Appendix 1
M&A Due Diligence Checklist
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) due diligence is a comprehensive assessment process that helps acquiring companies evaluate the potential risks and rewards of a transaction. A well-structured due diligence checklist ensures that all critical areas of the target company are analyzed before completing the deal. The following checklist provides an industry-standard guide for conducting thorough M&A due diligence across key areas such as financials, legal, operations, and ESG considerations.
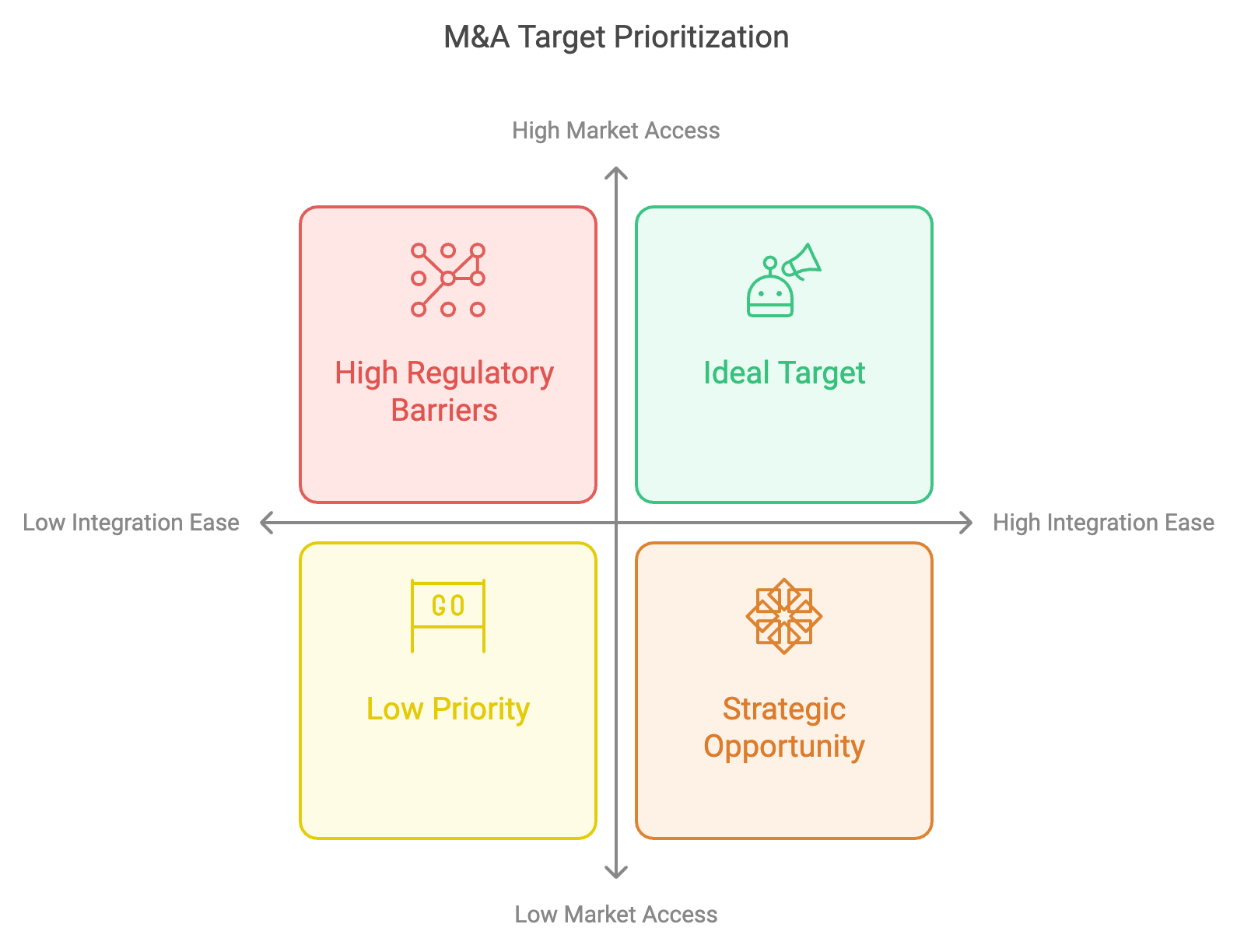
Figure 2.1: Target Prioritization of a Merger & Acquisitions.
1. Financial Due Diligence
Understanding the financial health of the target company is crucial for determining the value of the deal. This section focuses on validating financial performance, identifying liabilities, and assessing the potential for future growth.
Historical financial statements (3-5 years):
- Balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
- Auditor reports and footnotes.
Revenue breakdown and growth analysis:
- Revenue by product/service, geography, and customer segment.
- Comparison of actual performance against forecasts.
Profitability metrics:
- Gross margins, operating margins, and net margins.
- EBITDA analysis and adjustments.
Debt and liabilities:
- Outstanding debt, payment schedules, interest rates.
- Contingent liabilities and off-balance sheet items.
Working capital and cash flow:
- Cash conversion cycle, liquidity analysis, and credit terms.
- Assessment of free cash flow for reinvestment and debt servicing.
Tax compliance and liabilities:
- Historical tax filings, audits, and outstanding disputes.
- Tax incentives, credits, and deferrals.
2. Legal Due Diligence
Legal due diligence focuses on uncovering potential legal risks that may affect the transaction, such as litigation, intellectual property disputes, or regulatory compliance issues.
