential challenges, such as compatibility between different IT systems, data migration, and the alignment of technological priorities. The goal is to minimize disruptions while maximizing synergies. In some cases, this may require upgrading or consolidating technology platforms to ensure that the combined organization operates seamlessly. Effective technology integration not only prevents operational bottlenecks but also enables innovation by combining the best of both companies’ technological capabilities.
While physical assets and technology are important, one of the most valuable resources in any M&A transaction is human capital. In knowledge-intensive industries such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and finance, retaining key personnel from the acquired company is critical to realizing the full potential of the deal. The expertise, creativity, and relationships that employees bring to the table are often irreplaceable, and their contributions can drive innovation, product development, and market expansion post-merger.
For example, when Google acquired DeepMind, a leading artificial intelligence (AI) company, in 2014, it was not just acquiring technology or intellectual property—it was acquiring talent. DeepMind’s team of AI researchers and engineers were world leaders in their field, and Google recognized that retaining this talent was key to unlocking the full potential of the acquisition. Google took steps to ensure that DeepMind’s team was integrated into its broader AI strategy while maintaining a degree of autonomy that allowed them to continue their groundbreaking research. By nurturing this talent, Google was able to leverage DeepMind’s capabilities to make significant advancements in AI, including the development of AlphaGo, the first AI to defeat a world champion in the complex game of Go.
This example highlights the importance of identifying and nurturing key talent as part of the M&A integration process. Acquirers must not only focus on retaining high-performing employees but also ensure that they are placed in roles where they can thrive and contribute to the organization’s long-term success. To achieve this, companies may need to offer retention packages, provide career development opportunities, and create a collaborative culture where employees from both companies feel valued. Failing to retain key talent can result in the loss of critical institutional knowledge, reduced innovation capacity, and diminished competitive advantage.
M&A deals that successfully leverage the complementary strengths of both companies can open up new avenues for market expansion. By combining resources, capabilities, and expertise, the newly merged entity is often better positioned to enter new markets, launch new products, or increase its market share. This is particularly true when the target company brings capabilities that the acquirer lacks, such as access to new customer segments or geographic regions.
A prime example of this is Microsoft’s acquisition of LinkedIn in 2016. LinkedIn, the world’s largest professional networking platform, gave Microsoft access to a massive database of professionals, companies, and career-related insights. By integrating LinkedIn with its existing products, such as Office 365 and Dynamics 365, Microsoft was able to enhance its enterprise offerings and create new synergies that increased its value proposition for business customers. For instance, integrating LinkedIn’s data with Dynamics 365 gave Microsoft a competitive edge in customer relationship management (CRM) by enabling deeper insights into customer behavior and professional networks. This not only helped Microsoft expand its market share in the enterprise software space but also positioned it as a leader in cloud-based business solutions.
The Microsoft-LinkedIn deal demonstrates how leveraging complementary strengths can lead to market expansion and a stronger competitive position. The key to success in such deals is identifying where the two companies’ strengths align and developing a clear strategy for how those strengths will be combined to create new value. This often involves cross-functional collaboration between teams from both companies, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively and that the combined entity can pursue new growth opportunities.
In conclusion, the success of any M&A transaction depends on the acquirer’s ability to leverage the strengths and capabilities of both companies to create a competitive advantage. By focusing on resource synergies, technology integration, and human capital, companies can unlock new opportunities for innovation, market expansion, and sustained growth. The key to success lies in developing a detailed integration plan that addresses potential challenges while maximizing the value of each company’s assets. Whether it’s Amazon leveraging its logistical prowess with Whole Foods’ retail network, or Facebook integrating Instagram’s mobile platform with its advertising infrastructure, the ability to capitalize on complementary strengths is what turns M&A deals into engines of long-term success.
8.5. Case Studies
Case studies of successful mergers and acquisitions (M&A) serve as invaluable learning tools for understanding the complexities, challenges, and opportunities involved in integrating two companies. By examining real-world examples across diverse industries, we can gain insights into best practices for strategic decision-making, integration management, and the long-term impact of such transactions. In this section, we delve into several high-profile M&A deals, exploring the strategic rationale behind each transaction, the challenges faced during integration, and how these companies managed to align their M&A strategies with their broader corporate objectives. We focus on Microsoft’s acquisition of LinkedIn, ExxonMobil’s mergers, and Facebook’s acquisition of WhatsApp, illustrating how companies in different sectors successfully navigate M&A to drive growth and sustain competitive advantages.

Figure 8.6: Microsoft and LinkedIn case study.
In 2016, Microsoft’s $26.2 billion acquisition of LinkedIn stood out as one of the largest and most significant deals in the tech industry. The strategic rationale for this acquisition was clear: Microsoft sought to integrate LinkedIn’s massive professional networking platform into its ecosystem of enterprise products, including Office 365 and Dynamics 365. Microsoft recognized that LinkedIn’s data on professionals, companies, and career paths could be leveraged to enhance its cloud services and customer relationship management (CRM) solutions. By combining LinkedIn’s network with its software offerings, Microsoft aimed to create a more personalized and data-driven experience for its business users.
