Appendix 2
Sample Integration Plan Template
Mergers and acquisitions in the oil and gas industry present unique challenges due to the capital-intensive nature of the business, complex regulatory requirements, and the need for operational safety. A robust and comprehensive integration plan ensures a seamless transition while maximizing value from synergies. Below is a sample integration plan template designed specifically for the oil and gas sector. It covers key areas such as governance, operations, technology integration, human resources, and compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
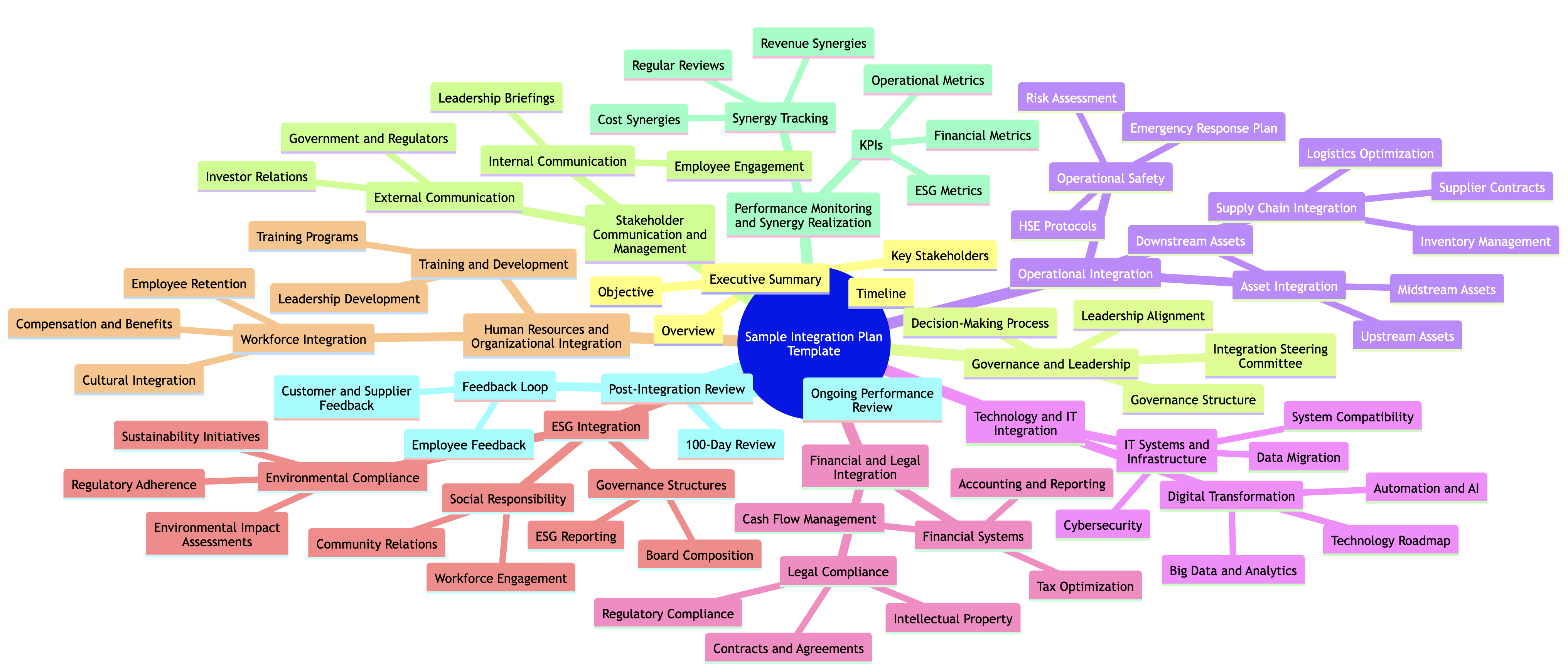
Figure 2.2: Strategic Objectives in M&A Planning.
1. Executive Summary
Understanding the high-level objectives and key elements of the integration is crucial for aligning all stakeholders and ensuring a smooth merger process.