Corporate structure and governance:
- Articles of incorporation, bylaws, and corporate charters.
- Organizational structure and board composition.
Contracts and agreements:
- Review of key contracts with customers, suppliers, partners, and employees.
- Non-compete, confidentiality, and licensing agreements.
Litigation and legal disputes:
- Ongoing or threatened litigation, arbitration, or regulatory investigations.
- Review of settlements, court rulings, and legal liabilities.
Intellectual property (IP):
- Patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and licenses.
- Review of IP ownership, disputes, and protection strategies.
Regulatory compliance:
- Review of compliance with industry regulations, licenses, and permits.
- Environmental, labor, and health and safety compliance.
3. Operational Due Diligence
Operational due diligence evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of the target company’s internal operations and business model.
Business model and strategy:
- Assessment of the company’s value proposition, market positioning, and competitive advantage.
- Strategic plans for growth, market expansion, and innovation.
Supply chain and logistics:
- Review of supplier contracts, relationships, and risks.
- Analysis of logistics, warehousing, and inventory management systems.
Technology and IT systems:
- Overview of core IT infrastructure, software, and cybersecurity.
- Evaluation of proprietary technologies and systems integration risks.
Production and operations:
- Assessment of manufacturing capacity, efficiency, and scalability.
- Review of operational bottlenecks, lead times, and quality control.
Human resources and talent:
- Key employee contracts, retention plans, and succession planning.
- Employee turnover, compensation structures, and labor agreements.
4. Market and Commercial Due Diligence
This section focuses on understanding the external market factors that influence the target company’s ability to grow and compete effectively.
Market position and competitive landscape:
- Industry trends, growth rates, and competitive dynamics.
- SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis.
Customer base and sales pipeline:
- Breakdown of customer segments, key accounts, and retention rates.
- Sales pipeline analysis, pricing strategies, and customer feedback.
Market risks and barriers:
- Barriers to entry, regulatory hurdles, and competitive threats.
- Risks related to technological disruption and market saturation.
5. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Due Diligence
ESG due diligence evaluates how well the target company aligns with sustainability goals, ethical business practices, and governance standards.
Environmental impact:
- Carbon footprint, energy use, waste management, and sustainability initiatives.
- Compliance with environmental regulations and potential liabilities.
Social responsibility:
- Labor practices, diversity and inclusion policies, and community engagement.
- Review of corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs and impact.
Corporate governance:
- Governance structures, executive compensation, and shareholder rights.
- Review of governance policies related to ethics, transparency, and accountability.
6. Strategic Fit and Synergy Analysis
This section focuses on how the target company aligns with the acquiring company’s strategic goals and the potential for synergy creation.
Strategic rationale:
- Evaluation of how the acquisition fits into the acquiring company’s long-term strategy.
- Analysis of market expansion, technology integration, or product line extension.
Synergy opportunities:
- Cost synergies: Reduction of operational redundancies, supply chain optimization, and economies of scale.
- Revenue synergies: Cross-selling opportunities, new market access, and customer base expansion.
Integration risks and challenges:
- Cultural fit, leadership alignment, and potential roadblocks to integration.
- Assessment of integration plans and timelines.
7. Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Identifying and managing risks is a critical part of the due diligence process, especially in complex M&A deals.
Key risks:
- Identification of major risks, including financial, legal, operational, and market risks.
- Quantification and prioritization of risks to focus on high-impact areas.
Risk mitigation strategies:
- Development of contingency plans to address identified risks.
- Risk-sharing mechanisms, such as earnouts, indemnities, and warranties in the deal structure.
8. Deal Structure and Valuation
This section assesses the financial terms of the deal, ensuring the price paid is aligned with the value of the target company.
Valuation methodologies:
- Application of valuation methods, such as discounted cash flow (DCF), comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions.
- Sensitivity analysis and stress-testing assumptions.
Purchase price and payment structure:
- Analysis of the proposed purchase price, including cash, stock, or hybrid payments.
- Review of deal contingencies, earnouts, and deferred payments.
Financing and capital structure:
- Assessment of the acquiring company’s financing plan and capital structure post-acquisition.
- Debt financing, equity raises, and potential dilution of shareholder value.
9. Post-Merger Integration (PMI) Planning
Successful M&A transactions require detailed planning for post-merger integration to realize value and ensure smooth operations.
Integration planning:
- Development of a comprehensive integration plan, including timelines and milestones.
- Identification of key integration teams and leadership roles.
Communication strategy:
- Internal and external communication plans to manage employee and stakeholder expectations.
- Transparency with customers, suppliers, and regulators to minimize disruption.
Tracking and measurement of success:
- Establishment of key performance indicators (KPIs) to track integration progress.
- Regular assessments of synergy realization, cultural integration, and operational efficiency.
A thorough M&A due diligence process is essential for identifying risks, uncovering opportunities, and making informed decisions in a transaction. By addressing each area in this checklist—financials, legal, operational, market, ESG, and strategic fit—companies can enhance the likelihood of achieving a successful merger or acquisition that delivers long-term value and aligns with their growth and sustainability goals.
This appendix serves as a comprehensive guide to M&A due diligence, providing a structured approach to evaluating potential acquisitions across multiple dimensions and ensuring that every deal is strategically sound and thoroughly vetted.
Comments