Best Practices: Microsoft’s acquisition of LinkedIn highlights several best practices in M&A, particularly around strategic alignment and long-term vision. Satya Nadella, Microsoft’s CEO, had a clear understanding of how LinkedIn could complement Microsoft’s existing products and services, ensuring that the acquisition wasn’t just about growth but about enhancing value across the entire enterprise. The integration was carefully managed to ensure that LinkedIn retained its distinct brand and culture while benefiting from Microsoft’s resources and technological infrastructure. This approach allowed LinkedIn to continue growing its user base and improving its platform, while Microsoft gained access to invaluable business data that strengthened its position in the enterprise software market.
Integration Challenges: One of the key challenges faced during this merger was ensuring a smooth technological integration while maintaining LinkedIn’s unique culture. Microsoft needed to carefully manage the transition without disrupting LinkedIn’s operations or alienating its user base. By keeping LinkedIn’s leadership intact and allowing the company to operate semi-independently, Microsoft avoided many of the pitfalls commonly associated with tech integrations. This case demonstrates how effective integration management—rooted in respect for the target’s culture and autonomy—can lead to a seamless merger and sustained growth.
Long-Term Impact: Today, LinkedIn plays a critical role in Microsoft’s business strategy, driving revenue through advertising, premium subscriptions, and integrated services with Microsoft’s enterprise products. The acquisition has solidified Microsoft’s leadership in cloud services and business software, demonstrating the long-term value of strategically aligned M&A transactions.

Figure 8.7: Exxon and Mobil case study.
The energy industry has long been characterized by capital-intensive operations and large-scale mergers aimed at consolidating resources and gaining operational efficiencies. Exxon’s merger with Mobil in 1999, which created ExxonMobil, is one of the most prominent examples of a successful M&A deal in the oil and gas sector. The strategic rationale behind the merger was to combine the two companies’ vast reserves, refining capabilities, and distribution networks to create one of the world’s largest and most efficient energy companies.
Best Practices: The ExxonMobil merger exemplifies how companies in capital-intensive industries can achieve significant operational synergies through M&A. By combining Exxon’s and Mobil’s assets, the newly formed company was able to streamline operations, reduce costs, and increase production efficiency. The merger also enabled ExxonMobil to better withstand fluctuations in oil prices and economic cycles, ensuring long-term stability and profitability. A key best practice demonstrated in this case was the clear identification of synergies before the merger, with both companies focusing on how to optimize their supply chains, distribution networks, and refining operations.
Integration Challenges: One of the major challenges in the ExxonMobil merger was the integration of two massive corporate cultures and management structures. Both Exxon and Mobil had long histories and distinct corporate identities, which created potential friction during the integration process. ExxonMobil addressed this challenge by clearly defining its new corporate structure early on and emphasizing a unified corporate culture focused on operational excellence and efficiency. This structured approach to integration helped minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition, allowing the company to quickly capitalize on the synergies identified during the merger.
Long-Term Impact: ExxonMobil has since become a global leader in the energy sector, with the merger enabling the company to achieve economies of scale, expand its global footprint, and invest in new technologies. The long-term success of this merger highlights the importance of thorough integration planning and the focus on operational synergies in capital-intensive industries.
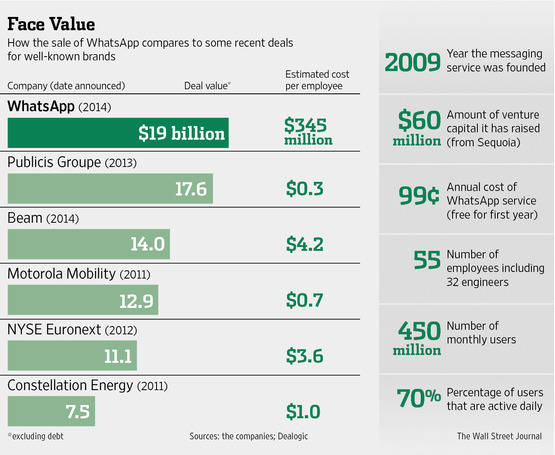
Figure 8.8: Facebook and WhatsApp case study.
In 2014, Facebook acquired WhatsApp for $19 billion, making it one of the largest tech acquisitions in history. WhatsApp, a messaging platform with a vast global user base, offered Facebook an opportunity to expand its reach in mobile communication and strengthen its presence in international markets. The strategic rationale behind the acquisition was to capitalize on WhatsApp’s massive user base—particularly in emerging markets—and to integrate its messaging capabilities into Facebook’s ecosystem of apps and services.