Objective: Summarize the primary goals of the integration, including financial objectives, operational efficiencies, and strategic goals (e.g., market expansion, cost reduction, etc.).
Overview: Provide a high-level overview of the acquired entity and the rationale behind the acquisition.
Timeline: Outline the expected timeline for integration milestones (e.g., 100-day plan, 6-month review, 1-year post-merger assessment).
Key Stakeholders: Identify key executives, managers, and integration leads across both companies.
2. Governance and Leadership Alignment
Aligning governance structures and leadership roles is essential for unified decision-making and strategic direction post-acquisition.
Governance Structure: Define the new governance model post-acquisition, including board structure, reporting lines, and leadership roles.
Leadership Alignment: Align leadership from both organizations, ensuring clarity on roles and responsibilities.
Decision-Making Process: Establish how decisions will be made during and after the integration.
Integration Steering Committee: Form an oversight committee to monitor the integration’s progress and ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
- Members: Include key executives from finance, operations, legal, HR, IT, and compliance.
- Meeting Cadence: Weekly or bi-weekly meetings during the initial phase, with monthly reviews as the integration stabilizes.
3. Operational Integration
Streamlining operations ensures that the merged entity operates efficiently and leverages synergies effectively.
Asset Integration:
- Upstream Assets: Assess and integrate oil and gas fields, production facilities, and drilling platforms.
- Midstream Assets: Integrate pipelines, transportation infrastructure, and storage facilities, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Downstream Assets: Refineries, petrochemical plants, and distribution networks should be optimized for efficiency.
- Asset Management: Develop a unified asset management system, prioritizing safety, maintenance, and regulatory compliance.
Supply Chain Integration:
- Supplier Contracts: Review and consolidate supplier agreements to capture synergies in procurement and supply chain management.
- Logistics Optimization: Merge logistics operations, including the transportation of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products.
- Inventory Management: Harmonize inventory systems to reduce redundancies and optimize stock levels.
Operational Safety and Risk Management:
- Health, Safety, and Environmental (HSE) Protocols: Review and standardize HSE protocols across both entities to ensure compliance with local and international regulations.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential operational risks, such as equipment failure, pipeline leaks, or environmental hazards.
- Emergency Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive emergency response plan, ensuring readiness for oil spills, fires, and other emergencies.
4. Technology and IT Integration
Integrating technology and IT systems is vital for maintaining operational continuity and driving innovation.
IT Systems and Infrastructure:
- System Compatibility: Assess the compatibility of IT systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- Data Migration: Develop a plan for secure data migration between systems, ensuring minimal downtime and data integrity.
- Cybersecurity: Strengthen cybersecurity protocols to protect critical infrastructure from cyberattacks during the integration process.
Digital Transformation and Innovation:
- Automation and AI: Identify opportunities for automation in operations, including predictive maintenance using IoT and AI in exploration and drilling.
- Analytics and Big Data: Leverage big data analytics to optimize production, monitor asset performance, and drive decision-making.
- Technology Roadmap: Create a roadmap for implementing new technologies and systems post-integration, ensuring continuous innovation.
5. Financial and Legal Integration
Aligning financial and legal frameworks is essential for unified reporting, compliance, and financial stability.
Financial Systems Integration:
- Accounting and Reporting Systems: Align accounting systems for unified financial reporting. Ensure that systems meet regulatory standards and facilitate consolidated financial statements.
- Cash Flow Management: Integrate cash management processes, focusing on optimizing working capital and streamlining capital expenditures.
- Tax Optimization: Review and optimize the tax structure to take advantage of efficiencies in cross-border transactions, asset transfers, and tax credits.
Legal Compliance:
- Contracts and Agreements: Review all existing contracts, licenses, and agreements to ensure compliance and minimize legal risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure adherence to environmental laws, anti-corruption regulations (e.g., FCPA), and local legal frameworks, especially in international deals.
- Intellectual Property (IP): Secure IP assets such as drilling technologies, proprietary extraction methods, and patents related to enhanced oil recovery (EOR).
6. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Integration
Integrating ESG principles ensures that the merged entity upholds sustainability, ethical standards, and strong governance.
Environmental Compliance:
- Sustainability Initiatives: Harmonize sustainability efforts such as emission reduction targets, water usage, and carbon capture technologies.
- Regulatory Adherence: Ensure compliance with environmental regulations, including emissions standards, waste management, and land reclamation.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): Conduct EIAs for ongoing and planned projects to understand potential environmental liabilities.
Social Responsibility:
- Community Relations: Engage with local communities affected by operations, particularly in oil-producing regions, to maintain trust and social license to operate.
- Workforce Engagement: Foster positive labor relations, focusing on safe working conditions, fair compensation, and diversity and inclusion initiatives.
Governance Structures:
- Board Composition: Integrate governance practices from both organizations, ensuring strong oversight and ethical practices.
- ESG Reporting: Develop a unified ESG reporting framework for stakeholders and investors, emphasizing transparency in environmental performance and corporate responsibility.
7. Human Resources and Organizational Integration
Effective human resources integration is key to maintaining morale, retaining talent, and fostering a cohesive corporate culture.
Workforce Integration:
- Employee Retention and Communication: Identify key talent and establish retention strategies. Develop a clear communication plan to keep all employees informed about integration progress.
- Compensation and Benefits: Align compensation packages, benefits, and retirement plans across both entities.
- Cultural Integration: Conduct cultural assessments to understand the differences between the companies and develop strategies for fostering a cohesive corporate culture.
Training and Development:
- Training Programs: Implement training programs to upskill employees on new systems, safety protocols, and leadership practices.
- Leadership Development: Identify and groom future leaders within the combined organization, ensuring smooth succession planning.
8. Stakeholder Communication and Management
Transparent and effective communication with all stakeholders ensures alignment, trust, and support throughout the integration process.
Internal Communication:
- Employee Engagement: Create regular updates for employees, focusing on milestones achieved and upcoming changes in roles or operations.
- Leadership Briefings: Hold leadership meetings to ensure alignment and maintain transparency across different levels of the organization.
External Communication:
- Investor Relations: Communicate with investors about the expected benefits of the merger, projected synergies, and financial forecasts.
- Government and Regulators: Maintain open communication channels with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with environmental, safety, and operational standards.
9. Performance Monitoring and Synergy Realization
Monitoring performance and tracking synergy realization are essential for evaluating the success of the integration and making necessary adjustments.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Financial Metrics: Track revenue growth, EBITDA margins, and cost-saving synergies.
- Operational Metrics: Monitor production efficiency, asset utilization rates, and HSE performance.
- ESG Metrics: Track reductions in carbon emissions, water usage, and community engagement efforts.
Synergy Tracking:
- Cost Synergies: Identify cost savings in areas such as procurement, labor, and shared services.
- Revenue Synergies: Track cross-selling opportunities and market expansion from the combined entity.
- Regular Reviews: Hold periodic reviews to assess integration progress and make necessary adjustments to achieve synergies.
10. Post-Integration Review and Continuous Improvement
Continuous evaluation and improvement post-integration ensure long-term success and the ability to adapt to evolving business environments.
Post-Merger Evaluation:
- 100-Day Review: Conduct a comprehensive review after the first 100 days, assessing the success of the integration against the original plan.
- Ongoing Performance Review: Schedule quarterly and annual reviews to track long-term integration success and identify areas for continuous improvement.
Feedback Loop:
- Employee Feedback: Collect feedback from employees on the integration process and identify opportunities for improvement in future M&A activities.
- Customer and Supplier Feedback: Solicit input from key stakeholders to ensure that the merger is delivering value without disrupting service or product quality.
This integration plan template provides a detailed roadmap for managing the complexities of mergers and acquisitions in the oil and gas industry. It covers key areas such as operational integration, financial alignment, human resources, and regulatory compliance, ensuring that the combined entity operates smoothly and capitalizes on synergies. A strong focus on safety, sustainability, and communication is essential for long-term success in this high-stakes industry.
Comments