Best Practices: The WhatsApp acquisition is an example of how an M&A deal can be driven by the need for market expansion and user acquisition. At the time of the acquisition, WhatsApp had over 450 million users, many of whom were in regions where Facebook’s growth had slowed. By acquiring WhatsApp, Facebook was able to tap into these new markets and strengthen its position as the dominant player in mobile communication. One of the key best practices in this case was Facebook’s decision to keep WhatsApp as a standalone app, allowing it to maintain its brand identity and avoid alienating its user base. This approach ensured that the integration was smooth and did not disrupt WhatsApp’s core service, which had been a key factor in its popularity.
Integration Challenges: One of the biggest challenges faced by Facebook during the integration of WhatsApp was aligning the two companies’ business models. WhatsApp had a subscription-based revenue model, while Facebook relied heavily on advertising. To address this challenge, Facebook initially left WhatsApp’s business model intact, giving the platform time to grow and expand its user base without introducing disruptive changes. Over time, Facebook has explored ways to monetize WhatsApp, including the introduction of business messaging services and payment features, while maintaining the app’s core functionality.
Long-Term Impact: WhatsApp has become a key component of Facebook’s strategy to dominate mobile communication, particularly in international markets. With over 2 billion users worldwide, WhatsApp continues to grow, and Facebook’s investment in the platform has paid off in terms of user acquisition and market expansion. The acquisition demonstrates the importance of flexibility in integration, allowing the acquired company to maintain its identity while gradually aligning with the acquirer’s broader business strategy.
These case studies offer valuable insights into the best practices that underpin successful M&A transactions. Microsoft’s acquisition of LinkedIn demonstrates the importance of aligning M&A deals with long-term corporate strategies and integrating resources in a way that enhances both companies’ value propositions. ExxonMobil’s merger highlights how operational synergies can drive success in capital-intensive industries, while Facebook’s acquisition of WhatsApp showcases the potential of M&A to expand into new markets and acquire users at scale. Each case illustrates how companies can navigate integration challenges—whether technological, cultural, or operational—by focusing on clear objectives, strategic decision-making, and the careful management of post-merger integration.
Additionally, these case studies provide industry-specific insights, showing how M&A strategies differ depending on the sector. In technology, the focus is often on innovation, user acquisition, and technological integration, while in the energy sector, operational efficiencies and economies of scale are critical drivers of success. Understanding these differences is crucial for companies looking to pursue M&A in their respective industries.
The case studies explored in this section demonstrate that while every M&A transaction is unique, the common thread linking successful deals is a well-thought-out strategy that aligns with broader corporate objectives. Whether the goal is expanding into new markets, acquiring innovative technologies, or achieving operational efficiencies, companies must be clear about their strategic priorities and execute their plans with precision. By learning from the successes of others, companies can navigate the complexities of M&A and unlock new opportunities for growth and competitive advantage.
8.6. Successful Integrations in the Digital Sector
The digital sector, driven by rapid innovation, technological advancements, and disruptive business models, has become a fertile ground for mergers and acquisitions (M&A). Companies in this sector constantly face competitive pressures, pushing them to expand capabilities, enhance technological infrastructure, and maintain a pace of innovation. Successful integrations in the digital space, such as Google’s acquisition of YouTube and Amazon’s purchase of Whole Foods, have demonstrated how M&A can be leveraged to accelerate growth and drive long-term value. This section explores these high-profile transactions, emphasizing the key factors that contributed to their success: speed of integration, technological synergies, and innovation-driven growth.
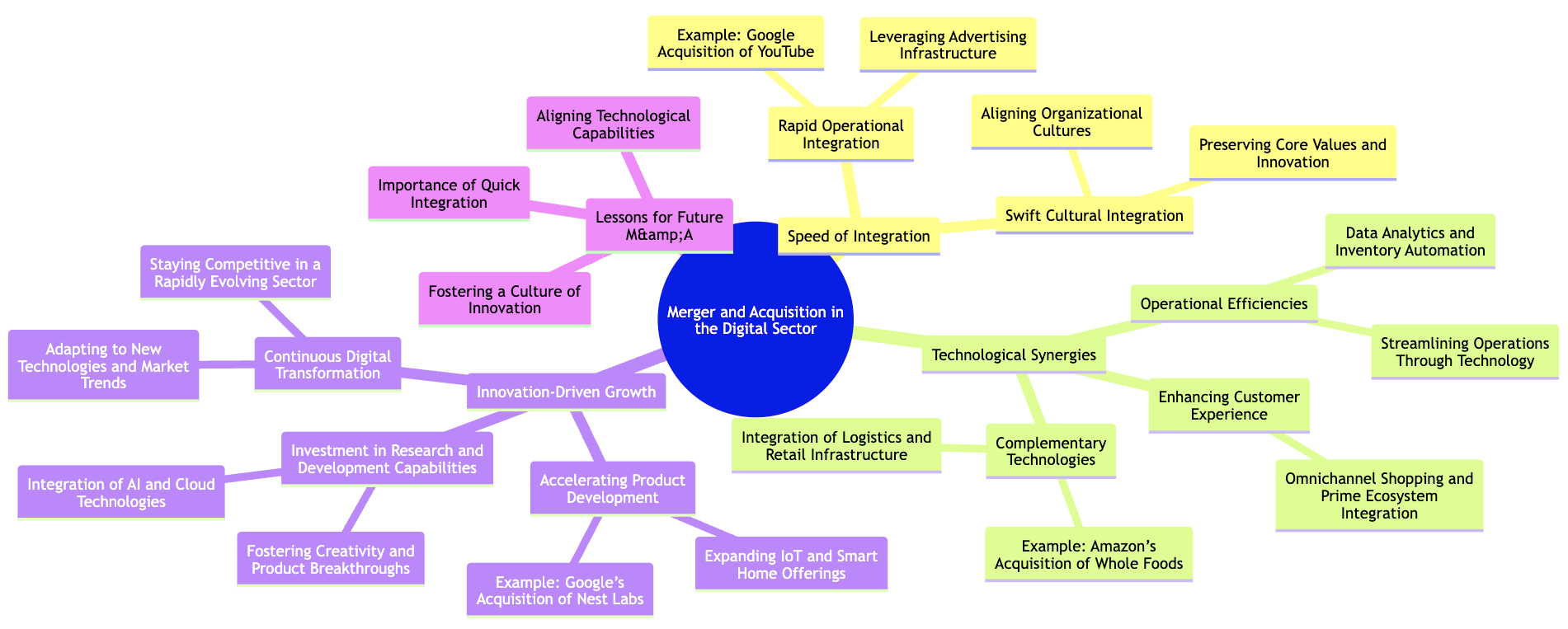
Figure 8.9: Key aspects of successful M&A in digital industry.
One of the defining characteristics of the digital sector is its fast pace of change. Technologies evolve rapidly, customer expectations shift, and competitors are constantly looking for the next breakthrough. In this environment, the ability to integrate quickly and efficiently is often the key to capturing value from an acquisition. Delays in integration—whether in operations, technology, or culture—can result in missed opportunities, lost revenue, and a failure to realize the full potential of the deal.
A prime example of speed in integration is Google’s acquisition of YouTube in 2006. At the time of the acquisition, YouTube was a fast-growing video-sharing platform with a large user base but minimal revenue. Google recognized the potential of online video content and quickly moved to integrate YouTube into its broader ecosystem, particularly its advertising infrastructure. Google understood that video content would become a central component of digital advertising, and by swiftly integrating YouTube’s platform with its own data analytics and ad-serving capabilities, Google was able to transform YouTube into a highly profitable business in a short period of time. The rapid integration allowed YouTube to scale rapidly without disrupting its core user experience, helping it maintain its position as the leading video platform while generating billions of dollars in ad revenue for Google.
Speed of integration does not just refer to technology—it also applies to organizational culture. In many digital acquisitions, the target company operates at a different pace or with a different cultural mindset compared to the acquiring company. Integrating the cultures of two companies in the digital sector requires swift but thoughtful action to ensure that teams are aligned and motivated to collaborate. Google’s acquisition of YouTube is an example of how fast cultural integration was achieved without disrupting the creative freedom of YouTube’s team. By providing YouTube’s leadership the autonomy to manage the platform while offering the resources needed for rapid growth, Google was able to integrate the company successfully while preserving its innovative culture.
The lesson here is that, in the digital sector, speed is essential for maintaining the momentum of an acquired business. Companies must prioritize quick and efficient integration to capture the value that motivated the acquisition in the first place, ensuring that operations and technology are aligned to meet market demands without delay.
One of the key drivers of successful M&A in the digital sector is the ability to create technological synergies—combining the technological capabilities of both the acquiring and target companies to develop new products, enhance existing services, or drive operational efficiencies. Digital acquisitions often target companies with technologies that complement the acquirer’s core business, enabling them to innovate faster and stay ahead of competitors.
A standout example of leveraging technological synergies can be seen in Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods in 2017. Although Whole Foods was not a technology company per se, the acquisition was highly strategic for Amazon, as it allowed the e-commerce giant to integrate its technology and logistics infrastructure with Whole Foods’ physical retail presence. By doing so, Amazon effectively created an omnichannel experience for consumers, blending the convenience of online shopping with the in-store experience of a high-end grocery retailer. Amazon immediately began to implement its technological strengths—such as automation in inventory management, data analytics for customer preferences, and its Prime delivery service—to streamline Whole Foods’ operations and improve the customer experience.
One of the most significant technological synergies in this deal was Amazon’s integration of Whole Foods into its Prime ecosystem. Amazon introduced discounts and benefits for Prime members at Whole Foods stores, which not only increased foot traffic but also deepened customer loyalty to both Amazon and Whole Foods. Additionally, Amazon leveraged its logistical capabilities to roll out grocery delivery through Amazon Fresh and Prime Now, further blurring the line between physical and digital retail. The success of this integration underscores how complementary technologies can enhance customer experiences and drive new revenue streams.
In the digital sector, acquiring companies often target businesses with unique or proprietary technologies that can be integrated into their own platforms to expand capabilities. Technological integration should be carefully planned and executed to ensure that both companies’ systems work together seamlessly, without causing disruption. Moreover, companies must remain agile during the integration process, adapting to new technological challenges and opportunities as they arise.
The digital sector is synonymous with innovation, and M&A in this space is frequently motivated by the desire to accelerate product development, enhance research and development (R&D) capabilities, or gain access to cutting-edge technologies. For an acquisition to be successful in the long term, the acquiring company must foster an environment that prioritizes continued innovation and digital transformation. This requires not only integrating the target company’s technologies and operations but also nurturing its talent and maintaining a focus on innovation as a key driver of growth.
A strong example of innovation-driven growth through M&A can be found in Google’s acquisition of Nest Labs in 2014. Nest, known for its smart thermostats and home automation products, was a leader in the growing Internet of Things (IoT) space. Google acquired Nest as part of its broader strategy to dominate the smart home market and expand its presence in IoT. Post-acquisition, Google invested heavily in Nest’s R&D capabilities, enabling the company to develop new smart home products, such as security cameras, doorbells, and smoke detectors. By integrating Nest’s innovative technologies with its own AI and cloud capabilities, Google was able to push the boundaries of smart home innovation, ultimately creating a more seamless and connected home ecosystem.
What made this acquisition successful was Google’s recognition that Nest’s success was rooted in its culture of innovation. Rather than stifling this creativity, Google gave Nest the resources and autonomy it needed to continue developing breakthrough products. This case illustrates the importance of prioritizing R&D and product development in digital M&A deals. Companies must invest in the target’s innovation capabilities to ensure that the acquisition leads to long-term growth, not just short-term synergies.
Additionally, the digital sector demands continuous digital transformation, where companies must constantly evolve their business models to stay relevant. Acquiring companies in the digital space must be prepared to adapt quickly, embracing new technologies, business models, and market trends to remain competitive.
Successful M&A transactions in the digital sector hinge on the ability to integrate swiftly, leverage complementary technologies, and foster a culture of innovation. Speed of integration ensures that the acquired company’s momentum is not lost, allowing the acquirer to capture value quickly and adapt to the fast-changing digital landscape. Technological synergies are crucial for unlocking new product offerings and enhancing operational efficiencies, while innovation-driven growth ensures that the combined entity remains competitive in the long run.
Google’s acquisition of YouTube and Amazon’s purchase of Whole Foods both demonstrate how digital companies can successfully integrate and leverage the strengths of their acquisitions to create new growth opportunities. By focusing on speed, technology, and innovation, companies can navigate the complexities of digital M&A and position themselves for sustained success in an increasingly competitive market.
In summary, the digital sector requires companies to be agile, forward-thinking, and strategically aligned when pursuing M&A. The lessons from these successful integrations offer a roadmap for future deals, highlighting the importance of quick integration, technological alignment, and an unwavering focus on innovation as the keys to long-term success in the digital age.
8.7. Value Creation in Oil & Gas Acquisitions
The oil and gas industry is one of the most capital-intensive sectors globally, characterized by large-scale operations, significant infrastructure investments, and volatile market conditions. Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) in this industry present both unique challenges and substantial opportunities for value creation. Companies that execute M&A deals effectively in this sector typically focus on leveraging operational synergies, achieving cost reduction through streamlined processes, and navigating complex regulatory and environmental considerations. This section examines how companies in the oil and gas industry have successfully created value through M&A, using case studies like Exxon’s acquisition of Mobil as a reference point.
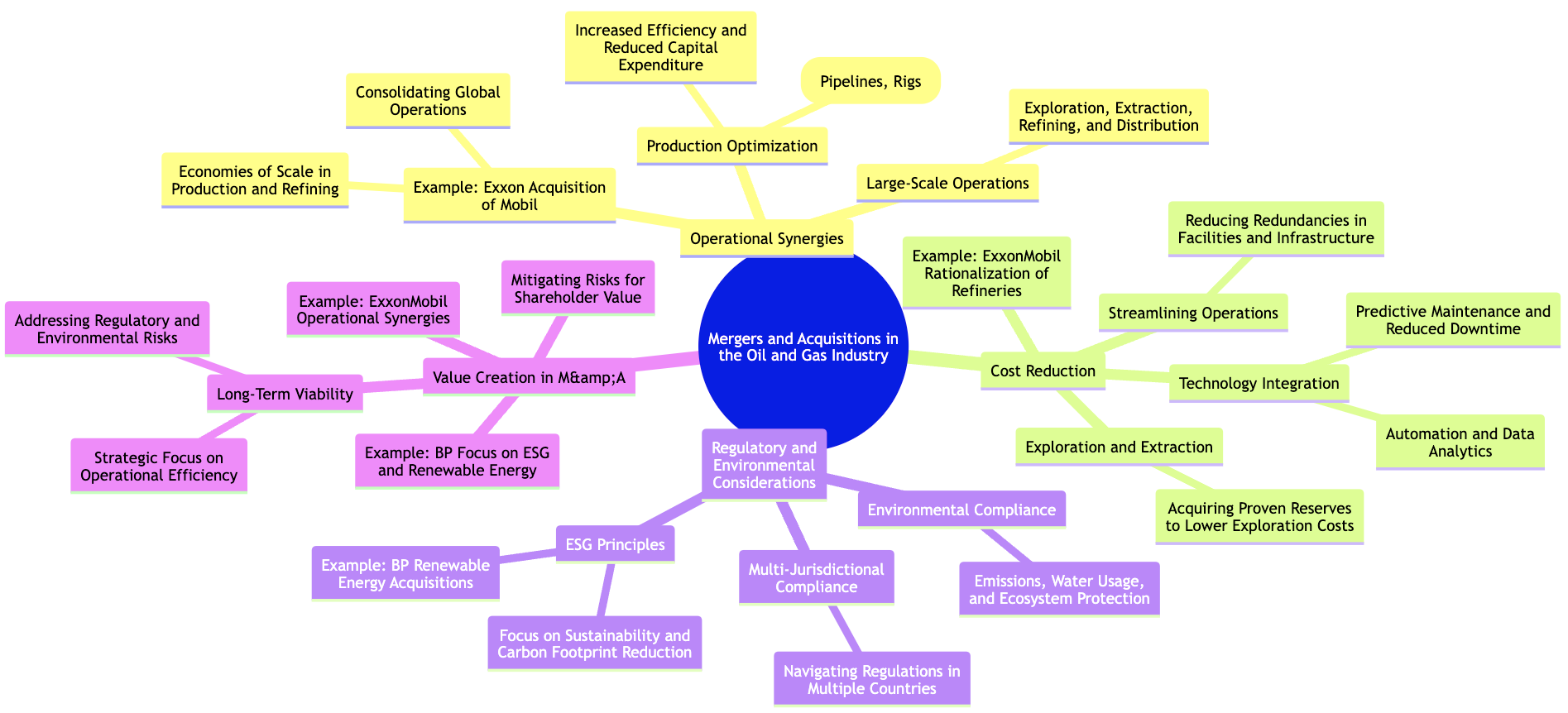
Figure 8.10: Key aspects of successful M&A in oil and gas industry.
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on large-scale operations that span exploration, extraction, refining, and distribution. Given the scope of these activities, operational synergies play a critical role in determining the success of mergers in this sector. Operational synergies occur when two merging companies combine their assets, infrastructure, and expertise to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase production capacity.
One of the most significant examples of leveraging operational synergies is Exxon’s acquisition of Mobil in 1999, a deal that created the world’s largest publicly traded oil company, ExxonMobil. The strategic rationale behind this merger was rooted in the potential for significant operational efficiencies. Exxon and Mobil were able to consolidate their global production and refining operations, resulting in increased economies of scale. By combining their supply chains and distribution networks, the newly merged entity optimized its logistical operations, ensuring smoother coordination across its global assets. Additionally, the integration of Mobil’s refineries and Exxon’s exploration capabilities created a vertically integrated company with unmatched production and distribution capacities.
Production optimization is another critical area where operational synergies can drive value. For example, in offshore drilling operations, companies often share infrastructure such as pipelines and rigs. A merger between two companies with adjacent drilling operations can lead to significant cost savings by reducing redundant infrastructure and optimizing the use of existing facilities. This kind of resource-sharing results in increased production efficiency and lower capital expenditure, providing a substantial return on investment for the acquiring company.
In summary, operational synergies in oil and gas acquisitions are essential for optimizing production, refining, and distribution. By consolidating infrastructure and coordinating operations across the supply chain, companies can achieve greater efficiency, reduce costs, and maximize resource extraction—all of which contribute to long-term value creation.
Another critical component of value creation in oil and gas acquisitions is cost reduction. The capital-intensive nature of the industry means that operational costs, particularly in exploration, extraction, and infrastructure maintenance, can be substantial. Successful acquirers often focus on identifying areas where they can streamline operations and reduce costs, thereby improving profitability.
Exploration and extraction are two areas where cost reduction can be particularly impactful. Exploration, the process of identifying and evaluating potential oil and gas reserves, is one of the most expensive stages in the oil and gas value chain. By acquiring companies with proven reserves, acquirers can reduce the risk and cost associated with exploration. For example, a company that acquires another with significant existing reserves can immediately begin extraction without the need for costly exploratory operations. This approach not only reduces expenses but also accelerates the timeline for generating revenue from the acquired assets.
In the case of infrastructure, companies often reduce costs by consolidating facilities and eliminating redundancies. For instance, after the ExxonMobil merger, the company was able to rationalize its refining operations by closing or repurposing underperforming refineries and maximizing the efficiency of those that remained. Similar efficiencies can be achieved in areas like pipeline infrastructure, storage facilities, and distribution networks. By reducing duplication and streamlining logistics, companies can lower their operating costs and improve margins.
Furthermore, technology integration can lead to cost savings in oil and gas M&A. The implementation of advanced technologies, such as automation and data analytics, allows companies to optimize their drilling, refining, and transportation processes. For example, by leveraging data from sensors and monitoring equipment, companies can predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing maintenance costs and minimizing downtime. Automation can also reduce the need for manual labor in hazardous environments, further cutting operational expenses.
Overall, cost reduction strategies in oil and gas acquisitions focus on improving operational efficiency, reducing capital expenditures, and utilizing technology to streamline processes. By cutting costs in exploration, extraction, and infrastructure, acquirers can significantly enhance the profitability of their newly acquired assets.
The oil and gas industry operates in a highly regulated environment, with strict rules governing everything from environmental impact to worker safety. As a result, regulatory and environmental considerations are critical factors in any M&A transaction within the sector. Companies must carefully assess the regulatory landscape of both the acquiring and target companies to ensure compliance with local, national, and international laws. Failure to do so can result in costly penalties, operational delays, and reputational damage.
One of the key regulatory challenges in oil and gas M&A is ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. The industry is subject to stringent environmental rules, particularly regarding emissions, water usage, waste management, and the protection of sensitive ecosystems. For example, acquiring a company with oil drilling operations in environmentally sensitive areas may require the acquirer to comply with additional regulations, such as impact assessments or emissions caps. This can increase the complexity of the transaction and require additional investments in environmental protection measures.
In recent years, the importance of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) concerns has grown significantly in the oil and gas sector. Investors, regulators, and the public are increasingly focused on how companies manage their environmental impact, including their carbon footprint and sustainability practices. As a result, companies engaging in M&A must not only comply with existing regulations but also demonstrate a commitment to ESG principles. Acquirers often face pressure to improve the sustainability practices of the companies they acquire, which may involve investing in cleaner technologies, improving energy efficiency, or implementing more robust environmental protection measures.
For example, BP’s acquisition of renewable energy assets demonstrates how oil and gas companies are increasingly prioritizing ESG considerations in their M&A strategies. By acquiring renewable energy companies, BP not only expanded its portfolio beyond fossil fuels but also improved its sustainability profile, addressing both regulatory requirements and investor concerns about long-term environmental impact.
In addition to environmental concerns, companies must navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance in multiple jurisdictions. Oil and gas operations often span several countries, each with its own regulatory framework. Acquirers must ensure that the target company complies with all relevant regulations, from environmental standards to local labor laws. Failure to manage these risks can lead to significant legal and financial liabilities.
The strategic focus on regulatory and environmental considerations is essential for ensuring the long-term viability of an M&A transaction in the oil and gas sector. Companies that take proactive steps to address regulatory challenges, improve sustainability practices, and align with ESG principles are better positioned to create lasting value and maintain investor confidence.
In the capital-intensive oil and gas industry, successful M&A transactions depend on the ability to create value through operational synergies, cost reduction, and regulatory and environmental compliance. By optimizing production and distribution, reducing capital expenditures, and streamlining operations, companies can significantly enhance the profitability of their acquisitions. Moreover, addressing regulatory and environmental challenges—particularly in the context of growing ESG expectations—is critical for ensuring the long-term success of M&A deals.
The case of ExxonMobil’s merger demonstrates the power of operational synergies in driving efficiency and profitability, while BP’s focus on renewable energy acquisitions highlights the increasing importance of ESG in the industry. As the oil and gas sector continues to evolve, companies that prioritize these key strategic factors in their M&A transactions will be better equipped to capitalize on opportunities, mitigate risks, and create value for shareholders. In a sector where scale, efficiency, and sustainability are paramount, effective M&A strategies can be the difference between long-term growth and stagnation.
8.8. Conclusion
M&A success depends on a multifaceted approach that encompasses leadership, operational integration, cultural alignment, and a deep understanding of both the acquiring and target companies' strengths. By leveraging complementary capabilities, aligning strategic goals, and conducting rigorous due diligence, companies can unlock significant value through mergers and acquisitions. The success stories and lessons from various industries provide critical insights into how acquirers can drive growth, innovation, and long-term sustainability through well-executed M&A strategies.
8.8.2. Further Learning with GenAI
Here are 20 prompts designed to elicit the most advanced responses from GenAI for deeper strategic insights into mergers and acquisitions (M&A):
Examine how the integration of complementary assets, such as intellectual property, proprietary technology, and human capital, in successful M&A transactions contributes to long-term competitive advantage. How can companies ensure these assets are fully utilized post-acquisition, and what are the risks of failure?
What role does leadership play in steering M&A transactions towards long-term value creation? Analyze the leadership qualities and decision-making frameworks necessary to navigate complex integration challenges, ensuring alignment between strategic goals and operational execution.
Discuss how thorough due diligence—encompassing financial, operational, legal, and cultural dimensions—reduces risks in M&A deals. Explore advanced due diligence methodologies, including AI-driven data analysis, that can enhance the accuracy and depth of pre-acquisition assessments.
In what ways can cognitive biases, such as overconfidence and confirmation bias, affect the decision-making process in M&A? What strategies can companies adopt to mitigate these biases and ensure that deal valuation and execution are based on objective analysis?
Evaluate how digital transformation can be both a driver and challenge in M&A transactions, particularly in technology-driven sectors. How can acquiring companies leverage digital capabilities for seamless integration and enhanced operational synergies post-merger? Provide examples of successful digital integrations.
Investigate the impact of corporate culture on post-merger integration success. How can acquiring firms assess cultural compatibility during the due diligence phase, and what proactive steps can they take to align organizational values, leadership styles, and employee engagement post-acquisition?
Analyze the strategic role of Integration Management Offices (IMOs) in large-scale M&A transactions. How can IMOs be structured to oversee not only the operational and technological integration but also ensure alignment of strategic vision and corporate governance in the newly merged entity?
Explore the financial valuation models, such as discounted cash flow (DCF) and comparable company analysis (CCA), used to assess target companies in M&A. How can companies enhance these models with scenario analysis and stress testing to account for post-merger risks and synergies?
What are the critical factors that differentiate successful M&A deals in capital-intensive industries like oil & gas? Analyze how operational efficiencies, cost synergies, and regulatory compliance contribute to value creation in these sectors, and provide real-world examples.
Examine the role of AI and machine learning in enhancing M&A strategy, from target identification to integration. How can AI-driven insights improve decision-making, financial modeling, and risk management throughout the M&A lifecycle? What are the current limitations of AI in this context?
How can companies overcome the integration challenges associated with legacy IT systems and technology platforms in post-merger environments? Discuss the technical and organizational strategies required to ensure that IT integration accelerates business synergies rather than causing operational bottlenecks.
Discuss how aligning executive compensation with long-term shareholder value post-acquisition can mitigate the risks associated with agency theory in M&A. What performance-based incentives can companies design to ensure that leadership focuses on sustainable value creation rather than short-term deal completion?
Analyze how cross-border M&A transactions introduce additional complexity in terms of regulatory compliance, cultural integration, and market adaptation. How can multinational companies address these challenges while leveraging cross-border synergies to expand into new markets?
Explore how advanced scenario planning and sensitivity analysis during the pre-deal valuation phase can help companies anticipate potential post-merger integration issues. How can these tools improve the accuracy of synergy estimates and identify critical integration risks?
Examine the role of human capital in post-merger integration, particularly in knowledge-intensive sectors such as technology and pharmaceuticals. How can acquiring companies retain key talent, align organizational objectives, and foster collaboration between teams to drive innovation and competitive advantage?
Discuss how regulatory frameworks, both domestic and international, impact the success of M&A deals in heavily regulated industries such as healthcare, finance, and energy. What best practices should companies follow to ensure regulatory compliance without stifling growth post-merger?
How can companies systematically evaluate the long-term success of M&A transactions? Develop a comprehensive framework for post-merger performance evaluation that includes financial metrics, cultural integration, employee retention, operational synergies, and market share growth.
Explore how integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into M&A strategy can enhance long-term value creation. How can companies ensure that ESG factors are prioritized during the due diligence and integration phases, particularly in sectors like energy and technology?
What are the key differences between horizontal and vertical M&A strategies in terms of value creation, operational integration, and market impact? Provide examples of both types of M&A transactions, discussing the risks, opportunities, and challenges unique to each.
Examine the factors that contribute to successful M&A transactions in the context of emerging markets. How can companies navigate the regulatory, economic, and cultural complexities of these markets to ensure that post-merger integration leads to sustainable growth and value creation?
These advanced and comprehensive prompts will encourage deep exploration of M&A topics and offer strategic insights, enhancing the understanding of complex concepts in mergers and acquisitions.
Comments